Contents
Sigmoid colon cancer can occur at any age. But in 60% of cases it is found in elderly patients about 50 years old. In this case, men are more often affected.
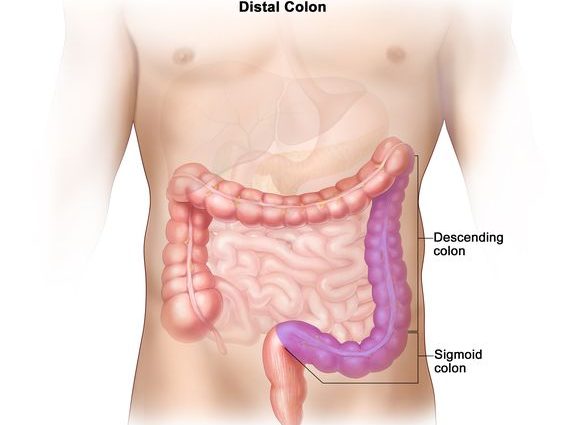
The sigmoid colon is located above the rectum on the left side of the abdomen. It has an S-shape. It is because of this that the food bolus, moving through the intestines, lingers in this area longer. The time of exposure of food processing products to the organ mucosa increases. This increases the chance of developing cancer.
What is sigmoid colon cancer
Sigmoid colon cancer is an oncological disease. In 95% of cases, the type of neoplasm found is adenocarcinoma. A tumor usually forms in the uppermost layer of the intestine – the mucosa.
According to statistics, most often this type of cancer is detected already in the last stages. The disease is difficult to notice in the early stages, often it does not make itself felt at all. It is important to be as attentive as possible to all suspicious symptoms, since in the last stages of sigmoid colon cancer is not treatable. The patient only relieves the symptoms.
Poor quality foods and unhealthy eating behavior adversely affect the intestines. Often, malnutrition causes constipation – stagnation of feces, decreased intestinal motility.
Causes of sigmoid colon cancer
Cancer of the sigmoid colon is provoked by a number of reasons. A combination of many factors can lead to such a disease.
Genetic predisposition plays an important role. If one of the relatives has already had bowel cancer, the likelihood of getting sick will be higher. There is also a predisposition to the formation of polyps – benign formations. But over time, they can turn into a malignant form.
It provokes illness and constant inflammatory processes in the intestines – colitis, Crohn’s disease and other pathologies.
With age, the risk of sigmoid colon cancer increases. But not years are the cause, but a change in a person’s lifestyle: low mobility, obesity, frequent medication.
For all people, an excessive passion for carcinogenic foods, meat, and fast carbohydrates will be dangerous. Cancer is caused by alcohol and smoking.
Constant intoxication of the body with decay products, exposure to toxins on the intestinal mucosa leads to atypical growth of the epithelium. The growing epithelium is a signal that a polyp has begun to form. This condition is considered precancerous and without observation and treatment, the polyp can be reborn.
In the sigmoid colon, blood flow is slowed down. This also slows down the growth of tumors, so they can develop for a long time. The wall of the peritoneum does not allow to notice at least some external signs of tumor growth. All this, plus the frequent absence of symptoms, makes sigmoid colon cancer difficult to diagnose.
Stages of sigmoid colon cancer
Cancer is divided into stages depending on the neglect of the disease. With each stage, the patient’s chance to survive and prolong life after treatment for at least 5 years decreases.
Stage 0. It is also called “cancer in situ” – in situ. This is the earliest stage of the disease. At this point, the pathological process occurs only in the intestinal mucosa.
Stage 1. There is already a tumor growth in the mucous membrane, but it does not go beyond it. The probability of cure at this stage is very high – in 96 – 99% of cases.
Stage 2. It is divided into two types depending on how the tumor grows.
- type II-A – the affected tissues spread into the intestinal lumen, blocking it by almost half, the survival rate is about 95%;
- type II-B – the tumor deepens into the tissue of the wall of the digestive tract, but metastatic cells do not spread, the percentage of survival in this type is lower.
Stage 3. It is at this stage that metastases can appear. Stage 3 is also divided into subtypes.
- type III-A – the tumor spreads into the intestinal lumen, there is no metastasis, but the tumor is so voluminous that it clogs almost the entire intestinal lumen, a positive prognosis is noted for 58 – 60% of patients;
- type III-B – the tumor penetrates the intestinal walls, single metastases to the lymph nodes are noticed, the survival rate also decreases – only 40 – 45% of cases.
Stage 4. In the last stage, metastases spread to distant organs and lymph nodes. The tumor at the same time deepens into the tissues of organs located nearby – most often in the liver. It is difficult to help patients at this stage; only 8-10% of patients can recover.
At this stage, there is also a division into subtypes, since the tumor affects different areas.
- subtype 4A – the tumor grows through all layers of the intestine, there is at least 1 distant metastasis (for example, to the lungs), while neighboring organs may not be affected at all by the tumor;
- subtype 4B – the tumor completely or partially sprouts the intestinal wall, there is at least 1 metastasis to distant organs or several to the lymph nodes, there may or may not be metastases to nearby organs;
- subtype 4C – the tumor has grown through the intestinal wall completely. There are metastases in nearby organs, the tumor can spread to distant parts of the peritoneum, there may not be distant metastases.
Symptoms of sigmoid colon cancer
In the initial stages, there may be no symptoms at all, and this is the danger of the disease. Those symptoms that do appear are often confused with other diseases or do not go to the doctor at all.
Cancer of the sigmoid colon can be manifested by flatulence, belching, rumbling in the abdomen. Diarrhea and constipation often alternate. Clots of mucus and blood may appear in the feces – many confuse this with hemorrhoids. With the development of a tumor, pain in the abdomen, discomfort during bowel movements, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the intestine are disturbing.
In the later stages of the disease, general symptoms appear: fatigue, frequent nausea, fever, headache. A person loses weight, loses appetite. The skin becomes grayish or yellowish, pale. The liver may be enlarged and the hemoglobin in the blood is reduced.
Treatment of sigmoid colon cancer
The treatment of such a disease is always complex – you can not do with only one method, even the best. Therapy will include surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
An important role is given to surgical treatment. If the tumor is small and its contours are clear, the affected tissue can be removed. Partially it is necessary to excise a part of the affected intestine, as well as lymph nodes. If the tumor is “simple” – small and low-grade, it can be removed with a gentle method. Through small punctures, an endoscope is inserted, which avoids abdominal surgery.
In the treatment of cancer of the last stage in advanced cases, the complete removal of the sigmoid colon is inevitable. To remove feces and gases, a colostomy is installed, sometimes for life, since it is impossible to remove food processing products in the usual way.
Diagnostics
The examination must be thorough, it is extremely dangerous to confuse cancer with other, less dangerous diseases.
If there are complaints, the doctor may conduct a digital examination of the rectum. Next, an endoscopic examination is prescribed: colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy. The procedures are painful, sometimes anesthesia is required. Some patients should not have a colonoscopy. During the study, the endoscope is inserted into the anus, examining the intestines. They also take a biopsy of suspicious areas – it will be possible to determine the composition and structure of the tumor, its variety. The treatment will also depend on this.
There is a less invasive method – irrigoscopy. The patient takes a barium solution that fills the intestines. Next, an x-ray is taken, which shows the structure of the intestine and its bends.
Both ultrasound and MRI of the abdominal cavity are used. With their help, you can assess the size of the tumor, the presence of metastases. Blood tests for tumor markers are also mandatory.
Modern treatments
In addition to surgical treatment, the tumor is affected more subtly. Chemotherapy destroys the affected tissue and prevents the tumor from growing. Toxic drugs affect the whole body, but the treatment is very effective. Chemotherapy inhibits tumor growth and prevents recurrence of the disease. It is prescribed both before and after surgery to consolidate the effect.
Radiotherapy is used with caution, as there is a risk of damage to the intestinal walls. It is also quite effective in cancer of the sigmoid colon.
Prevention of sigmoid colon cancer at home
All people should be screened. There are also state programs for screening bowel cancer – they are valid for everyone over 50 years old. The program includes a fecal blood test (to be taken every 2 years) and a colonoscopy (every 5 years).
It is important to watch your diet, avoid constipation and diarrhea, eat less meat and white flour, and more vegetables and fiber. Sports, an active lifestyle will help, otherwise intestinal motility will inevitably slow down.
It is important not to start treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases such as colitis. Avoid cigarettes and alcohol.
Popular questions and answers
To protect yourself from such a dangerous disease, arm yourself with information and visit a doctor on time at the slightest suspicion. Answered the most important questions about sigmoid colon cancer therapist Yulia Tkachenko.
Large studies have shown that a diet high in red meat, as well as low in plant fiber, whole grains, and calcium, is associated with the development of colon cancer. Urban dwellers are known to eat less whole grains and therefore suffer from bowel disease more frequently than rural dwellers.
Reduced physical activity and obesity also remain important factors, which are more typical for urban residents than for those who live in villages and villages.
Anxious symptoms are a change in the nature of the stool. Constipation alternates with offensive stools. There may be an admixture of blood, pain, a feeling of incomplete emptying.
In addition, there are a number of general symptoms, such as constant body temperature hanging up to 37-37,5 degrees, weight loss, loss of appetite and aversion to food, general weakness. All these symptoms indicate that you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
If you are concerned about abdominal pain or changes in stool, then you should start with a consultation with a gastroenterologist. And in case of problems with bowel movements and the appearance of blood in the stool, it is better to contact a proctologist. If only general symptoms are bothering you, you should consult a general practitioner or general practitioner.
Unfortunately, we cannot change the genetic predisposition, so it is necessary to correct lifestyle factors. Quitting smoking, being active, and losing weight to normal levels will help reduce the risk of colon cancer. You also need to watch your diet. It is very important to understand the need for regular screenings, after 50 years everyone needs it.