Contents
The stages of in vitro fertilization (IVF)
Conventional in vitro fertilization
The in vitro fertilization treatment program requires numerous appointments with specialists, who prepare the couple for the technique. The couple should be educated about complex steps such asinjection of hormonal drugs, the risks and Side effects, as well as waiting time required. The treatments are expensive.
In Quebec, since 2010, the Régie de l’Assurance Maladie (RAMQ) has set up the Quebec Assisted Procreation Program which offers free of charge a full range of services dealing with infertility, including the costs of three stimulated cycles9.
In France, 4 in vitro fertilization trials are fully covered by Health Insurance.
1. Stimulation of the ovaries
The first step is to give the woman hormone therapy, usually a GnRH agonist (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone) in order to rest the ovaries (see the section on medicines), for example Decapeptyl®, Suprefact®, Enantone® Synarel®, or Lupron®.
Then, the treatment then aims to increase the number of follicles produced by the ovary and control the timing of ovulation. The woman should receive injections of gonadotropins with FSH or LH activity to stimulate the follicles to mature and allow them to produce several oocytes. These are for example Puregon®, Gonal F®, Fostimon® Metrodin-HP®, Bravelle®, Humegon® Ménopur® Merional® Repronex® Fertinex® Fertinorm®, Humegon® Ménopur® Merional® Repronex® Fertinex® Fertinorm®, Elonva®, Luvéris® …
When the follicles have grown enough and hormone levels are adequate, ovulation is triggered by an injection of the hormone HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), for example HCG endo 1500®, HCG endo 5000® (Fr), Pregnyl®, Choriomon®, Profasi-HP®, Chorex®, Novarel®, Ovitrelle® Ovidrel® ®
Pelvic ultrasound and blood tests are done at each step to assess follicle growth.
No more follicles, no more eggs …
A woman’s ovaries usually produce and release only one mature egg per cycle. Although this is sufficient for normal conception, for successful in vitro fertilization, ideally more mature eggs should be obtained. It is therefore necessary to stimulate the patient’s ovarian activity more strongly than usual. Drugs given during in vitro fertilization treatment cause the development of multiple ovarian follicles, thus increasing the possible number of eggs, thus the chances of obtaining an implantable embryo.
2. Collection of mature oocytes
After 32 to 36 hours of hormonal stimulation, the ripe oocytes are collected using a small tube and a needle which are inserted into the vagina. This intervention is performed under local or general anesthesia with ultrasound control because it can be very painful. The oocytes are then selected in the laboratory.
Le semen is collected a few hours before (or thawed the same day), and the sperm are separated from the seminal fluid and stored at 37 ° C.
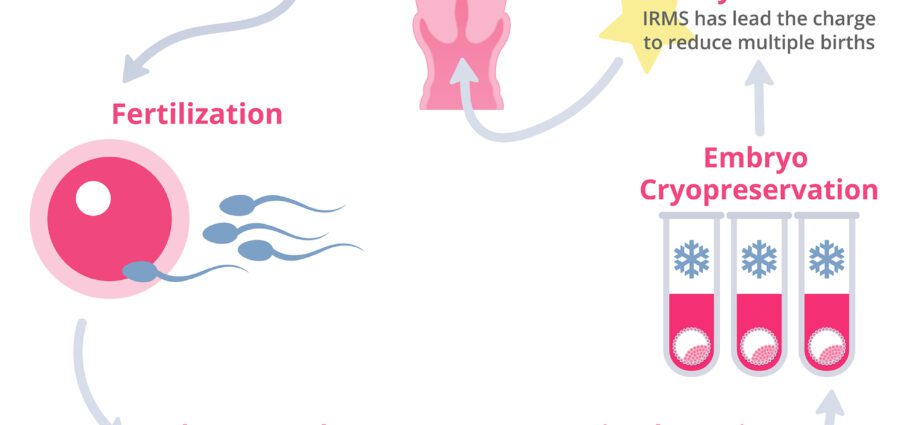
3. Fertilization
A few hours after their harvest, the spermatozoa and the oocytes are placed in contact in a culture liquid for several hours at body temperature. The motile spermatozoa come spontaneously, without external help, in contact with the oocyte. But only one sperm will fertilize this one. In general, on average, 50% of the oocytes are fertilized.
The fertilized oocytes (or zygotes) begin to multiply. In 24 hours, the zygotes become embryos of 2 to 4 cells.
4. Embryo transfer
Two to five days after fertilization, one or two embryos are transferred to the woman’s uterus. Embryo transfer is a simple and painless procedure carried out by means of a thin and flexible catheter inserted vaginally into the uterus. The embryo is deposited inside the uterus and develops there until implantation.
After this step, the woman can usually resume her normal activities.
One or more embryos (called supernumeraries) can also be stored by freezing for later testing.
Thereafter, the doctor can give hormonal medical treatment, and of course prescriptions for pregnancy tests to see if the IVF has been effective.
Several cycles of treatment are sometimes necessary before the pregnancy is successful. And unfortunately, some couples do not get pregnant despite several attempts.
Advice before IVF:
- Stop smoking (man and woman!), Because it greatly reduces the chances of getting pregnant.
- Exercise and strive for a healthy weight. It helps to have good fertility.
- For women: take vitamin B9 before you become pregnant, as this decreases the risk of malformation in the unborn child.
- Get a flu shot (it can lead to miscarriages).