Contents
Kidney diseases in men and women include various pathologies that interfere with the normal functioning of these organs of the urinary system. Each of the diseases has its own specifics, differs in the clinical picture and methods of treatment.
According to statistics, about 4% of the Russian population suffers from various kidney pathologies, although experts are of the opinion that this figure is significantly underestimated. The fact is that many kidney diseases are asymptomatic and people do not even know about the existing health problems. Therefore, it is so important to navigate the main kidney diseases, to know their symptoms and the main methods of treatment.
Often a person learns that he has an advanced stage of kidney disease quite by accident, coming to be examined for a completely different problem. Between themselves, doctors even call the kidneys dumb organs, since the first signs of the disease in some cases appear when they have already stopped working. Of course, a doctor can suspect a disease by a blood test, but for this it is necessary that this analysis falls into the hands of a nephrologist, which happens extremely rarely. Very often, for the first time, patients learn about the existence of such a doctor when they enter the hospital with a myocardial infarction.
The fact is that when the kidneys cease to function normally, the level of calcium in the blood increases sharply, which tends to be deposited on the vessels, making their lumen narrower. Therefore, it is not surprising that patients with renal insufficiency often die at the age of 30-40 years. In this case, cardiovascular diseases become the cause of death.
Statistics and reality in Russia and the USA
It is noteworthy that nephrology began to develop actively throughout the world after studies conducted in America revealed very disappointing numbers. It turned out that 12% of US residents have chronic kidney disease, and 10% of people are diagnosed with coronary heart disease. At the same time, people with heart disease receive treatment, because they know about the existing pathology, and people with kidney disease often suffer myocardial infarctions, not even suspecting what caused them to develop. Such a sad fate befalls 90% of renal patients.
Treating people with kidney pathologies is very expensive for the budget of any country, including Russia. For example, a hemodialysis procedure costs about 7000 rubles, and it needs to be done three times a week throughout the patient’s life. Therefore, not every patient is able to get treatment. So, out of one million people, only 212 people are provided with hemodialysis. And you can get treatment only in regions with a sufficient budget. The same goes for kidney transplants. There are transplantation centers in Krasnodar, Moscow and St. Petersburg, but they accept “their own” patients for treatment. Therefore, it is easier for a kidney patient from Rostov to transplant an organ in another country than, for example, in St. Petersburg. There is only one way out for such people – to move to another region in order to receive adequate treatment for their disease.
The treatment of people in whom kidney pathology is detected in a timely manner is cheaper, therefore it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan of the kidneys once a year, to take AS and LHC. This is especially true for people at risk: hypertensive patients, diabetics, people with obesity and atherosclerosis.
Causes of kidney problems
It is important to remember that the following factors can start kidney disease:
A sharp loss of body weight, which is due to the depletion of the fat capsule that surrounds the kidneys.
Obesity. Excess fat puts pressure on the kidneys, impairing their work. In addition, obesity worsens vascular tone.
Diabetes.
Bad habits (smoking and alcohol abuse). The blood thickens, as alcohol leads to dehydration of the body, and tobacco smoke is the strongest carcinogen. All this negatively affects the work of the kidneys.
High pressure that damages the kidney vessels and impairs their functioning.
You can suspect kidney disease in yourself if you are more attentive to your own health.
So, the symptoms of a violation in their work are:
Edema on the face with the formation of bags under the eyes, swelling of the lower extremities. By evening, these swelling subside. The skin becomes dry, pale, possibly yellowing.
Pain in the lumbar region may indicate pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis.
Fatigue, weakness, fever, headaches – all these symptoms make it possible to suspect kidney disease.
The reason for contacting a doctor should be a violation of the smell, color and volume of urine.
Kidney disease: pyelonephritis
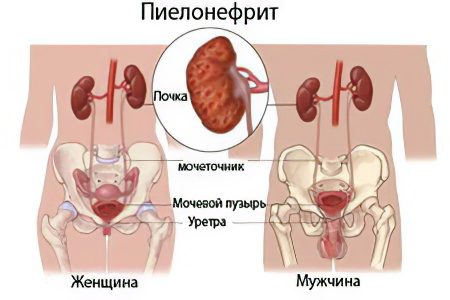
Pyelonephritis is a kidney disease of a chronic nature. The disease is widespread in urological practice. About 2/3 of all visits to the urologist end with a diagnosis of acute or chronic pyelonephritis with damage to one or both kidneys.
Causes of the disease
The causes of pyelonephritis are that pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply in the renal tissue:
Pathogenic microorganisms (in 90% of cases it is Escherichia coli) enter the kidney along the ascending path. Through the urethra, they enter the bladder and above. Women are more susceptible to this disease, which is explained by the anatomical structure of their urinary system.
Bacteria can enter the kidneys due to vesicle-urethral reflux. During this process, urine is thrown back into the pelvis of the kidney, since its outflow is impaired for one reason or another. Stagnation of urine in the kidneys contributes to the fact that bacteria begin to multiply in it, which provoke the development of the disease.
Rarely, but it is still possible to infect the kidneys by the hematogenous route, when bacteria enter them through the blood from another source of inflammation.
The risk of developing the disease increases if the ureters are clogged with a stone or pinched by an enlarged prostate.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of acute and chronic pyelonephritis will differ.
Signs indicating an acute stage of the disease:
Sudden development of the disease with an acute onset and an increase in body temperature to high levels (up to 39-40 ° C).
The patient sweats a lot, his appetite disappears, weakness increases.
Headaches can be accompanied by nausea and even vomiting.
Pain appears in the lumbar region. They can have different intensity, most often localized on one side.
Urine becomes cloudy and may turn red.
Blood tests show an increase in white blood cells and ESR.
As for chronic pyelonephritis, it is often asymptomatic and occurs against the background of undertreated acute pyelonephritis. A person may experience weakness and malaise, his appetite worsens, headaches often appear. Sometimes in the lumbar region there is a feeling of discomfort. If the disease is left without proper treatment, then eventually the patient will develop renal failure.
Treatment
If pyelonephritis occurs in an uncomplicated form, then the patient is shown conservative treatment in the urological department of the hospital. He is required to take antibiotics, which are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora detected in the urine test. Therapy should begin with the drug that has the maximum effectiveness. These can be antibacterial agents from the group of cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones. Ampicillin is used to treat pyelonephritis less and less.
In parallel, the patient is shown detoxification therapy, a diet with a low protein content in food is prescribed. After the body temperature returns to normal, the patient is transferred to a normal diet with an increase in the volume of fluid.
If the cause of the development of the disease is a violation of the outflow of urine, then it must be eliminated, after which antibiotics are prescribed, immunotherapy is carried out. Often, the restoration of the passage of urine is carried out in an operative way (removal of stones from the kidneys, nephroplexy, removal of prostate adenoma, etc.).
As for the chronic form of the disease, the treatment is built according to the same scheme, but it is longer. Short courses of antibiotic therapy are prescribed for people with chronic pyelonephritis even after a stable remission has been achieved.
Kidney disease: glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is an immunoinflammatory disease of the kidneys with a primary lesion of the renal glomeruli. Also, the renal tubules and interstitium are involved in the pathological process. Pathology can be primary, or it can develop against the background of other systemic diseases.
Very often, children suffer from glomerulonephritis, this disease is in second place after infectious lesions of the urinary system. In addition, it is glomerulonephritis that more often than other urological diseases leads to disability, as it provokes the earlier development of renal failure.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis are manifested in the following triad of signs:
Decrease in the amount of urine excreted, the appearance of blood in it. As a rule, the amount of urine separated decreases in the first 3 days from the onset of the disease, and then returns to normal. As for blood impurities, most often there is not much of it, macrohematuria is extremely rare.
The appearance of edema. The face swells, which is especially noticeable in the morning.
Increase in blood pressure. This symptom is observed in 60% of patients. Moreover, in childhood it provokes various pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
If the disease develops in childhood, then it most often proceeds very rapidly and ends with the complete recovery of the patient. In adulthood, even acute glomerulonephritis can have a blurred clinical picture, which contributes to the chronicity of the disease.
Sometimes fever, chills, loss of appetite, weakness and pain in the lumbar region are possible. Chronic glomerulonephritis tends to relapse, which most often occurs in autumn and spring.
Causes of the disease
The following causes of glomerulonephritis can be distinguished:
Streptococcal infection of acute or chronic course. Angina, tonsillitis, pneumonia, streptoderma, scarlet fever can lead to the development of kidney disease.
Sometimes the cause of inflammation of the kidneys is measles, respiratory viral infections and chickenpox.
Prolonged hypothermia of the body, especially under conditions of high humidity, often leads to the development of the disease. In this case, doctors call glomerulonephritis “trench”.
There is evidence that the disease can develop against the background of toxoplasmosis and meningitis.
As for streptococcal infection, not everyone causes kidney disease, namely nephritogenic strains of the bacterium.
Treatment
Treatment of glomerulonephritis having an acute course is carried out in a hospital. The patient is recommended dietary table number 7 and strict bed rest. In parallel, therapy with antibacterial drugs is carried out, including: Penicillin, Ampiox, Erythromycin.
All patients with glomerulonephritis are shown to correct immunity. For this purpose, hormonal drugs are prescribed – Prednisolone and non-hormonal drugs – Imuran Cyclophosphamide. To relieve inflammation, Voltaren is recommended. If necessary, patients are prescribed diuretics to reduce swelling, and also carry out therapy aimed at normalizing blood pressure.
As for the chronic form of the disease, it is treated according to a similar scheme, but for a longer time. During the period of remission, patients are shown sanatorium treatment and a two-year observation by a nephrologist.
Kidney disease: kidney failure
Acute renal failure is a violation of the functioning of the kidneys, which in some cases can be reversed. The pathology is characterized by a pronounced or complete stoppage of the organs. All the functions performed by the kidneys suffer: excretory, secretory, filtration.
Causes of the disease
The causes of acute renal failure are manifold.
It is more convenient to consider them through the forms of this pathology:
Reduced cardiac effusion due to heart failure, arrhythmias, cardiogenic shock, etc., can lead to prerenal renal failure, which is accompanied by an acute hemodynamic disorder. Acute bleeding, severe diarrhea with dehydration of the body, ascites, and extensive burns can also provoke this form of the disease. body. Anaphylactic and bacteriotoxic shock often cause kidney failure.
The renal form of acute renal failure leads to ischemia of the tissues of the kidney, or its toxic damage (in case of poisoning with poisons, heavy metals, when taking nephrotoxic drugs). Somewhat less often, the cause is inflammation of the kidney, alcoholic or drug coma, kidney injury, accompanied by prolonged compression of the tissues of the organ.
Acute obstruction (blockage) of the urinary tract leads to postrenal renal failure. It can occur due to urolithiasis, with tumors of the prostate and bladder, with tuberculosis infection.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of acute renal failure occur in four main phases, including:
A person does not experience characteristic symptoms indicating a violation of the functioning of the kidneys during the manifestation of the disease, since signs of the underlying pathology come to the fore. Perhaps the occurrence of weakness, drowsiness, loss of appetite. But these symptoms are most often attributed to the manifestation of an etiological disease.
The amount of urine excreted begins to decrease, the patient develops diarrhea, vomiting. The person becomes inhibited, he wants to sleep, the development of a coma is possible. Other organs often suffer, including the heart, pancreas. The development of sepsis and pneumonia is not excluded. This stage is called oligoanuric. It lasts about two weeks.
If there are no complications of the disease, then the person gradually begins to recover. The amount of urine excreted increases, the water-salt balance of the body returns to normal.
Acute renal failure ends with the recovery of the patient. This stage is quite long and can take up to one year. During this time, there is a gradual restoration of all body functions.
Treatment
Treatment of acute renal failure is aimed primarily at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the disease. In parallel, measures are taken to normalize the pressure, to replenish the lost volumes of fluid. If necessary, the patient is washed with the intestines.
The method of extracorporeal hemocorrection allows you to cleanse the body of poisonous substances that have accumulated as a result of disruption of the kidneys. Hemocorrection includes hemosorption and plasmapheresis.
If an obstruction is the cause of the kidney dysfunction, then it is removed surgically.
To normalize diuresis, Furosemide and osmotic diuretics are indicated. Patients require a diet low in protein and limited in potassium. If necessary, the patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs, but their dose should be selected with great care.
Hemodialysis is performed as a method that prevents the development of serious complications. Modern urological practice actively uses it even in the early stages of the development of acute renal failure, as well as for the purpose of prevention.
Kidney disease: urolithiasis (nephrolithiasis)
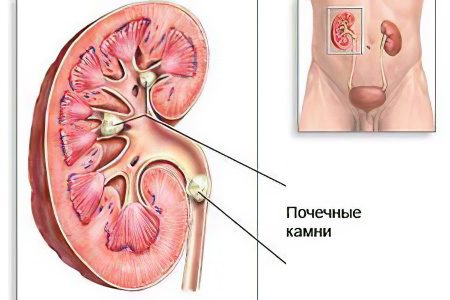
Urolithiasis is a disease accompanied by the formation of kidney stones (their formation in the bladder and other organs is not excluded). The disease is widespread, can manifest at any age, but is most often diagnosed in people 25-50 years old.
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the formation of kidney stones are based on the process of crystallization of urine.
Factors provocateurs can be:
Hereditary predisposition.
Non-compliance with the drinking regime, especially when living in hot climatic zones. It is dangerous to regularly drink water with a high content of calcium salts in it, as well as an addiction to spicy, fatty and salty foods.
Dehydration of the body as a result of diseases accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea.
Avitaminosis, in particular, a lack of vitamin D and vitamin A in the body.
Various diseases of the body: osteoporosis, osteomyelitis, hyperparathyroidism, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, ulcers, colitis), infections of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, nephrotuberculosis), as well as prostatitis and prostate adenoma. Any condition that interferes with the normal outflow of urine is dangerous.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of urolithiasis of the kidneys depend on the volume of stones, their number and composition. The main signs of the disease are:
Pain of varying intensity with localization in the lumbar region;
Renal colic;
blood in the urine;
Pus in the urine;
Sometimes a kidney stone passes on its own along with urine.
At the same time, about 15% of patients do not even suspect that they have kidney stones, since they do not manifest themselves in any way.
Treatment
There are two possible treatment options for kidney stones: conservative and surgical. However, both of them have as their goal the removal of stones from the organs.
If a patient has a small stone, which does not exceed 3 mm in volume, then he is recommended to drink plenty of water and eat a diet with the exception of meat dishes.
If the stone is urate, then you should follow a diet with an emphasis on dairy drinks and foods of plant origin, it is important to drink mineral water (alkaline). Acidic mineral water is recommended for phosphate stones. In addition, it is possible to prescribe drugs that help dissolve stones, as well as diuretics and nitrofurans. However, such treatment can only be carried out by a nephrologist.
If the patient is admitted with renal colic, then Baralgin, Platifillin or Pantopon is urgently administered to him to eliminate pain. Novocaine blockade of the spermatic cord or round ligament of the uterus, depending on the gender of the patient, is performed if renal colic does not go away with the administration of painkillers.
The operation is necessary if there are regular renal colic, pyelonephritis develops, ureteral stricture, or other conditions that threaten the health of the patient.
Kidney disease: hydronephrosis
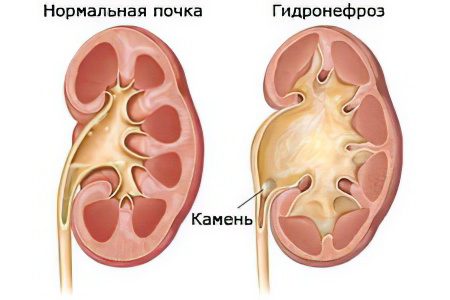
Hydronephrosis is an atrophy of the renal tissue, which develops due to the expansion of the pyelocaliceal complex, which is caused by a violation of the passage of urine. Under the age of 60, women are more susceptible to the disease, while after 60 years, pathology is more often diagnosed in men. This is due to the development of prostate adenoma or prostate cancer.
Atrophy of nephrons and tubules of the kidney is the outcome of the disease. It begins with the fact that due to problems with the outflow of urine, the pressure in the ureter increases, the filtration function suffers, and the blood flow of the organ is disturbed.
Causes of the disease
The causes of hydronephrosis are as follows:
The presence of a tumor, polyp, stones or blood clots in the ureter.
Fungal diseases of the urethra.
Infections of the urethra (tuberculosis, endometriosis, etc.), its strictures and diverticula.
Cervical cancer, childbearing, uterine prolapse, ovarian cyst, prostate tumor, aortic aneurysm in the peritoneum, anomalies in the location of the renal artery.
Urolithiasis, diverticulum of the bladder, contracture of its neck, vesicoureteral reflux and other pathologies of this organ.
Congenital obstruction of the urinary tract, their trauma and inflammation.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of hydronephrosis depend on how long the person has had a blockage in the urinary tract and what has caused the problem.
The following options for the development of the clinical picture are possible:
The acute development of the disease is manifested in severe lumbar pain with their irradiation in the groin, perineum and genitals. Urination becomes more frequent and painful. Nausea and even vomiting may occur. Blood is often found in the blood.
The latent course of the disease is most often observed with unilateral aseptic hydronephrosis. There may be minor back pain that gets worse after exercise. In addition, a person begins to consume more fluid. As the pathology progresses, chronic fatigue joins, blood pressure rises.
It is noteworthy that people with hydronephrosis prefer to lie on their stomach during night rest. This improves the outflow of urine from the diseased kidney, as it leads to a redistribution of pressure inside the abdominal cavity.
Anomalies in the development of the kidneys
Kidney nephroptosis
Kidney nephroptosis is characterized by pathological mobility of the organ with its displacement of more than 2 cm with a vertical position of the body and more than 3 cm with forced breathing.
The causes of nephroptosis may be due to a decrease in the muscle tone of the abdominal press, hypermobility of the joints. There are occupational risk factors. So, drivers, hairdressers, surgeons, loaders are more susceptible to nephroptosis, which is due either to prolonged physical stress while in one position, or constant vibrations. It is possible to develop pathology due to various skeletal anomalies, for example, in the absence of vertebrae. Sometimes nephroptosis occurs in women who are carrying a large child.
Symptoms of nephroptosis are manifested in pulling pains radiating to the abdomen. When the kidney returns to its place, the pain disappears. Perhaps the formation of renal colic, disruption of the digestive system, neurasthenia due to chronic pelvic pain. In severe pathology, the development of renal failure, persistent urinary infections are possible.
Conservative treatment with wearing special bandages, performing gymnastic exercises and with enhanced nutrition is prescribed for mild nephroptosis. If the pathology is complicated and leads to serious disorders in the functioning of the kidneys and other organs, then surgical treatment is necessary. The operation is called “nephropexy”, it consists in returning the kidney to its original place with subsequent fixation of the organ to nearby structures.
Polycystic kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease refers to a congenital anomaly in the development of organs and is characterized by the formation of multiple cysts in them. Both kidneys are always involved in the pathological process.
The causes of polycystic kidney disease are caused by genetic disorders inherited in an autosomal domain.
Symptoms of the disease in newborns develop rapidly and lead to the death of the child. In adulthood, the signs of the disease grow slowly, are characterized by a gradual disruption of the kidneys by the type of chronic renal failure.
Treatment of polycystic kidney disease is reduced to symptomatic therapy. To eliminate infections, antibacterial drugs and uroseptic agents are used. It is important to engage in the prevention of kidney disease: you need to give up hard physical work, follow a diet, engage in the timely elimination of foci of chronic infection. At the terminal stage of renal failure, the question of organ transplantation arises. Hemodialysis is recommended to keep the body functioning.
Kidney dystopia
Kidney dystopia is a violation of their location. This anomaly refers to congenital malformations. The kidneys can be located low, they can be displaced into the pelvic cavity, into the chest, etc.
The cause of kidney dystopia is anomalies in the development of the fetus that occur during fetal development.
Symptoms of dystopia may not manifest themselves in any way, but may be expressed in dull lumbar pain. The area of their distribution depends on where exactly the kidneys are located.
Treatment is limited to conservative therapy, which is designed to prevent the development of kidney infection, as well as the formation of stones in them. Surgical removal of the kidney is performed when it dies.
Malignant tumor of the kidney
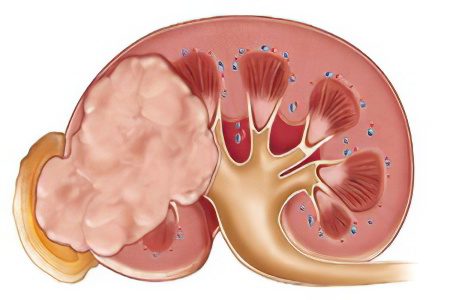
A malignant tumor of the kidneys is a whole group of diseases that combines various malignant transformations of the kidney tissue. Among the total mass of oncological diseases, kidney cancer occurs in 2-3% of cases. Most often, people over the age of 40 suffer from the disease.
Causes
The causes of a malignant tumor of the kidney are due to multiple factors, including:
Gene mutations.
Hereditary predisposition.
Bad habits.
Uncontrolled intake of drugs (hormones, diuretics, analgesics).
Chronic renal failure, polycystic kidney disease, nephrosclerosis of various etiologies.
Carcinogenic poisoning of the body, exposure to radiation.
Kidney injury.
Symptoms
Most often, the symptoms of a malignant tumor of the kidney do not manifest themselves. The asymptomatic course is characteristic of the early stages of the development of the disease.
As it progresses, the patient develops the following triad of symptoms:
Impurities of blood in the urine.
Pain in the lumbar region.
The appearance of a tumor that can be palpated.
Naturally, all three signs will be simultaneously observed only in the later stages of the development of the disease. Other manifestations of a malignant neoplasm of the kidney are: fever, loss of appetite, swelling of the lower extremities, dystrophy, etc.
Treatment
Treatment of a malignant tumor of the kidney is reduced to the surgical removal of the neoplasm. It is resorted to even in the later stages of the development of the disease and in the presence of metastases. This allows you to increase the life of the patient and improve its quality.
Resection of the kidney or global removal of the organ is used. As an additional method of treatment that increases the effectiveness of the operation, immunotherapy, chemotherapy and targeted therapy are used. Palliative treatment is carried out with extensive metastasis of the tumor to the lymph nodes.









