Contents
When it comes to chitin, school biology lessons immediately come to mind. Arthropods, crustaceans and everything connected with them …
But, despite this, chitin was also very useful for humans.
General characteristics of chitin
Chitin was first discovered in 1821 by the director of the botanical garden, Henry Bracon. In the course of chemical experiments, he revealed a substance that is resistant to dissolution in sulfuric acid. And two years later, chitin was extracted from the shells of the tarantula. At the same time, the term “chitin” was proposed by the French scientist Audier, who studied the substance using the outer shells (external skeleton) of insects.
Chitin is a polysaccharide that belongs to the group of hard-to-digest carbohydrates. In terms of its physicochemical properties, as well as its biological role, it is close to plant fiber.
Chitin is part of the cell wall of fungi, as well as some bacteria.
Formed by the amino sugar residues of acetylglucosamine, chitin is one of the most abundant polysaccharides in nature.
It is a substance found in fungi, bacteria, arthropods. Several types of chitin have been identified, differing in their chemical composition and properties.
* Indicated approximate quantity (g) in 100 g of product.
Chitin (French chitine, from Greek chiton – clothes, skin, shell), a natural compound from the group of polysaccharides; the main component of the external skeleton (cuticle) of arthropods and a number of other invertebrates; it is also part of the cell wall of fungi and bacteria. Performs protective and supporting functions, providing cell rigidity. The term “X.” proposed by the French scientist A. Odier, who (1823) studied the hard outer cover of insects. H. consists of N-acetylglucosamine residues linked by b- (1 ® 4)-glycosidic bonds.
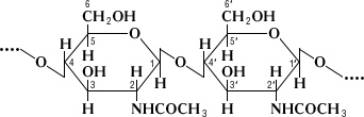
The molecular weight can reach 260,000. It does not dissolve in water, dilute acids, alkalis, alcohol, and other organic solvents, it dissolves in concentrated salt solutions (lithium, calcium thiocyanate), and is destroyed in concentrated solutions of mineral acids (when heated). Chlorine is always associated with proteins in natural sources. Chlorine is similar in structure, physicochemical properties, and biological role to plant cellulose.
Chlorine biosynthesis in the body occurs with the participation of a donor, the residue N-acetylglucosamine-uridine diphosphate-M-acetyl-glucosamine, and acceptors, chitodextrins, with the participation of an enzymatic glycosyltransferase system associated with intracellular membranes. Chlorine is broken down biologically to free N-acetylglucosamine by the enzyme chitinase, which is found in a number of bacteria, among the digestive enzymes of soil amoebas, some snails, earthworms, and also in crustaceans during the molting period. When organisms die, chlorine and its degradation products are converted in soil and sea silt into humic-like compounds and contribute to the accumulation of nitrogen in the soil.
Daily need for chitin
Consuming more than 3000mg per day can lead to problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, it is advisable to observe the golden mean in the use of any power components.
The need for chitin increases:
- with overweight;
- violation of the metabolism of fats in the body;
- high blood cholesterol;
- liver steatosis;
- with an excess of fat in the diet;
- frequent constipation;
- diabetes mellitus;
- allergies and intoxication of the body.
The need for chitin decreases:
- with excessive gas formation;
- dysbacteriosis;
- gastritis, pancreatitis and other inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Digestibility of chitin
Chitin is a solid transparent substance that is not digested in the human body. Like cellulose, chitin improves gastrointestinal motility and has other beneficial properties for the body.
Useful properties of chitin and its effect on the body
Based on the materials of some medical studies, conclusions were drawn about the benefits of chitin for the human body. Chitin is used for hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, as an immunomodulatory substance that prevents early aging of the body. As well as fiber, chitin improves the functioning of the intestines, facilitating the evacuation of the contents, well cleanses the intestinal villi. Cleans blood vessels from harmful cholesterol.
The latest medical research shows the benefits of chitin in the prevention and treatment of many cancers.
Interaction with other elements
Chitin interacts with polysaccharides and proteins. It is insoluble in water and other organic solvents, although it retains moisture in the body. When heated, interacting with some salts, it is hydrolyzed, that is, destroyed. Reduces the absorption of chlorine ions into the circulatory system, thereby correcting the water-salt balance in the body.
Signs of a lack of chitin in the body:
- obesity, overweight;
- sluggish work of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT);
- unpleasant body odor (excess toxins and toxins);
- frequent allergic diseases;
- cartilage and joint problems.
Signs of excess chitin in the body:
- abnormalities in the stomach (nausea);
- flatulence, bloating;
- discomfort in the pancreas;
- allergic reactions to chitin.
Factors affecting the content of chitin in the body
The human body does not produce chitin on its own, therefore its content in the body entirely depends on the presence in the diet. Based on this, it follows that if you want to be healthy, you need to regularly consume chitin in the form of its monomer – chitosan.
Chitin for beauty and health
Recently, cosmetologists are increasingly writing about the positive effect discovered from the use of medical and cosmetic products with chitin. It is added to shampoos to increase hair volume and elasticity, used in lotions, added to creams, shower gels, and personal hygiene products (gel toothpastes) are produced. It is found in various styling sprays and varnishes.
Chitin is used as dietary supplements in the diet to improve skin elasticity, as an anti-inflammatory and moisturizer. Creates a protective film on the skin and hair, thereby facilitating the process of combing, prevents the skin from losing moisture and brittle nails.
Argentine scientists have identified the peculiarity of chitin as an assistant to the regenerator of the quickest healing of the skin in case of damage. In addition, chitin is transformed by heating into a new water-soluble substance. chitosan, which is part of anti-aging cosmetics. Thanks to anti-aging cosmetics, the skin is smoothed out faster, wrinkles become less noticeable. The skin acquires a fresher and younger look, thanks to the property of chitin to relieve spasm of the smallest capillaries of the skin.
As for the benefits of chitin for the slimness of your figure, it is obvious. Chitosan is also called animal fiber, which binds in the body and removes excess fats, helps with overeating, increases the number of bifidobacteria in the intestines and gently promotes weight loss. In addition, it is responsible for the adsorption of pollutants, after the evacuation of which, our body feels light and free.
Chitin in Nature
In nature, chitin performs protective and supporting functions, providing the strength of crustaceans, fungi and bacteria. In this it is similar to cellulose, which is the supporting material of the plant cell wall. But chitin is more reactive, according to the materials of the Russian Chitin Society. When heated and treated with concentrated alkali, it turns into chitosan. This polymer can dissolve in dilute acid solutions, as well as bind and react with other chemicals. Thus, sometimes chemists refer to chitosan as a “constructor” that can be used to create various polymers. To obtain pure chitin, protein, calcium and other minerals are removed from organic substances containing it, converting them into a soluble form. The result is a chitinous crumb.
“Crustaceans, fungi and insects are used to obtain chitin. By the way, this substance was first discovered in champignons. The use of chitin and its derivative chitosan is only expanding. The polysaccharide is used in food supplements, medicines, anti-burn drugs, soluble surgical sutures, is used for anti-radiation purposes, and in many others. Chitosan is a useful thing that requires further study”
Chitin in medicine
Due to the fact that chitosan perfectly reacts with other chemicals, drugs and receptors, for example, can be “hung” on the polymer chain. Thus, the active substance will be released only where it is needed, without exposing the entire body to toxicosis. Moreover, chitosan itself is completely non-toxic to living beings.


Chitosan is also used as a dietary supplement. For example, its low molecular weight fraction is directly absorbed into the blood and works at the level of the immune system. The medium molecular fraction is an antibacterial component that inhibits the development of pathogenic microflora in the intestine. In addition, it contributes to the formation of a film on the intestinal mucosa, which protects them from inflammation. In this case, the film dissolves quickly, which is important for use in medicine. The high molecular weight fraction of chitosan serves as a sorbent for toxins present in the gastrointestinal tract.
“We know many sorbents that also have properties that are harmful to humans – they are absorbed and deposited in muscles and bones. Chitosan is devoid of all these side effects. Moreover, it can absorb herbal extracts, which, in conjunction with it, do not lose their beneficial properties for a long time, and be used as a dietary supplement. Chitosan is also used in a gel form for the treatment of oral diseases or burns.”
In addition, chitosan has an antitumor effect, so it can be used to prevent cancer. The substance lowers cholesterol levels, as it binds dietary lipids and prevents the absorption of fats from the intestines. Research is also underway on the use of chitosan as medical implants.


Chitin and gene therapy
Gene therapy is now actively developing. With the help of the scientific method, it is possible to eliminate the activity of one or another “harmful” gene or insert another one in its place. But in order to do this, it is necessary to somehow deliver the “necessary” gene information into the cell. Previously, viruses were used for this, but this system has many drawbacks: carcinogenicity and high cost were primarily. But with the help of chitosan, it is possible to deliver the necessary gene information into the cell without harmful consequences and relatively cheaply.
“ Non-viral RNA delivery vectors can literally be musically tuned with chemical modifications. Chitosan is a more efficient vector than liposomes or cationic polymers because it binds to DNA better. In addition, such systems are non-toxic and can be obtained at room temperature ,” the scientist said.
Chitin in the food industry
The absorbency of chitosan is used in brewing to remove sediment. The so-called turbidity in the drink is formed due to the components of raw materials and auxiliary materials in the form of proteins, carbohydrates, living cells and oxalates. To remove living cells, chitosan is used at the stage of clarification of the product.
In addition, chitosan film reduces the rate of spread of microbes in raw meat, inhibits the appearance of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.


“Usually, fresh meat is kept for no more than two days. As a result of experiments with chitosan, we managed to increase the storage time by one and a half to two times. In some cases, the period reached up to two weeks. In addition, from the point of view of consumer properties, a chitosan film is an ideal package, since it is practically invisible.”
Chitosan is also used in the food industry for the coagulation of whey proteins in the dairy industry, for the production of iodized food products based on the creation of iodine-chitosan complexes, and for other purposes.










Chitina imbolnaveste veti vedea in urmatoarele studii