Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
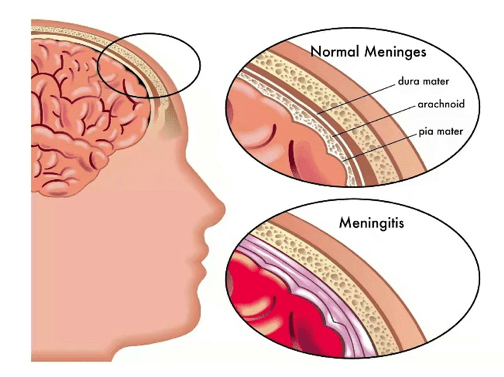
Meningococcal inflammation can result from various infectious agents such as meningococcal and pneumococcal bacteria, viruses and protozoa. Depending on the causative agent of the disease, it can be sudden and very turbulent (meningococcus) or slowly progressive and insidious (tuberculosis).
Inflammation of the meninges and the brain – symptoms
The very rapid development of the disease, the first symptom of which may be a headache, is typical of the so-called purulent, i.e. bacterial meningitis, and viral meningitis and encephalitis. In typical cases, apart from severe headaches, nausea and vomiting, there is also:
- fever,
- chills.
Neurological examination reveals meningeal symptoms, expressed as a reflex increase in the tension of the paraspinal muscles:
- in the patient it is impossible to bend the head to the chest, because the neck is stiff, and the patient cannot raise the straightened lower limb,
- in some patients, brain dysfunction in the form of psychomotor agitation and hyperalgesia to stimuli quickly occurs,
- there are disturbances of consciousness up to complete loss of consciousness,
- when the brain is involved, epileptic seizures and other cerebral symptoms occur.
Diagnosis of meningitis and brain inflammation
The basis for the diagnosis of this ailment is the analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid, which reveals an increase in the concentration of protein and the number of white blood cells (granulocytes in the case of purulent meningitis and lymphocytes in the case of viral meningitis).
How to treat meningitis and encephalitis?
Although better and better methods of treatment exist and newer and newer antibiotics are introduced, meningitis is still regarded as a serious, life-threatening disease. Even in cases with a relatively mild course, at the beginning of the disease, complications may appear that significantly worsen the prognosis, such as:
- swelling of the brain
- status epilepticus.
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website.