Contents
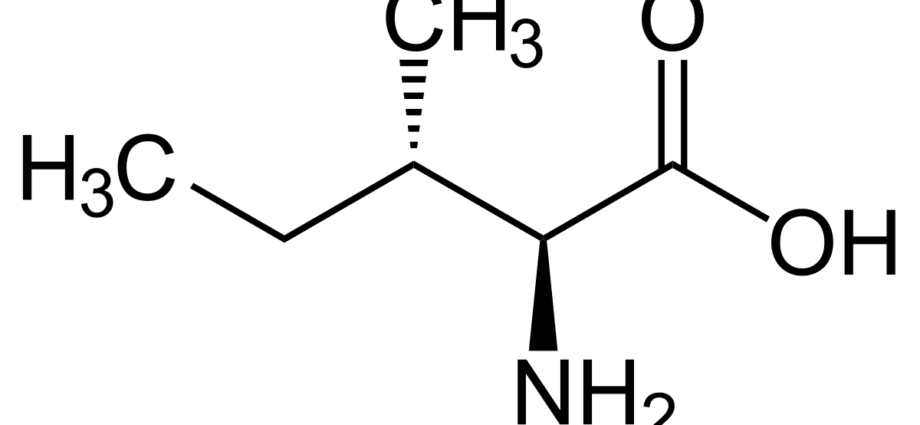
It is an aliphatic α-amino acid found in all natural proteins. It is one of the essential amino acids, since it cannot be synthesized in the human body on its own and is supplied there only with food. Produced by plants and microorganisms from pyruvic acid.
Isoleucine Rich Foods:
General characteristics of isoleucine
Isoleucine belongs to the group of proteinogenic amino acids. It participates in the synthesis of tissues throughout the body. It is a source of energy in the implementation of the nervous-regulatory activity of the central nervous system.
Daily requirement for isoleucine
The body’s daily requirement for isoleucine is 3-4 grams.
At the same time, in order to achieve the best result, it is required to maintain a balance of the use of essential amino acids. The most acceptable option is the following: 1 milligram of isoleucine requires 2 mg of leucine and 2 mg of valine.
In order to provide a daily intake of isoleucine, a person needs to eat about 300-400 grams of beef or poultry meat. If you use vegetable protein, then in order to obtain the required amount of the above-named amino acid, you need to eat 300-400 grams. beans or walnuts. And if you eat only buckwheat (for example, on a fasting day), then its amount should be 800 grams per day.
The need for isoleucine increases:
- with tremors (tremors) of the muscles;
- with symptomatic hypoglycemia;
- with chronic lack of appetite (anorexia);
- with damage to muscles and tissues of internal organs;
- with nervousness and disorders of the nervous system.
The need for isoleucine is reduced:
- with violations of the gastrointestinal tract;
- with increased protein intake;
- for allergic reactions to isoleucine;
- with diseases of the liver and kidneys.
Digestibility of isoleucine
Since isoleucine is an essential acid, its intake is essential for the health of the body. At the same time, the assimilation of isoleucine depends, first of all, on whether a person has liver and kidney damage. Second, the absorption of isoleucine depends on accompanying acids such as valine and leucine. Only in the presence of the above-mentioned acids, this amino acid has every chance of being absorbed.
Useful properties of isoleucine and its effect on the body:
- it regulates blood sugar levels;
- stabilizes energy supply processes;
- carries out the synthesis of hemoglobin;
- promotes the restoration of muscle tissue;
- increases the body’s endurance;
- promotes the fastest healing of tissues;
- regulates blood cholesterol levels.
Interaction with other elements:
Isoleucine belongs to the group of hydrophobic amino acids. Therefore, it does not mix well with water. At the same time, it interacts well with plant and animal proteins, which take an active role in the life support of the whole organism.
In addition, isoleucine can be combined with unsaturated fatty acids found in sunflower and cotton seeds, almond seeds, peanuts, and olives.
Signs of a lack of isoleucine in the body:
- severe headaches and dizziness;
- irritability and fatigue;
- weakening of immunity;
- depressive state;
- muscular dystrophy;
- hypoglycemia.
Signs of excess isoleucine in the body:
- thickening of the blood;
- increasing the concentration of ammonia and free radicals in the body;
- apathy;
- allergic reactions.
People with kidney and liver diseases should not get carried away with supplements containing this amino acid!
Isoleucine for beauty and health
As mentioned earlier, isoleucine takes an active part in the implementation of the higher nervous activity of our body. At the same time, it not only regulates the energy potential of a person, but also provides our body with the ability to regenerate. It is this condition that makes it possible to classify isoleucine among the amino acids responsible for maintaining the health and beauty of the whole organism. After all, healthy, elastic skin, strong nerves and a radiant look are the main signs of the health of our body.