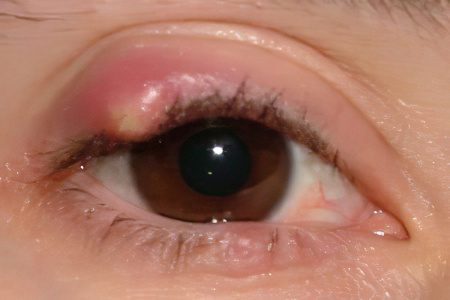
Chalazion (hailstone) – swelling of the eyelid caused by blockage of the sebaceous (meibomian) gland and the accumulation of fluid in it. It can appear on the eyelids of both eyes, often visually resembles barley, but its difference is in the chronic course. This pathology is observed in adults and children. Meibomian glands are branched sebaceous glands located deep in the cartilage of the upper and lower eyelids. These are the excretory ducts that open at the lash line.
During normal functional activity, they produce a fatty secretion that moisturizes the tear film and lubricates the corneas and the edges of the eyelids, reducing friction between the edge of the eyelids and the anterior surface of the eye during blinking. Blockage leads to the fact that a fatty secret accumulates in the duct, the gland increases in size and a capsule is formed.
If the chalazion does not open and bothers a person for a long period, then a cyst may form, which is very dangerous for the body. Basically, the pathology develops slowly. The first sign – a swollen eyelid becomes noticeable after 2 weeks. Basically, chalazion is distinguished by a benign chronic course. The disease can manifest itself even after the end of treatment.
[Video] What is a chalazion:









