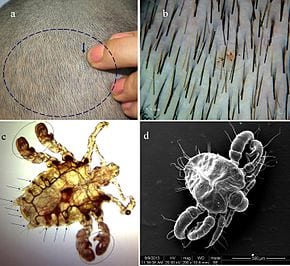
General description of the disease
In the people it is called lice from the Latin word pediculus – in translation “louse.” This disease is parasitic, appears after infection of lice (blood-sucking ectoparasitic insects). All types of warm-blooded animals, including mammals and birds, can suffer from it. It should be noted that all parts of the body are susceptible to infection, but often this term is applied by default to one of the types of head lice, the most common – infection of the head with a specific type of lice.
The reasons that provoke the occurrence of head lice
Anyone, regardless of age, gender, race or ethnicity and personal hygiene standards, is susceptible to head lice if they come into contact with an infected person.
- 1 Head lice usually common in children. They are infected in places of large crowds of people – kindergartens, schools, colleges, clinics, etc.
- 2 Pubic lice most often affect the group of people who have sex. Most often they are affected by people aged 15 to 40 years.
- 3 Body lice most often occurs in people with poor personal hygiene, who do not have the opportunity to bathe regularly, and often change their clothes. Mostly adults suffer from them.
Pediculosis occurs all over the world. The condition is observed in both developed and developing regions of the world.
It is very important to note that lice do not fly – they move by clinging to people’s hair or clothing with their paws. So there are several risk groups that are most exposed to lice infestation.
- People in crowded places.
- People who do not follow hygiene, do not have regular access to a shower, rarely change their clothes. Very often people without a fixed abode, street children, suffer from head lice.
- Transitional populations: people who move from one place to another, refugees.
- People with long hair. As a rule, they are more at risk of catching head lice, as the lice easily cling to the hair.
We would like to note that the identification of a person for a particular risk factor is not a prerequisite for infection. As well as his absence in any of the listed risk groups cannot guarantee that he will not become infected with head lice.
Head lice symptoms
The very first symptom, which is common to all types of lice, is the presence of very small red spots on the body at the site of the bite, as well as an intense itching sensation when the lice feed. This can manifest as scratches on the back of the head or around the ears, indicating the presence of head lice, or an itchy sensation in the genital area, indicating the presence of pubic lice. Lice can often be seen with the naked eye, and their nits appear as very small white lumps on the hair.
In general, the symptoms of different types of head lice differ and depend on the type of its type:
Head lice:
- severe itching, as a result – wounds on the head;
- bad smell, dull, lifeless hair;
- abnormal enlargement of the occipital and cervical lymph nodes;
- rash caused by hypersensitivity.
Body lice:
- the appearance of small, red, inflammatory dots on the shoulders, trunk and buttocks;
- dry, discolored, thick-skinned, scaly skin;
- secondary bacterial infections;
- skin scars;
- in very severe cases, accompanying symptoms may include headaches, fever, and malaise.
Pubic lice:
- skin irritation;
- small blue-gray spots that appear on the thighs and genitals[3].
Types of head lice
- Head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis) are in the hair on the head. Most often, children are at risk – schoolchildren or campers. Lice are often transmitted through items of clothing (for example, shirt collars, hats), as well as through hair accessories such as hairpins, elastic bands or combs. This is because head lice or their eggs can stick to objects and pass from one person to another. Adult lice live on the host for up to 3 days, and their eggs hatch within a week. Contrary to popular belief, head lice can settle on clean hair just as often as on dirty hair.
- Body lice (The human body louse) – these are evolved head lice, which were able to slightly change their structure, and feed on blood from different parts of the body. They are transmitted through shared clothing or bedding and live there. Very often, their eggs attach to tissue fibers, especially along inner seams, pockets, and other areas of contact with the body. The female typically lays 9 to 10 eggs per day and a total of 270 to 300 eggs throughout her life. The eggs are incubated with the heat of the human body and hatch after about a week. Body lice can cause serious illnesses such as typhus and fever.
- Pubic lice (Phthirus pubis) – live on the skin and hair of the pubis, genitals, around the anus. Sometimes they can move to other parts of the body where there is hair – for example, in the armpits or chest, abdomen[2].
Complications of head lice
Pediculosis can lead to very unpleasant consequences in the form of the appearance of abscesses on the skin, sources of inflammation. After all, lice feed on human blood, and one individual needs about 4-5 meals a day. When they bite through the skin, they inject an enzyme under it, which provokes very severe itching. And a person, trying to eliminate this most unpleasant feeling, simply combs the wound. As a result, it becomes even more inflamed, becomes open for any bacteria and infections to enter it. That is why very often head lice ends with pyoderma – the formation of abscesses on the body, an increase in body temperature.
It is also common for a person to be allergic to lice bites. This is rare, but allergies can appear in the form of a large number of rashes where more bites are concentrated. From this, the temperature often rises and the lymph nodes swell.
The most dangerous consequence of head lice is infection with infections, which can be carried directly by lice. They can provoke typhus or relapsing fever, Volyn fever. History knows cases when it was because of these parasitic insects that whole epidemics broke out, which led to the death of a large number of people. In our time, this is very unlikely, since over the centuries the living conditions, hygiene, sanitary standards have greatly improved, but still we recommend not to postpone the treatment of head lice, and immediately start fighting lice.
Prevention of pediculosis
The following preventive and safety measures can be taken to reduce the incidence of head lice.
- 1 Avoid close physical contact with infected individuals.
- 2 Avoid sharing clothing, beds, combs and hairbrushes with people who may be infected with head lice.
- 3 Conducting preventive conversations in schools and other educational institutions about how head lice is transmitted, how it is treated, and what precautions should be taken to prevent its spread. The importance of good hygiene and sanitation should be emphasized, children should be taught not to share hats, headphones, combs, bicycle helmets, and any head itching should be reported.
- 4 You can conduct regular examinations of children, especially in schools, colleges, summer camps, in order to establish the presence of a focus of infection, start treatment and establish temporary quarantine.
- 5 In crowded places, it is best to keep long hair tied in a high ponytail and collect it away from your face.
Treatment of head lice in official medicine
Lice are diagnosed by external signs. The consequences of their vital activity are often noticeable – irritation, trauma to the skin, wounds, rashes. Often you can see the lice themselves and their eggs with the naked eye.
Typically, treatment for head lice includes drug therapy, as well as the use of products to maintain personal cleanliness and hygiene.
To combat head lice, special medicinal shampoos containing pyrethrins (natural insecticidal compounds) are used. In other cases, it is very important to process not only the affected areas on the body, but also clothes and bedding. They should be washed in hot water and dried in a dryer at high temperature for about 20 minutes. Used combs and brushes must also be washed. The room of infected people should be as cleaned as possible of possible lice eggs laid – the so-called nits.
Hats, scarves, combs and other cosmetic accessories used by an infected person should be rinsed with hot water and dried using hot air[3].
Since lice cannot live in isolation from people, in order to dry them on pillows, you can seal them in an airtight bag for 10-14 days. It is advisable to vacuum all carpets, furniture, car seats.
Useful products for head lice
When infected with head lice, it is recommended to adhere to the standard diet that is prescribed to healthy people. The diet should be as complete and balanced as possible. It is recommended to eat in small portions 4-6 times a day. Allowed and dairy products, and eggs (boiled or as part of other dishes), and soups and cereals. Meat, fish, legumes, fruits and vegetables in any form, herbs, fresh juices are also very useful.
Traditional medicine for head lice
- 1 It is recommended to comb out head lice with a comb with very dense, fine teeth.
- 2 Rub cranberry juice into the scalp. It is recommended to do this daily for 10-12 days.
- 3 For rubbing into the affected areas, you can prepare a special decoction based on 2 tablespoons of dry mint and a glass of pomegranate juice. This mixture needs to be boiled for 10 minutes and smeared on the skin with a clean cotton swab.
- 4 Another mixture for rubbing into the skin: you need to mix 10 grams of larkspur, 5 grams of citric acid, pour a glass of boiling water over them. This mixture should be infused for 6 hours, then it must be filtered, and rubbed into the skin for 5-10 days[4].
- 5 Mayonnaise should be applied to the hair along its entire length, wrapped in a plastic bag, wrapped in a towel and left overnight – the fat will clog the spiracles of the lice.
- 6 Tar soap – they can wash your hair and affected areas, since the active substance tar, as well as the alkaline composition of the soap, helps to poison and suffocate parasites.
- 7 Tea tree oil applied neat to the skin or added to shampoo will help ward off lice with its rich scent as well as suffocate parasites.
- 8 Lice cannot withstand high temperatures. Even 35 degrees Celsius is already a lot for them. That is why it is recommended to dry the hair with a hairdryer after washing to combat head lice. You can also walk on them with an iron or curling iron – the nits simply burst and can be easily removed with tongs.
Dangerous and harmful products for head lice
During head lice, it is recommended to exclude from the diet fatty poultry and meat, as well as spicy foods – mustard, pepper, various sauces with the addition of these components.
It is also important to refrain from drinking alcohol, so as not to cause additional harm to an already sensitive and weakened body. Sweets and flour products (except for pasta made from durum wheat and whole grain bread) are also prohibited.
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!