Contents
What is leukemia
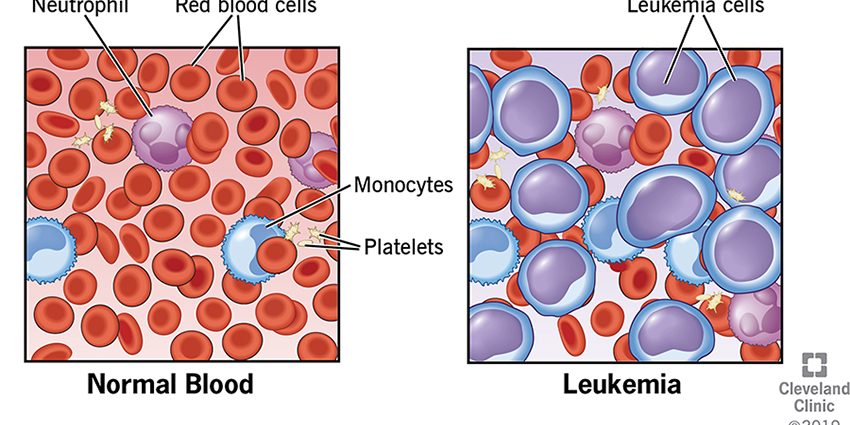
Leukemia or leukemia is a malignant disease of the hematopoietic system. To be more precise – the bone marrow and lymphatic system, and is also called blood cancer. Leukemia is commonly referred to as blood cancer.
In the human body, blood cells are in constant circulation. Used cells die, and new ones are formed from bone marrow stem cells. New progenitor cells first divide and then mature into full-fledged cells. In healthy people, there is a finely regulated system of balance between used, dead and newly formed cells. But in patients with leukemia, this balance is greatly disturbed. New cells multiply uncontrollably, not maturing to the level of full-fledged cells. In the course of leukemia, they become more and more.
There are four types of leukemia.
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. This type is most common in children.
- Acute myeloid leukemia.
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It occurs in adults over 55 years of age and has been reported in several members of the same family.
- Chronic myeloid leukemia.
Causes of leukemia in adults
The exact causes of the disease are unknown. But reasons can include:
- severe exposure (radiotherapy);
- exposure to carcinogens (eg, benzene);
- viruses;
- some modifications of genes (hereditary predisposition).
Symptoms of leukemia in adults
Oncologist Dina Sakaeva highlights a number of symptoms of the disease:
- anemia;
- hemorrhagic syndrome, because there are not enough platelets in the body;
- bleeding;
- bruising;
- hemorrhage in the mucous membranes – in the tongue, skin;
- the appearance of small dots and spots;
- temperature increase;
- nausea, vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- the appearance of metastases, when tumor cells enter healthy organs.
Stages of leukemia in adults
Stage 1. In the first stage of leukemia, the cancer invades the lymph nodes, which increase in size. The patient can notice enlarged nodes himself.
Stage 2. In this case, either the liver or the spleen, or both at the same time, increases in patients. This symptom occurs due to an increase in the number of lymphocytes inside these organs.
Stage 3. It is diagnosed when a person develops anemia (hemoglobin level does not exceed 10 units).
Stage 4. In this case, it is characterized by a low level of platelets, or thrombocytopenia. The number of platelets in the patient’s blood does not exceed 100 thousand.
Treatment of leukemia in adults
If left untreated, leukemia can lead to death within a matter of months. It is important to start treatment on time.
Chemotherapy is a necessary basis for any type of treatment for leukemia. “Chemistry” attacks leukemia cells at various points in order to completely destroy malignant tumors.
Radiation therapy – high doses of ionizing radiation are used to destroy cancer cells. There is a decrease in enlarged lymph nodes, spleen. This type of therapy is used before bone marrow and stem cell transplantation.
Targeted Therapy used in CML (tyrosine kinase inhibitors inhibit important processes in leukemic cells), but chemotherapy and interferon therapy are also used. However, a complete cure is not possible. It can only be achieved with a bone marrow transplant from a healthy donor.
Bone marrow transplant – Bone marrow transplantation. Donors can be siblings of patients.
Diagnostics
An appointment with an oncologist begins with a conversation with the patient. The doctor finds out in detail the patient’s complaints, the history of the disease and the life of the patient, the presence of pathology in the next of kin. Next, an examination of the systems and organs begins to identify violations: to palpate groups of lymph nodes, the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe liver and spleen, since they can be enlarged with leukemia.
Blood cancer can be diagnosed by:
- CBC: If you have cancer, it will show an increase in white blood cells and a decrease in other blood cells.
- coagulogram – analysis of blood coagulation parameters.
- immunogram – a study of the main indicators of the human immune system.
Also, the doctor may prescribe additional examination methods to determine the type / stage of blood cancer:
- puncture biopsy of the bone marrow with subsequent histological examination;
- puncture biopsy of the lymph nodes;
- spinal puncture – to detect immature blood cells, identify them and determine sensitivity to certain chemotherapy drugs.
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Prevention of leukemia in adults at home
Specific methods of prevention against leukemia have not been developed. Oncologists only advise to lead a healthy lifestyle, which includes a balanced diet, light physical activity, adequate rest and sleep, and stress reduction. Those who are at risk (there are those in the family who had cancer) should be tested at least once a year and monitor their health.
Popular questions and answers
Answers Dina Sakaeva, Deputy Head Physician in Oncology, Professor of the Department of Pharmacology with a Course in Clinical Pharmacology, Member of the Board of RUSSCO, Doctor of Medical Sciences:
● Vegetables, berries and fruits. Organize yourself at least two snacks a day, in which you will eat fruits, and use vegetables as a side dish. Vegetables are useful both fresh, baked, and steamed;
● Chicken, fish, meat, eggs. It is very important to include enough quality protein in the diet, which can be obtained from this food group. In addition to proteins of animal origin, those that are of plant origin are also perfect – these are, first of all, legumes. Because of the treatment, many patients experience a change in taste sensations, and not everyone is ready to eat meat. If you don’t like it anymore, you can try eating it with a lot of different aromatic and mild spices. However, you can replace it with seafood or other sources of protein.
● Bread and cereals. In normal nutritional diets, these foods are considered potentially dangerous due to their high calorie content, but in chemotherapy they are great for breakfast.
● Dairy products. Products of this group should be present in the diet daily, preferably fermented milk.
Sample menu for chemotherapy:
● Breakfast – porridge and sandwich with cheese;
● lunch – a glass of kefir or natural yogurt or fruit;
● lunch – light vegetable soup and salad;
● afternoon snack – fruit or fruit salad with yogurt dressing;
● dinner – a portion of meat, fish or poultry with a side dish of vegetables;
● before going to bed – fermented milk products.