Ear plug: recognize and remove the earwax plug
Do not be deaf anymore, if your ears are blocked it may be due to the earwax plug. Created naturally, it can be safely removed using various methods.
What is the earplug?
The “earplug” refers to an accumulation of cerumen in the ear canal. Often called “human wax”, mainly because of the similarity between the two terms, earwax is not really “wax”. It is actually a mixture of two substances, produced by the skin of the ear. A kind of perspiration very specific to this area. Its color will generally be yellow, sometimes darker orange.
This “wax” will be produced permanently, and can form a plug in various cases:
- excess of natural production;
- poor evacuation;
- improper handling (pushing earwax with cotton swabs, or hearing aids such as prostheses).
What is earwax used for?
We may wonder what is the use of this famous “human wax”, produced naturally by our body. Its primary objective remains to protect the internal duct. By lining the wall, it reinforces the defenses of the duct by absorbing dust and other external elements.
Symptoms of an earwax plug
The presence of earwax in the ear does not necessarily cause symptoms since its presence is natural. On the other hand, its excess will lead to various disorders:
Hearing reduction or loss
In one or both ears, the earplug can gradually cause hearing loss. We will therefore hear progressively less well on one side than on the other, if only one ear has the excess. Sometimes only certain sounds may be less well heard.
Acouphènes
Tinnitus is a ringing heard directly in the ear, which does not originate from the outside environment. If you haven’t heard it before, maybe the presence of earwax is the cause.
Otitis
Due to the presence of earwax, the ear will be less well ventilated. This lack of ventilation can cause otitis externa, which is inflammation of the outer ear canal. It is often called “swimmer’s otitis” because it usually occurs after swimming, which causes the ear plug to “swell”.
Pain, discomfort, dizziness
Ear pain, especially when it is felt “inside”. It can also result in irritation or itching. Dizziness may occur.
Identify the earplug
How do you know if you really have an earplug? There are two methods: either dare to ask an acquaintance to examine your ear, or even yourself.
For this, a simple smartphone is enough: it requires a little agility, but you can try to take a picture of the inside of your ear, with the flash on, to check if a blockage has formed. In case of symptoms, a medical consultation may also be necessary.
How to remove it without risk?
Removing an earplug is not without risk: by pressing on it, it can sink into the ear canal and damage the eardrum. So here are some methods to safely remove it:
Cotton swab: Attention!
The cotton swab remains the most used method to remove earwax, but paradoxically it is sometimes the cause. Indeed, the earwax is naturally evacuated in the ear canal, but if it is pushed, compacted by the action of a cotton swab, it will accumulate in the deepest area, and suddenly cause a real “ear plug”.
To avoid this, we must therefore be content to use the cotton swab at the entrance to the ear only, rubbing the contours, without ever “pushing” to the bottom of the duct.
Ear washing
At the water :
This is the simplest and most natural method: wash your ears well. A little water in the canal, using a bulb, may be enough to cause the earplug to flow.
To complete the washing, various tools are also sold in pharmacies or supermarkets such as pliers or an ear cleaner. However, these aids should be handled with care, without ever forcing to the back of the ear, under penalty of damaging the eardrum.
Using cleaning products:
If the cap resists washing, it will need to be softened first. For this, there are freely available commercially different products to be injected into the ear. Once the cork has softened, it can be washed.
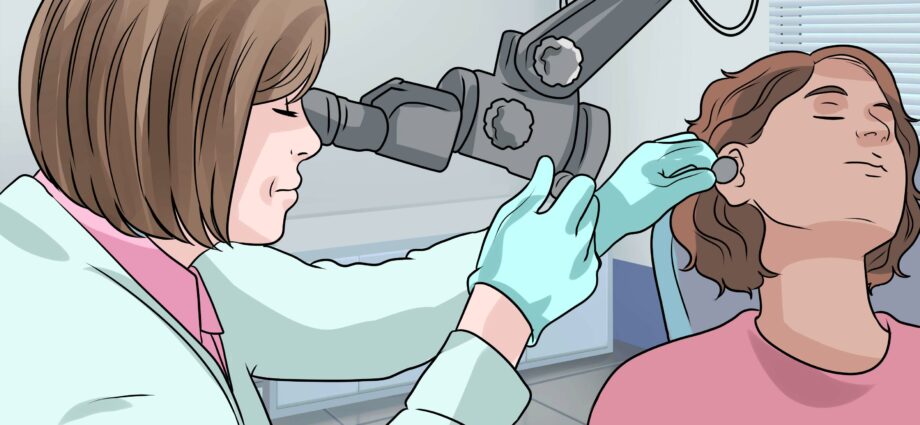
Medical intervention
If nothing has worked to remove the earwax, you will need to consult an ENT doctor. Thanks to a small forceps, and his dexterity, he will be able to directly remove the plug in your ear. An operation that does not require anesthesia and will take just a few minutes.
Note that if you have managed to remove your plug, but the pain persists, it is better to consult a specialist to ensure that no damage has been caused in the ear canal.










muna gdy.idan aka mari mutum kunnenshi ya fashe menene mafita.