What is tachycardia?
We speak of tachycardia when, at rest, apart from physical exercise, the heart beats too quickly, more than 100 pulsations per minutes. A heart is considered to beat normally when it is between 60 and 90 beats per minute.
In tachycardia, the heart beats quickly, and sometimes irregularly. This acceleration of the heartbeat can be permanent or transient. In some cases it may not lead to no sign. In other cases, it can cause dizziness, lightheadedness or palpitations, or even loss of consciousness. Tachycardia can therefore range from a mild disorder to a very serious disorder that can lead to cardiac arrest.
How does the heart rate vary? The heart rate varies depending on the body’s need for oxygen. The more oxygen the body needs, the faster the heart beats, in order to circulate more red blood cells, our oxygen carriers. Thus, during a physical exercise, our muscles needing more oxygen, the heart accelerates. The increased heart rate is not the only adaptation of our heart, it can also beat faster, that is to say, contract in a more powerful way. The rhythm of the heartbeat is also determined by the way the heart works. In some heart diseases, there may be hiccups in the way the heart sets its rhythm. |
There are several types of tachycardia:
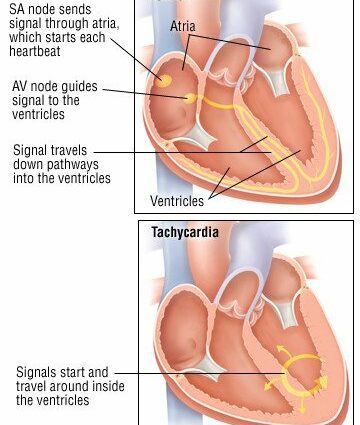
– Sinus tachycardia : it is not due to a heart problem but to an adaptation of the heart to a particular circumstance. It is called sinus because the general rhythm of the heartbeat is determined by a specific place in this organ called the sinus node (an area normally source of regular and adapted electrical impulses causing cardiac contractions). This sinus acceleration of the heart can be normal, as when it is linked to physical exertion, lack of oxygen at altitude, stress, pregnancy (the heart accelerates naturally at this time of life) or taking an stimulant such as Coffee.
In the case of physical exercise, for example, the heart speeds up in order to provide more oxygen to the working muscles. It is therefore a adaptation. In the case of altitude, oxygen being rarer, the heart accelerates to allow enough oxygen to be brought to the body despite its scarcity in the ambient air.
But this sinus acceleration of the heart may be linked to a situation abnormal in which the heart adapts by accelerating its rhythm. This happens, for example, in the event of fever, dehydration, taking a toxic substance (alcohol, cannabis, certain drugs or medications), anemia or even hyperthyroidism.
In the case of dehydration for example, the volume of fluid in the vessels being reduced, the heart accelerates to compensate. In the case of anemia, the lack of red blood cells leading to a lack of oxygenation, the heart speeds up its rate to try to provide enough oxygen to all the organs of the body. With sinus tachycardia, quite often the person does not realize that their heart is beating fast. This tachycardia can be discovery by the doctor.
Sinus tachycardia may also be related to tired heart. If the heart fails to contract effectively enough, the sinus node tells it to contract more often to allow enough oxygen to flow throughout the body.
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (STOP) People with this STOP have difficulty moving from a lying down to an upright posture. During this change of position, the heart accelerates excessively. This increased heart rate is often accompanied by a headache, feeling sick, tired, nausea, sweating, chest discomfort, and sometimes even fainting. This problem may be related to certain illnesses, such as diabetes, or taking certain medications. It is treated with a good supply of water and mineral salts, a physical training program for the legs to improve the return of venous blood to the heart, and possibly drugs such as corticosteroids, beta blockers or other treatments. |
— Tachycardia related to a heart problem: fortunately, it is rarer than sinus tachycardia. Because the heart has an abnormality, it speeds up while the body does not need a faster beating heart.
— Tachycardia linked to Bouveret’s disease : it is relatively frequent (more than one in 450 people) and most often relatively benign. This is an abnormality in the electrical system of the heart. This anomaly sometimes leads to attacks of tachycardia brutal for a while before stopping just as abruptly. The heart can then beat more than 200 per minute. This is annoying and often causes discomfort forcing you to lie down for a while. Despite this anomaly, the hearts of these people are not sick and this problem does not decrease life expectancy.
Another type of tachycardia is Wolf-Parkinson White syndrome, which is also an abnormality in the electrical system of the heart. It is called paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
Ventricular tachycardias: these are accelerated contractions of the ventricles of the heart linked to heart disease (various diseases). Ventricles are pumps used to send oxygen-rich blood throughout the body (left ventricle) or oxygen-poor blood to the lungs (right ventricle). The problem is, when the ventricles start to beat too quickly, the ventricular cavity doesn’t have time to fill with blood. The ventricle no longer plays a role of pumps effective. There is then a risk of stopping the efficiency of the heart and therefore a fatal risk.
Ventricular tachycardia is therefore a cardiological emergency. Some cases are relatively mild and others extremely serious.
In the most severe cases, ventricular tachycardia may progress to ventricular fibrillation corresponding to desynchronized contractions of muscle fibers. Instead of contracting all at once in the ventricles, the muscle fibers each contract at any time. The cardiac contraction then becomes ineffective in ejecting blood, and this has the same effect as cardiac arrest. Hence the gravity. Using a defibrillator can save the person.
Atrial or atrial tachycardia : it is an acceleration of the contraction of part of the heart: the Headsets. The latter are small cavities, smaller than the ventricles, whose role is to eject blood to the left ventricle for the left atrium and to the right ventricle for the right atrium. In general, the rate of these tachycardias is high (240 to 350), but the ventricles beat more slowly, often half the time compared to the atria, which is still very fast. The person may not be embarrassed in some cases, or may perceive it in other cases.










*