STDs and STIs: all about sexually transmitted diseases and infections
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), now called sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are infectious diseases that are caused by the transmission of pathogens during sexual intercourse. An STD requires early detection to limit the risk of complications.
What is an STD?
STD is the abbreviation for sexually transmitted disease. Formerly known as venereal disease, an STD is an infectious disease that can be caused by different pathogens. These are transmitted during sexual intercourse, whatever its type, between two partners. Some STDs can also be transmitted through blood and breast milk.
What is an STI?
STI is the abbreviation for sexually transmitted infection. In recent years, the acronym IST has tended to replace the abbreviation MST. According to public health authorities, “to use the acronym IST is to encourage screening (even) in the absence of symptoms”. Therefore, the only difference between an STI and an STD is in the terminology used. The acronyms IST and MST designate the same diseases.
What are the causes of an STD (STI)?
An STI can be caused by more than XNUMX sexually transmitted pathogens. These can be:
- bacteria, Such as Treponema pallidum, Neisseria gonorrhoeae et Chlamydia trachomatis ;
- viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), Herpes simplex (HSV) and human papillomavirus (PHV);
- parasitesIncluding Trichomonas vaginalis.
What are the main STDs (STIs)?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the eight pathogens mentioned above are involved in the majority of STD cases. Among these are:
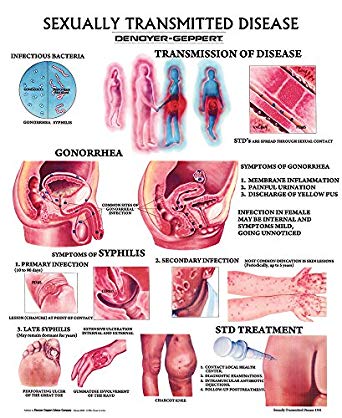
- syphilis, infection with the bacteria Treponema pallidum, which manifests as a chancre and which can progress and lead to other complications if not taken care of in time;
- gonorrhea, also called gonorrhea or “hot-piss”, which corresponds to an infection by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae ;
- the chlamydiose, often called chlamydia, which is caused by infection with the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis and which is one of the most common STIs in Western countries;
- trichomoniasis, infection with the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, which is most often manifested in women by vaginal discharge accompanied by itching and burning;
- infection with the virus hepatitis B (VHB), which results in liver damage;
- genital herpes, caused by the virus Herpes simplex, mainly type 2 (HSV-2), which manifests as vesicular lesions in the genitals;
- infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which is responsible for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS);
- infection by human papillomavirus, which can cause condyloma, external genital lesions, and which can promote the development of cervical cancer.
Who is affected by STDs (STIs)?
STDs can be transmitted during sex, of any type, between two partners. They are often diagnosed in young adults. Some STIs can also be passed from mother to child.
What are the symptoms of STDs (STIs)?
Symptoms vary from one STD to another. They can also be different in men and women. However, there are some suggestive signs of an STI, such as:
- damage to the genitals, which can result in irritation, itching, redness, burns, lesions or even pimples;
- unusual discharge from the vagina, penis or anus;
- burning during urination;
- dyspaneuria, that is to say pain and / or burning felt during sexual intercourse;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- associated signs like fever and headache.
What are the risk factors for STDs?
The main risk factor for STDs is risky sex, that is, unprotected sex.
How to prevent an STD?
It is possible to prevent the development of an STD by limiting the risk of infection:
- adequate protection during sexual intercourse, in particular by wearing a male or female condom;
- vaccination against certain infectious agents, such as hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human papillomavirus (HPV).
If in doubt, it is also recommended to perform an STD test. Early detection allows rapid medical treatment and limits the risk of contagion.
How to screen for an STD / STI?
An STI test is recommended in case of doubt or risky sex. This screening is all the more important as it is possible to be a carrier of an STI without realizing it. For more information on these screening tests, you can get information from:
- a health professional such as a general practitioner, a gynecologist or a midwife;
- a free information, screening and diagnostic center (CeGIDD);
- a family planning and education center (CPEF).
How to treat an STD (STI)?
The medical management of an STD depends on the infectious agent involved. While some STIs are curable, others are incurable and are still the subject of scientific research.
Some curable STDs include syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis. Scientific studies continue to find medical treatment for incurable STDs such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, hepatitis B and genital herpes.