Contents
It turns out that a device for obtaining enlarged images is needed at work and for dentists. We are talking about a new trend in the treatment and hygiene of the oral cavity.
Everyone knows that the world around us is many-sided and multifaceted, but not everyone can imagine how much, even when it comes to what is going on in the mouth. For example, 1 g of dental plaque contains about 1011 bacteria. And his image, magnified 400 times, looks like a cracked surface of a clay deposit of light beetroot, through which the roots of plants are visible. With the advent of dental microscopes, the quality of dental services has risen to a new level. The owner of one of the dental centers in Moscow Dr. SHIPKOV dental clinic Vladimir Shipkov tells in what areas the dental microscope is used and how the quality of dental services has changed due to this.
Dentist, chief physician of the Dr. SHIPKOV dental clinic
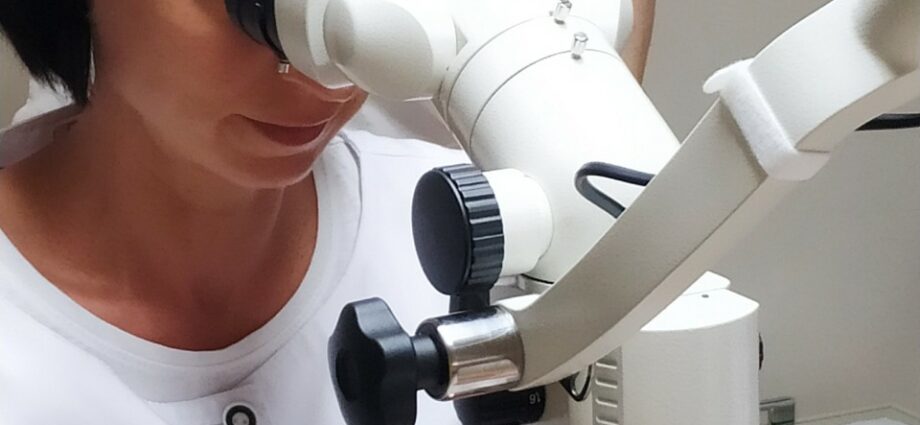
What is a dental microscope?
A microscope is a device for enlarging an image that is invisible or poorly visible to the naked eye. The dental variety differs from the laboratory first of all in the fastening, which is a system of hinged levers. Thanks to them, the doctor can practically effortlessly move the device in all planes and fix it at any point. Modern models allow you to take pictures and shoot in HD format. Today, dental treatment under a microscope is no longer something out of the ordinary, but has become the gold standard of dental practice. This state of affairs can be easily explained: the quality of dental services provided using a dental microscope will almost always be an order of magnitude higher than similar ones without one.1.
What is a dental microscope for?
Among the uninitiated ordinary people, there is an opinion that microscopes in dentistry are the prerogative of endodontists (they specialize in the treatment and retreatment of dental canals). In fact, this is not the case. Microscopes have long been used in many areas of dental practice.
Diagnostics
It is not always advisable from the point of view of time expenditures to carry out the initial examination of the patient using a magnifying device, but its presence in the process will be an undoubted advantage. Usually, a microscope is resorted to to confirm the doctor’s assumptions obtained during the collection of anamnesis, or it is better to examine what is difficult to see with the naked eye. For example, it is not always possible to see a crack on the enamel surface without magnifying optics, and even more so on the canal wall. With a microscope, it will not be difficult to detect hidden carious lesions under old fillings or between adjacent teeth, which is extremely difficult to do without powerful optics.
Professional hygiene
It is especially indicated for patients with crowding, hypersensitivity of the teeth, periodontal disease. The dentist or hygienist, thanks to the microscope, can remove the smallest particles of mineralized deposits from the enamel without damaging the tooth tissue and soft tissues. Optics allow you to safely clean the necks of the teeth, covered with gum pockets, to polish the enamel and roots.
The microscope not only helps the doctor to act more accurately, but also increases the efficiency of specialized equipment – the innovative Air Flow system, the PerioScan artificial intelligence device, and the Vector Paro Pro ultrasound system. With the advent of the microscope, removing soft plaque, pigmentation, and hard deposits from hard-to-reach places has ceased to be a problem.
Therapy
Caries is one of the most common pathological processes in the oral cavity. According to the WHO, in developed countries 80-90% of the population is exposed to it, regardless of education, standard of living and living conditions.2… Having at hand powerful magnifying optics, the dentist-therapist will detect the first manifestations of caries in time, including in hard-to-reach places. And having found it, it will remove the affected tissue and keep it healthy, which is not always possible to do without a microscope. Optics also improves the quality of depulpation (nerve removal). It is extremely important to remove its smallest particles and clean the canal well – this is the best prevention of recurrence and the guarantee of the longevity of the restoration.
Endodontics (dental root canal treatment)
Each tooth has one to three canals. Some of them have four, and rarely when at least one of them has a straight structure, usually their structure is curved, and often very intricate. Previously, endodontists in their work were based only on X-rays and their own experience, moving along the canals literally by touch. As a result, there is often insufficient quality processing and fragments of tools inside. The microscope gave doctors the opportunity to monitor the progress of the process in real time and with multiple magnification of the image. It allows you to qualitatively process, seal, unseal the channels, and, if necessary, remove the fragments of tools left there. Almost completely eliminates the risks of incomplete filling and perforation, guarantees the absence of complications.
- Photo Shoot:
- Dentist’s personal archive
Surgical intervention
Osteoplasty and gingival plastic are some of the most difficult areas in modern dentistry. The use of a microscope during their implementation significantly increases the accuracy of surgical procedures, minimizes the likelihood of injury to adjacent tissues, significantly improves the quality of the work performed, including when navigation templates and preliminary planning are used. The consequence is a brilliant result and a shorter recovery period. Removal of cysts and granulomas (inflammatory formations at the apex of the root) is also much safer and more effective to carry out under a microscope, like a number of other surgical operations.
Benefits of using a microscope in dentistry:
diagnostic accuracy;
full control over the course of manipulations and operations;
improving the quality of work;
reduction of the rehabilitation period.
The advantages are undeniable, and there are no contraindications, even relative ones, for using a microscope.
You can find more examples of how teeth look under a microscope in our gallery.