Contents
Hand bones
The hand (from the Latin manus, “side of the body”) is an organ made up of 27 bones, participating in particular in its flexibility and mobility.
Hand anatomy
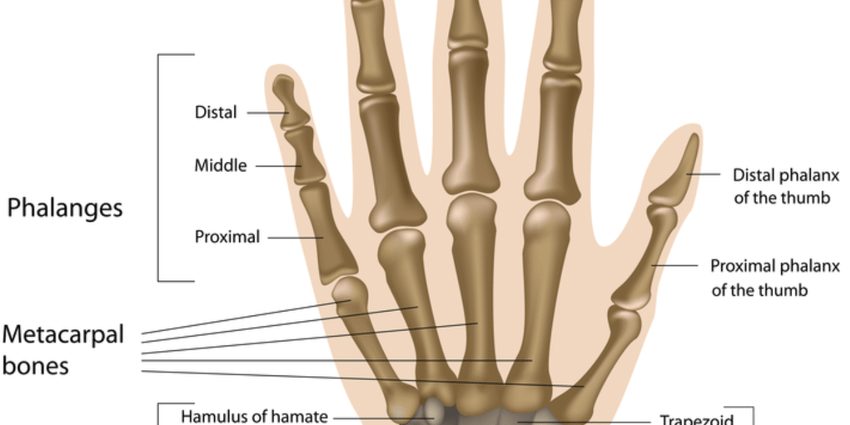
The skeleton of the hand has twenty-seven bones (1):
- The carpus, made up of two rows of four short bones, together with the radius and ulna form the wrist joint (2)
- The pastern, made up of five long bones, forms the skeleton of the palm and is placed in the extension of each finger
- The fourteen phalanges form the five fingers of the hand
Hand movements
Hand movements. The bones, linked by the joints, are set in motion thanks to numerous tendons and muscles reacting to different nerve messages. The wrist allows lateral movements, extension (upwards), flexion (downwards).
Gripping. The essential function of the hand is grip, the ability of an organ to grasp objects (3).
Hand bone pathologies
fractures. The bones of the hand are easily subject to impact and fractures. Extra-articular fractures must be distinguished from joint fractures involving the joint and requiring a thorough assessment of the lesions.
- Fracture of the phalanges. Fractured bones of the fingers cause stiffness affecting the mobility of the fingers (4).
- Fracture of the metacarpals. Located in the palm of the hand, these bones can fracture in the event of a fall with a closed fist or a violent blow with the hand (4).
- Scaphoid fracture. Carpal bone, the scaphoid can be fractured in the event of a fall on the wrist or forearm (5) (6).
- Wrist fracture. Frequent, this fracture requires a rapid and adapted immobilization of the wrist to avoid displacement.
Bone pathologies.
- Kienbock disease. This disease is necrosis of one of the carpal bones when nutrient supply from the blood is interrupted (7).
- Osteoporosis Bone fragility and risk of fractures caused by loss of bone density observed in subjects from the age of 60 on average.
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). The wrist is one of the upper limbs affected by musculoskeletal disorders, recognized as occupational diseases and arising during excessive, repetitive or sudden stress on a limb.
- Tendonitis of the wrist (de Quervain). It corresponds to the inflammation of the tendons in the wrist (9).
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: This syndrome refers to disorders associated with compression of the median nerve at the level of the carpal tunnel, made up of the carpal bones. It manifests as tingling in the fingers and loss of muscle strength (10).
Arthritis. It corresponds to conditions manifested by pain in the joints, ligaments, tendons or bones. Characterized by the wear and tear of the cartilage protecting the bones of the joints, osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. The joints of the hands and wrists can also be affected by inflammation in the case of rheumatoid arthritis (11). These conditions can lead to deformity of the fingers.
Hand bone treatment
Prevention of shock and pain in the hand. To limit fractures and musculoskeletal disorders, prevention by wearing protection or learning appropriate gestures is essential.
Orthopedic treatment. Depending on the type of fracture, the installation of a plaster or a resin will be carried out to immobilize the wrist.
Drug treatments. Depending on the disease, different treatments are prescribed to regulate or strengthen bone tissue.
Surgical treatment. Depending on the type of fracture, surgery may be performed with the placement of pins or screw plates. Treatment of Kienböck’s disease also requires surgical treatment.
Hand exams
Medical imaging examination. The clinical examination is often supplemented by an x-ray. In some cases, doctors will use an MRI, CT scan, or arthrography to assess and identify lesions.
History and symbolism of the hand
Communication tool. Hand gestures are often associated with speaking.










ለመታከም የት ሆስፒታል ህክምናው ይሰጣል ከዚህም ባሻገር ስልክ ጥቁርበ 0996476180 በዚህ ያገኙኛል ይደውሉ መልካም