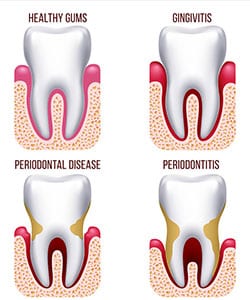
Periodontal disease is a fairly rare disease. But it is very often confused with periodontitis – the second most common oral disease, immediately after tooth decay. It is characterized by inflammation of the tissues that surround the tooth – periodontium… But periodontal disease is already a systemic damage to these very tissues, it is a more serious disease. It can either worsen or be accompanied by other diseases, such as hormonal disorders, diabetes mellitus, hypovitaminosis, decreased immunity, etc.
Causes of periodontal disease
The risk of periodontal disease increases with age. It also depends on geographic conditions of residence, diet, social status, race and gender (men are more susceptible to this phenomenon). You can also observe a link between the severity of periodontal disease and poor oral hygiene.
Often, inflammation of the gum tissue and periodontal tissue is associated with dental plaque present on the surface of the teeth, because 90% of it consists of bacteria. The more pronounced the deposits on the surface of the teeth, the more bacteria damage the gums and other periodontal structures.
In addition, gingival diseases are also affected by tartar Is a mineralized dental plate present on the surface of the teeth, both above and below the gums. The mineral scaffolds of the calculus cause the plaque to be very close to the tissues (the surface of the coarse plaque promotes the accumulation of living plaque) and has a direct pathogenic effect on the teeth and the surrounding structure. Areas that are extremely susceptible to calculus include the tooth surface around the openings of the salivary glands, uneven tooth surfaces (overhanging fillers, prosthetics, etc.).
Other factors that can provoke the appearance of periodontal disease are the amount and content of saliva, overhanging or loose fillings, defective prosthetic elements, breathing through the mouth, anatomical defects in the oral tissue, traumatic occlusion, some irritations – chemical, thermal, allergic and systemic (general disease, for example, immunological, hormonal, metabolic)[1].
Symptoms of periodontal disease
The most common symptoms of periodontal disease are bleeding gums, leucorrhoea, inflammation, lagging of the gums from the teeth, and the appearance of pus from the gums. A sick person’s teeth may diverge, or, conversely, move. At times, changes in location are not particularly noticeable on examination, but are felt when biting or chewing. Bad breath or a strange taste that accompanies a person constantly can also be considered a symptom of periodontal disease.
It is worth noting that it does not always appear quickly. Sometimes the disease can develop for years, practically without making itself felt, or without bringing great discomfort to a person with its symptoms.[4].
Types of periodontal disease
There are three degrees of severity of this disease:
- easy;
- average;
- heavy.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that periodontal disease is a long-term disease. In its development, it goes through several stages. The first stage is gingivitis – inflammation of the gums. During this period, the gums itch, there is a feeling that they are becoming loose.
Bleeding of the gums later appears. Some patients experience gum pain when brushing their teeth and eating solid foods.
But due to the fact that the pain is still not severe, many patients postpone going to the doctor. Especially if the pain disappears after two to three days. Typically, patients seek dental care when the base of the tooth is exposed and when a tooth gingival indentation forms. At this stage, increased bleeding and painful sensations often occur.
Complications of periodontal disease
If periodontal disease is left untreated, exacerbations and health problems can occur.
- Recurrent gum abscesses (painful, purulent abscesses).
- Increased damage to the periodontal ligament (tissue that connects the tooth to the socket).
- Damage and loss of the alveolar bone (the bone in the jaw that holds the root of the tooth).
- Receding gums.
- Loose teeth.
- Loss of teeth[3].
Prevention of periodontal disease
The most important factor in the prevention of periodontal disease is high-quality oral hygiene, which consists in proper cleaning of teeth, use of water sprinklers for the mouth, special brushes that clean the space between teeth, a dental check-up every 6 months for healthy people, and every 4 months for people with an established diagnosis. periodontal disease, as well as regular plaque removal.
It should be remembered that undetected and untreated, even at the first stage, the disease can lead to large recessions of the tissues of the oral cavity and the loss of teeth. In the later stages of the disease, surgical treatment may be necessary, which inevitably means more discomfort for the patient[2].
Prevention also requires addressing other factors that are detrimental to oral hygiene. For example, incorrect fillings or prosthetic elements, it is also important to consider problems with occlusion or other dental defects (for example, orthodontic).
Another effective way to prevent disease is to maintain a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition. The diet should certainly include vegetables, fruits, whole wheat, healthy proteins.
Treatment of periodontal disease in mainstream medicine
Usually, periodontal disease is treated in three stages. They include the following measures:
I – the initial phase, in which the causes of the disease are removed
At this stage, simple oral care steps must be followed to remove plaque and tartar and achieve satisfactory oral hygiene.
- Carry out professional teeth cleaning at the dentist (remove all dental deposits).
- Carry out dental plastics in places where dental plaque accumulates.
- Eliminate annoying factors.
- Learn to professionally take care of your oral cavity.
- Maintain good oral hygiene at home.
The following tools should be used:
- mechanical equipment for plaque removal (ultrasound, aerosol);
- hand tools;
- mechanical tools for removing soft plaques and stains (sandblasting device);
- polishing tools (rubber tips, strips, polishing pastes, etc.)
II – Correction phase, in which it is necessary to remove the remnants of the disease
At this stage, patients undergo surgical procedures to correct or regenerate damaged periodontal structures. These procedures are aimed at the complete reconstruction of structures damaged due to the disease and the maintenance of teeth – periodontitis structures.
III – Phase supporting treatment outcomes
Dentist visits, professional dental cleaning, laser therapy, pharmacological treatment[1].
Useful products for periodontal disease
First of all, people suffering from periodontal disease need to include in the diet as many fruits and vegetables as possible. There are several important reasons for this. Firstly, they will help to replenish the balance of vitamins and nutrients in the body. Secondly, solid foods are an excellent trainer for weakened teeth and gums. And the fiber they contain will benefit the body and help the stomach to work properly. When chewing, it is important to try to evenly distribute the load over the oral cavity so that all areas have time to actively work.
Pay particular attention to citruses, carrots, bell peppers. These foods are rich in vitamins A and C, which are faithful helpers in the fight against periodontal disease.
The second important nutritional factor that will help strengthen your gums and teeth is dairy products. Try to enrich the diet with cottage cheese, milk, sour cream, cheese. If they are natural, that’s even better. And so that calcium is absorbed as well as possible, do not deny yourself walks in the fresh air under the sun.
Traditional medicine for periodontal disease
- 1 To strengthen teeth with periodontal disease, it is recommended to drink freshly squeezed raw potato juice. Be sure to rinse your mouth after drinking, as concentrated potato juice has a detrimental effect on sensitive tooth enamel.
- 2 You need to stir honey with burnt salt in a ratio of 3: 1 or 2: 1. Combine these two ingredients well, stir to dissolve the salt, roll up a ball of honey and salt, put it in a clean handkerchief and rub your teeth with it.
- 3 Oak bark helps to relieve inflammation. It also helps to eliminate bleeding. To do this, prepare a decoction of 2 tablespoons of oak bark powder, 1 spoon of linden blossom. Pour a teaspoon of this mixture with a glass of boiled hot water, heat over the fire for 3 minutes, then cool, strain. Rinse your mouth with warm broth.
- 4 Another recipe for bleeding gums: pour a spoonful of chopped stinging nettle leaf with a glass of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, then strain and take as an infusion. It is enough to drink half a glass of this liquid three times a day after meals.
- 5 If you are pestered by purulent abscesses, you need to prepare a mixture for mouth baths. To do this, mix a teaspoon of dry herb of Pochuy Knotweed, a glass of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours, and then strain. Baths should be done with hot infusion. You can also take it orally – 0.3 cups three times a day before meals [4].
Dangerous and harmful foods for periodontal disease
To combat periodontal disease, you need to exclude from the diet foods that can stick to the gums and provoke the appearance of plaque on the teeth. These are chips, sweets, all kinds of confectionery and flour products. It is also better to minimize the consumption of tea, coffee. Smoking is contraindicated.
And naturally, it is very important to have regular check-ups with the dentist, to brush your teeth thoroughly and correctly twice a day to avoid the formation of plaque and the accumulation of bacteria on the teeth.
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!