Contents
General description of the disease
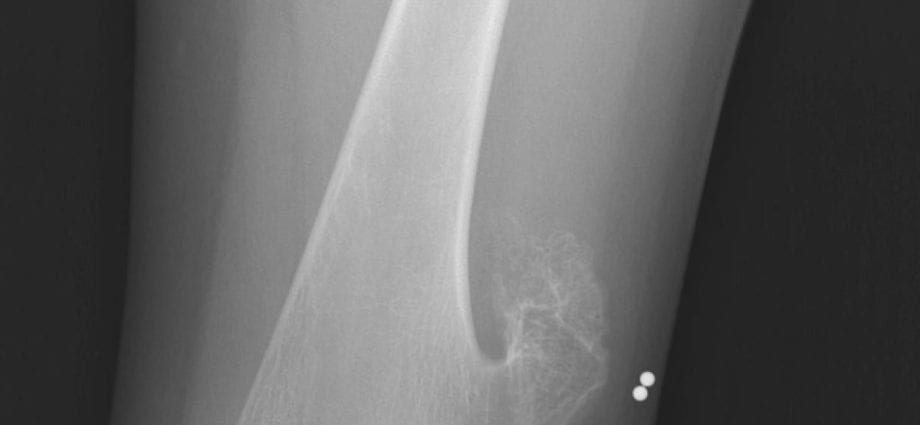
Exostosis is a benign bone growth, the formation of which occurs from cartilage tissue, after which it becomes covered with a bone shell and hardens.
The size of exostosis can be very different – from a small pea to a nut and even a large orange. It can be in the form of a thorn, cauliflower, mushroom on a thin stem. Moreover, they can be multiple (sometimes the total number of growths can reach ten) or single.
Types and signs of exostosis:
- solitary osteochondral exostosis – bone growths are motionless, can be of different sizes, while the skin above them does not change; when large sizes are reached, they can press on the nerve trunks, blood vessels, as a result of which severe pain occurs in the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe location of the tumor-like formation;
- multiple exostous chondrodysplasia – the main symptoms of this type are various deformities of the knee joints, clubhand, short stature (they arise due to the fact that with an increase in the build-up, it touches the adjacent bone, which is damaged and bent).
The largest number of cases of exostosis of these two types occurs on the hip bones, shoulder joint, tibia, scapula, collarbone.
Much less often, this disease affects the feet and hands. Also, not a single case of damage to the bone-cartilaginous exostosis of the skull has been recorded.
If exostosis affects the vertebral part, then with its further development and growth into the spinal canal, compression of the spinal cord may occur.
The causes of exostosis:
- 1 heredity;
- 2 trauma and inflammation that occurs in this case;
- 3 infringement, bruises;
- 4 abnormal development of cartilage and periosteum;
- 5 various infectious diseases (for example, syphilis);
- 6 inflammatory process in fibrositis or mucous bags;
- 7 disturbances in the work of the endocrine system.
Complications
With a rapid growth of the growth, it can grow from a benign one into a malignant neoplasm.
Diagnostics
This disease is diagnosed in most cases by accident, when passing an X-ray examination or when subcutaneous formations are detected by touch.
Exostosis is considered a childhood disease, and the most active period of increased induration falls on puberty.
Before the appearance of subcutaneous seals, the disease cannot be determined in any way.
On average, patients have no clinical signs for 8-10 years.
Useful foods for exostosis
As a preventive measure for exostosis (to prevent bone fractures and inflammation), it is necessary to use: fermented milk and dairy products, fish (especially sardine, tuna, salmon, flounder, capelin, pollock), greens (spinach, celery), vegetables (cabbage, beets, pumpkin, bell peppers, tomatoes), fruits (apricots, persimmons, citrus fruits, currants and all C-containing fruits and berries), nuts, bran bread, mushrooms (white), vegetable fats.
To strengthen bones and to quickly join them in the event of a fracture, you need to drink carrot juice, a decoction of comfrey and wheat.
Traditional medicine for exostosis
With exostosis, manual therapy, acupuncture, and massage are recommended. But, nevertheless, the main method of treatment is the surgical removal of the growth. This neoplasm on the bone requires surgical intervention only when it reaches a large size, deforms adjacent bones and presses on organs, blood vessels, nerves, and at the same time problems with musculoskeletal functions arise and severe pain is disturbing. Also, surgical removal is performed for cosmetic purposes.
It should be noted that in most cases exostoses grow up to 20 years old, then they simply remain the same size and do not bother.
People who have been found and diagnosed with exostosis should regularly undergo histological examination and be monitored by doctors.
Dangerous and harmful foods for exostosis
- store sauces, mayonnaises, dressings, sausages, canned food, sausages;
- sweet soda;
- fast food;
- alcoholic beverages;
- fast food;
- foods with E codes, dyes, trans fats, fillers;
- strongly brewed tea and coffee in large doses.
The entire list of these products contains carcinogens that will accelerate the process of tumor growth and its transformation from benign to malignant.
Excess calcium in the body can accumulate on the bones and, as well, create some growths. Therefore, with an excess of calcium, you need to limit the consumption of dairy products, eggs, parsley and cabbage. Hypercalcemia can occur from hard water, so it is best to use softened or distilled water for drinking.
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!