Contents
Acute bronchitis
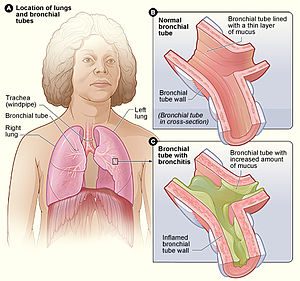
La bronchitis is characterized by inflammation of the bronchi, the ducts that carry inhaled air from the trachea to the lungs. Inflammation makes the more difficult breathing, because the walls of the bronchi are swollen and produce a significant amount of mucus. Bronchitis is accompanied by cough deep.
For the vast majority of people, bronchitis lasts 2-3 weeks and is not a problem. The cough may, however, persist a little longer. We name this bronchitis, acute bronchitis, to distinguish it from chronic bronchitis, which lasts more than 3 months per year.
Acute bronchitis most commonly occurs in thefall or tohiver. It is frequent: the majority of individuals have it at least once during their life.
Remark. People who contract acute bronchitis and whose bronchi are weakened by another breathing illness, like asthma, have more pronounced symptoms. In addition, the risks of complications and the treatments are different. It will not be discussed in this sheet.
Symptoms of bronchitis
- A cough deep. Coughing intensifies when lying down, outdoors when the air is cold and dry, and if the air is loaded with irritants, such as cigarette smoke.
- benefits expectorations slimy, clear, yellowish or greenish in color.
- Un general discomfort : chills, fatigue, decreased appetite, headaches, physical aches. There may be a slight fever.
- Chest pain and a feeling of compression in the lungs.
- Shortness of breath.
Note. Sometimes bronchitis is accompanied by sinusitis, pharyngitis or laryngitis. In case of pharyngitis, the throat is irritated and there is pain when swallowing. In case of laryngitis, the voice becomes hoarse or goes outright.
Causes and risk factors of bronchitis
Viral infection
La most common cause of acute bronchitis is a viral infection. The viruses are inhaled and then spread to the bronchi. Often a cold or the flu precedes bronchitis. Viral bronchitis is contagious.
A bacteria
More rarely, infection can be caused by bacteria (for example, those which can also cause pneumonia) or, by whooping cough.
Irritation of the lungs
Inhaling fine particles in the air that irritate the lungs, such as that contained in cigarette smoke and fumes from a woodstove, can trigger or worsen bronchitis. A strong presence of mold can also be irritating, as can dust or toxic gases in the workplace, as well as smog. Once inhaled, these particles weaken the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. In particular, they trigger inflammatory reactions. Some people are more sensitive to it. This is particularly the case for children and people who suffer from allergic rhinitis or asthma.
In parts of Africa and Southeast Asia, the problem is acute. Many acute and chronic respiratory infections are generated by the smoke produced by the burning of charcoal when cooking food.1. Women and young children are the most affected, sometimes fatally.
Asthma
Finally, acute bronchitis can also be a sign ofasthma. In fact, in studies, researchers have observed that many people who see a doctor for acute bronchitis actually have asthma without knowing it.22.
Risk factors
- Smoking and exposure to second-hand smoke.
- Live or work in a place where chemical products circulate in the air and irritate the lungs.
- Being exposed to a strong Pollution atmospheric. In times of fog (smog), cases of bronchitis are more frequent. In addition, the fog accentuates the symptoms of bronchitis
People at risk
The children and and elderly.
People whose immune system is weakened by chronic stress, another disease, etc.
People with asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema or heart failure.
People with cystic fibrosis because their airways get blocked with secretions, which contributes to infections.
Evolution
A simple bronchitis is not worrying in a healthy person. In the majority of cases, symptoms will go away on their own without treatment within 21 days.
Yes, bronchitis persists more than 3 months or if repeated bronchitis occurs, it is important to get the correct treatment. See a doctor again (see our Chronic Bronchitis sheet).
In addition, sometimes acute bronchitis worsens into pneumonia. This situation is more common among elderly.