Contents
Most often, children get burns at a younger age. At this time, they are especially inquisitive, clumsy and do not know the feeling of fear. Children want to touch the stove, touch the flame, take a mug of boiling water. And it is for young children that a burn poses a special danger, much greater than for an adult. The skin of the child is very thin and almost not protected by the stratum corneum and sebum. Therefore, even a small effect of temperature causes burns that affect the deep layers of tissues.
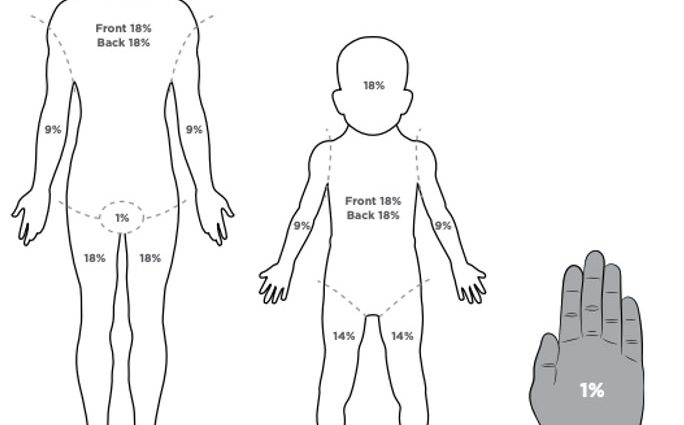
Damage to more than 5% of the skin surface can lead to burn disease, which disrupts the functioning of many organ systems and can lead to death. The prognosis after extensive burns in children is disappointing. Even after healing, rough scars often remain, joint mobility is impaired, and sometimes it is even necessary to amputate a limb.
Therefore, it is not necessary to draw a parallel between the same trauma in adults and children – the latter will endure it much harder, and time may be lost.
Minor burns can be treated at home, under medical supervision. Extensive injuries can only be treated in a hospital, the help of a surgeon, frequent dressings, and droppers may be required.
Most children’s burns are thermal: from fire, steam, hot objects. But you can also get burned from electric shock, household chemicals, sunlight and radiation.
First aid for a child’s burn
First of all, you need to stop exposure to heat as soon as possible. The easiest way to do this is by pouring cold water on the burned area, right over your clothes. Cooling reduces swelling and relieves pain, has a great influence on the further healing of burn wounds.
Next, you need to carefully and quickly remove clothes, freeing the skin. You can cut the fabric so as not to tighten or injure the burn site. If the clothes are stuck to the skin, do not tear them off – leave everything as it is. Continue to cool the burned area with water.
If the burn is small, you need to take the child to the emergency room or clinic. And if extensive, urgently call an ambulance.
The surface of the burn is easily infected, to avoid this, dressings can be used for the period of transportation to the point of medical care. The bandage should not contain oils, fats, dyes – this will complicate the cleaning of wounds and recognition of the depth of the lesion. Put a dry sterile diaper or bandage on top, do not smear the burn with brilliant green, oil and other folk remedies – this disrupts heat exchange in the tissues. The burned layers of the skin cannot cool due to the oily film, and the lesion will only get deeper.
You can give your child age-appropriate painkillers on the way to the health facility.
Treatment of a burn in a child
After providing first aid, the child is taken to the doctor, and he determines further treatment. Regardless of the degree of damage, all burns go through three stages of healing: inflammation, regeneration, scar formation. Each stage requires different medications and wound care.
When the burn is fresh, the wound is cleaned of dead skin, if any, to prevent damage to the blisters and infection. To do this, use bandages and antiseptics. Then a new tissue begins to form – to speed up the process, special ointments and vitamins are used. After the formation of a scar, the skin is restored, but sometimes the scars are very large. Then physiotherapy, laser resurfacing, emollient creams, resolving scars can be prescribed.
Diagnostics
Even with a small burn, the child is treated only under the supervision of a doctor. The doctor determines the degree of damage and the area of the burn, and, if necessary, sends the child to the burn department in the hospital. A lesion area of more than 10% almost always leads to hospitalization, at least for observation on the first day.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of an external examination. The area and depth of the lesion is written as a fraction: the numerator indicates the area of the burn and the depth, and the denominator indicates the degree of burn. Blood tests may be ordered, especially if the burn is severe.
Modern treatments
A moderate burn usually heals in about 2-3 weeks. In severe cases, if the injury has affected the joints, ligaments and other deep tissues, the victim may stay in the burn unit for a long time.
Wounds are constantly treated with antiseptics, since the addition of an infection is very dangerous. To protect the exposed surface of the burn, special dressings are used. One of the modern methods is the application of hydrogel dressings. The hydrogel swells as it absorbs fluid from the wound and turns into a gel. Thus, a humid environment is maintained. The dressing itself does not cause allergies and allows air to pass through so that the wound heals faster. Hydrogel bandages and dressings are impregnated with special substances with analgesic and disinfecting effect. Some have added silver ions.
The hydrogel is transparent, so you can monitor the condition of the burn right through it without removing the bandage each time. Most importantly, the hydrogel does not stick to the skin – burns are constantly “wet”, and usually the dressings have to be soaked so as not to rip off the dried bandage from the wound.
For light burns, hydrogel is not required – it is enough to periodically treat the inflamed skin with antiseptics and drugs that accelerate regeneration.
Prevention of a burn in a child at home
Most burns to small children are caused precisely by an oversight of their parents. Toddlers do not yet know that hot things are dangerous, and fire cannot be touched, so it is important not to leave such things unattended. When the children are older, you need to explain to them why you can not touch certain objects. Many children try to break the ban without explanation just out of curiosity.
Before bathing, feeding hot food, be sure to first check the degree of heating, because children are more sensitive to temperature.
Popular questions and answers
In order not to miss the complications of burns in a child, we will learn how to act in pediatrician, head of the children’s clinic of the Maternity Hospital No. V.V. Vinogradov Vladislav Zyablitsky.
When should you see a doctor for a burn in a child?
What are the consequences of a burn in a child?
Even after the burn has healed, there may be problems – eczema and dermatitis, scarring, baldness. The prognosis depends on the area and depth of the burns, age and the correct first aid. In such a matter, it is better to “overdo”.