Contents
Bursitis – Causes, Symptoms, Treatments
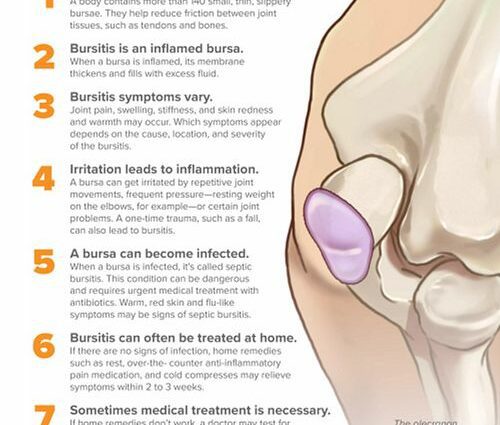
Bursitis, also called hygroma, is characterized by inflammation of the bursa, this “small bag” filled with fluid, and serving as a cushion between the tendon and the bone.
Bursitis, what is it?
Definition of bursitis
Bursitis is characterized by inflammation and swelling in the bursa.
The purse is a kind of “bag” filled with a fluid, under the skin. The bursa behaves like a small “pad” between tendons and bones. Bursitis is then an inflammation at the level of these small pads, support and junction, between the bones and the tendons.
Bursitis most commonly develops at:
- of the shoulders ;
- of the elbows ;
- of the knees ;
- of hip.
Other areas may also present with bursitis, but to a lesser extent. Among these: the ankles, the feet or the Achilles tendon.
Bursitis and tendinitis are two main damage resulting from inflammation of the soft tissue.
Causes of bursitis
The development of bursitis is the result of inflammation. The latter, itself the result of surgery or repeated movements involving the impacted limb.
The risk of developing such soft tissue damage is increased by physical activity involving a significant number of repetitive movements.
People who spend a significant amount of time in a “kneeling” position will then tend to develop bursitis of the knees. Another cause, more rare, can also be linked to bursitis: an infection.
Who is affected by bursitis?
Anyone can be affected by the development of bursitis. Nevertheless, people who demonstrate physical activity (sports, at work, daily, etc.) involving a large number of repeated gestures and movements, will be more at risk of developing such an attack.
Symptoms and treatments for bursitis
Symptoms of bursitis
The main symptoms of this inflammation of the bursa are pain and stiffness in the affected area.
The severity of these symptoms varies depending on the level of inflammation and can also cause swelling.
The pain is generally felt, to a greater extent, during movement or even pressure in the affected area.
In the context of an infection (septic bursitis), other symptoms may also be associated:
- a state febrile ;
- an infection that deepens in the skin;
- of the skin lesions ;
Risk factors for bursitis
Being, generally, the consequence of daily activity (work, sport, etc.), repeated and supported movements of the elbow, knees, and other limbs, can be risk factors for the development of bursitis.
Diagnose, prevent and treat bursitis
The first diagnosis is usually visual : pain, swelling, etc.
Analysis of a sample of fluid circulating in the affected bursa may also support the diagnosis. This means of diagnosis makes it possible in particular to search for the possible infectious cause.
Other analyzes and additional examinations can also be the subject of a diagnosis and management of the pathology:
- l’blood analyse ;
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI);
The majority of cases of bursitis are very treatable. The use of ice helps reduce the level of inflammation, reduce pain and deflate the affected area.
In order to alleviate the pain, painkillers may also be prescribed: aspirin, paracetamol or ibuprofen.
The pain is usually persistent for a few weeks. In addition, the swelling can extend over a longer period of time.
However, precautions can be taken in the context of limiting the risk of bursitis: avoiding the kneeling position in the long term, or even warming up before a sporting exercise.