Contents
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy is the medical term that is commonly used to refer to the swelling of the lymph nodes. Having swollen glands is a sign of damage to the body. Lymphadenopathy can thus be perceived as a warning signal. They can be linked to mild and transient infections, but can also have more serious causes.
Lymphadenopathy
Definition of lymphadenopathy
By definition, lymphadenopathy is an abnormality in the lymph nodes. However, this medical term is more often used to refer to adenomegaly, which is a swelling of the lymph nodes. This phenomenon occurs when the organism is attacked.
This is because lymph nodes are small organs that play a key role in the immune system for the elimination of pathogens. The lymph nodes are in particular the seat of proliferation of lymphocytes, immune cells whose function is to eliminate pathogens. When the lymph nodes swell / swell, the body is dealing with aggression.
Different types of lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy can affect a single type of lymph node, or occur in several nodes simultaneously. In this second case, we speak of polyadenopathy or sometimes generalized lymphadenopathy.
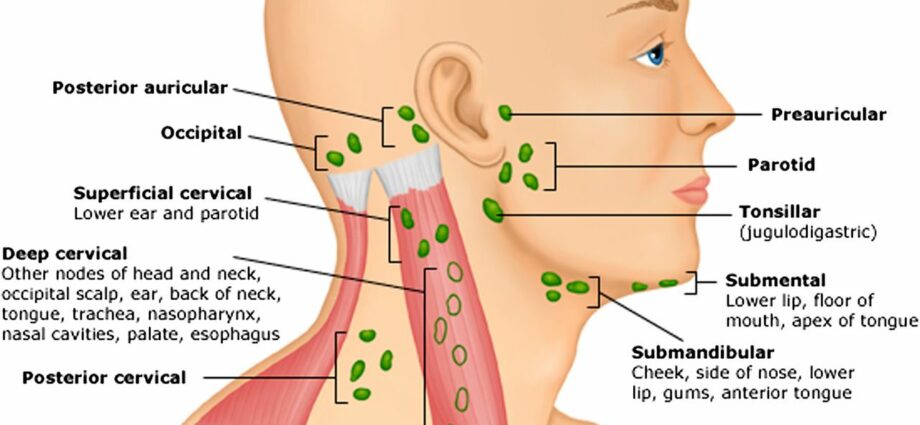
It should in fact be known that the body has many lymph nodes distributed at different levels. The best known are those of the neck. Usually, they are easily palpable. They are part of the superficial lymph nodes, such as those located in the groin and armpits. Conversely, there are also deep ganglia present in the thorax and abdomen.
In fact, it is also possible to distinguish:
- superficial lymphadenopathy, including cervical lymphadenopathy affecting the lymph nodes in the neck, axillary lymphadenopathy which occurs in the armpits and inguinal lymphadenopathy in the groin;
- deep lymphadenopathy, such as mediastinal lymphadenopathy which occurs at the level of the mediastinum in the thorax.
Causes of lymphadenopathy
The most common case is cervical lymphadenopathy, which occurs in the ganglia of the neck. It may in particular be due to:
- an infection of the ENT sphere, such as pharyngitis;
- an infection of a salivary gland;
- a tooth abscess;
- etc.
If the causes mentioned above are generally benign and temporary, other more serious attacks can be at the origin of lymphadenopathy. There are often two types: infectious lymphadenopathy and cancerous lymphadenopathy.
Infectious lymphadenopathy can be due to:
- a staph or strep infection;
- cat scratch disease;
- the tularémie;
- sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as syphilis;
- tuberculosis ;
- toxoplasmosis;
- infectious mononucleosis;
- etc.
Cancerous lymphadenopathy is linked to:
- cancer of the lymphatic system, more commonly known as lymphoma;
- lymph node metastases, that is to say secondary tumors which may result from cancers in the ENT sphere, tongue, thyroid, abdomen, pelvis, breast, genitals external organs, anal canal or skin.
Diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
Superficial lymphadenopathy is usually easy to diagnose. The swelling of the superficial nodes is palpable, even visible in the case of cervical lymphadenopathy. During the consultation, the health professional will be interested in the location of the lymphadenopathy and the “consistency” of the lymph nodes. These observations will guide the diagnosis which will then be supported by the analysis of the symptoms perceived.
Medical examinations can be set up to complete the diagnosis in certain cases of superficial lymphadenopathy, and systematically for deep lymphadenopathy. Possible examinations include:
- lymph node fine needle aspiration, a sample taken from the lymph nodes using a needle;
- a lymph node biopsy, which involves removing and analyzing a lymph node;
- a blood count, which can be used to confirm infectious lymphadenopathy;
- microbiological examinations to identify the germ involved in infectious lymphadenopathy;
- imaging examinations, especially in cases of deep lymphadenopathy.
Symptoms of lymphadenopathy
The symptoms of lymphadenopathy are numerous and extremely varied. They depend on the type of lymphadenopathy, and especially on the cause of the swelling of the nodes. However, it is possible to distinguish certain symptoms typical of superficial lymphadenopathy. These are usually characterized by swollen / swollen and painful glands.
Special case of inflammatory lymphadenopathy
Sometimes the swelling of the nodes is accompanied by an inflammatory reaction. Inflammatory lymphadenopathy is then often characterized by a rise in fever.
Treatments for lymphadenopathy
Swollen glands have different causes and can be accompanied by different symptoms. Therefore, there are many treatments for lymphadenopathy. Their main objective is to treat the cause of lymphadenopathy. Support may, for example, be based on:
- treatment with antibiotics for infectious lymphadenopathy;
- anti-inflammatory treatment for inflammatory lymphadenopathy;
- chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy or even surgery for cancerous lymphadenopathy.
Prevent lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy has many possible causes. There may therefore be many ways to prevent it. Herbal medicine can, for example, help prevent certain forms of infectious lymphadenopathy. To find out more, do not hesitate to consult our list of essential oils with anti-infectious properties.