Contents
General description of the disease
Parkinson’s disease is a disease of the central nervous system of a degenerative chronic nature, in which a person is unable to control his movements. Most of the elderly and elderly people suffer from this disease.
Read also our dedicated article, Nutrition for the Brain and Nutrition for Nerves.
The causes of the disease have not yet been precisely determined. Scientists put forward such theories and possible causes of Parkinson’s disease:
- free radicals damage the cells of the substantia nigra of the brain, as a result of which the oxidation of brain molecules occurs;
- intoxication of brain tissue, disruptions in the functioning of the liver and kidneys;
- heredity (a quarter of patients had relatives with Parkinson’s disease);
- genetic factor (scientists in the field of genetics have identified several gene mutations, in the presence of which Parkinson’s disease develops in the body in youth);
- lack of vitamin D;
- degeneration of brain neurons, the appearance of mitochondria with defects caused by various mutations;
- encephalitis (viral and bacterial);
- the presence of atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the tissues of the brain;
- suffered concussion and traumatic brain injury.
Parkinson’s disease symptoms
In the early stages, it is very difficult to determine the disease, because it is almost asymptomatic. A deep examination is required to make a diagnosis.
The first symptoms that can identify Parkinson’s disease:
- 1 general breakdown, weakness;
- 2 the gait becomes uncertain and unsteady, steps are small (the patient “minces”);
- 3 fuzzy nasal speech, unfinished phrases, confused thoughts;
- 4 the spelling of letters changes – they become angular, small and “trembling”;
- 5 a sharp change in mood;
- 6 muscles are in constant tension;
- 7 muscles contract quickly (tremor sets in, first of one arm, then of all limbs).
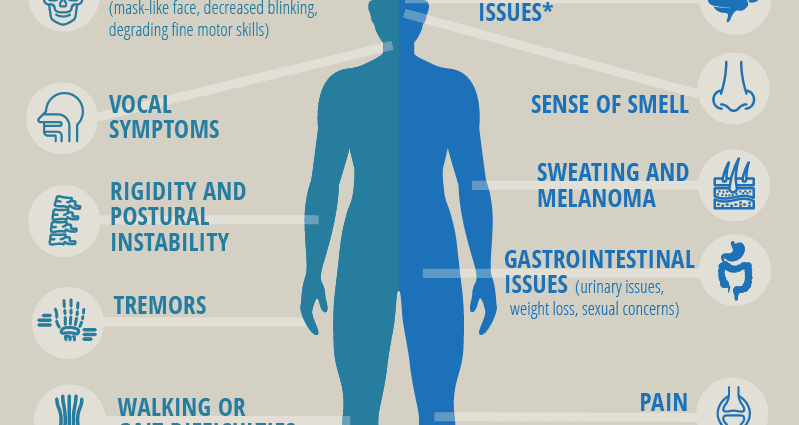
The main symptoms of the disease:
- mask-like facial expression (no facial expressions);
- muscle stiffness;
- limbs are constantly in a bent state;
- tremor of the limbs and lower jaw;
- all movements are slow (even the usual washing and dressing can be delayed for a couple of hours);
- weight loss, poor appetite, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- constant falls, lack of control over movements;
- due to incessant spasms and muscle contractions, severe pains occur throughout the body;
- posture resembles “begging for alms”;
- enuresis, constipation;
- depressive states, a constant feeling of fear, but at the same time common sense remains;
- memory disorders;
- disturbances in the work of the skin and subcutaneous glands (excessive sweating or, conversely, dry skin, dandruff);
- nightmares, insomnia.
Healthy foods for Parkinson’s disease
Since patients have a large percentage of constipation, it is necessary to eat a large amount of fiber, which fruits and vegetables contain. Many people have problems with chewing and swallowing, so food is best served boiled, steamed or stewed.
Fruits and vegetables with a tight skin should be peeled and pitted.
The patient should focus on: liver, eggs (only boiled or omelet), butter, sour cream, ice cream, cream, yogurt, kefir, porridge (especially rice, oatmeal), cereals, fish, corn, beets, carrots, apples , prunes, dried apricots, strawberries, strawberries, garlic and all greens.
You need to drink at least 6 glasses of liquid a day.
Folk remedies for Parkinson’s disease:
- 1 Drink a glass of linden tea daily on an empty stomach. Drink a month after a month (a month of treatment – a month off) and so on throughout the year.
- 2 Broth from oats. Take a glass of oats, place in 1 liter of clean water, leave to infuse for 8 hours. At the end of the time, boil for half an hour. Allow to cool and leave for another half day (12 hours). Filter. Then you need to add fresh filtered water so that you get a whole liter of broth. Drink 1,5 glasses a day, split into 3 doses. The method of taking is the same as when taking linden tea described above.
- 3 Take a head of 1 garlic, peel, chop, put in a half liter jar, pour 200 milliliters of sunflower oil (not refined). Insist for 24 hours (once every four hours you need to shake the mixture), then add freshly squeezed juice from one lemon to the resulting liquid. Shake well. Take a quarter of a teaspoon half an hour before meals three times a day. The dosage and time of administration should be closely monitored. After 3 months of taking, a break of a month is needed, then the treatment should be repeated again, which will last 3 months.
- 4 St. John’s wort infusion is prepared as follows: pour 30 grams of chopped, dried herbs with a glass of hot water. Place in a thermos, leave for 2 hours. Filter. This is the daily rate, which must be divided into 3 doses. Drink the infusion for 45 days, after which – a break for 30 days, then repeat the treatment course (also, you need to drink a decoction for 45 days).
- 5 Drink oregano tea for 90 days.
- 6 Every day you need to memorize short poems and recite them. This will help restore speech and improve memory.
- 7 To facilitate the process of eating, it is better for the patient to eat with a spoon, and it is worth wrapping its edge with pieces of cloth so that there is a large gripping area. Liquid so that it does not spill is better to drink through a straw.
- 8 To relax the muscles, the patient needs a relaxing massage and baths with essential oils and herbal decoctions (optional).
Dangerous and unhealthy foods for Parkinson’s disease
- fried, solid foods;
- seeds and nuts;
- dry biscuits, cakes;
- semi-finished products and instant food;
- canned food, sausages, smoked meats.
All of these foods can cause constipation (due to the intake of toxins), make it difficult to eat (due to hardness and dryness).
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!