Contents
The contraceptive implant and stopping menstruation: what is the link?
The contraceptive implant is a subcutaneous device that continuously delivers a micro-progestogen into the blood. In one in five women, the contraceptive implant causes amenorrhea, so there is no need to worry if you are not having a period.
How does the contraceptive implant work?
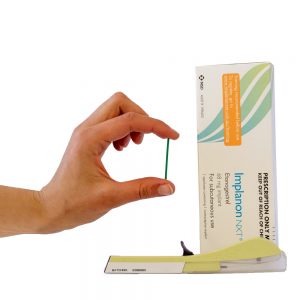
The contraceptive implant is in the form of a small flexible stick 4 cm long and 2 mm in diameter. It contains an active substance, etonogestrel, a synthetic hormone close to progesterone. This micro-progestin prevents the onset of pregnancy by blocking ovulation and causing changes in the cervical mucus that prevent the passage of sperm to the uterus.
How is the implant inserted?
Inserted under local anesthesia in the arm, just under the skin, the implant continuously delivers a small amount of etonogestrel into the bloodstream. It can be left in place for 3 years. In overweight women, the dose of hormones may be insufficient for optimal protection over 3 years, so the implant is usually removed or changed after 2 years.
In France, only one subcutaneous progestogen contraceptive specialty is currently available. This is Nexplanon.
Who is the contraceptive implant intended for?
The subcutaneous contraceptive implant is prescribed as a second line, in women with a contraindication or intolerance to estrogen-progestogen contraceptives and intrauterine devices, or in women who have difficulty taking the pill every day.
Is the contraceptive implant 100% reliable?
The effectiveness of the molecule used is close to 100% and, unlike the pill, there is no risk of forgetting. Also the Pearl index, which measures the theoretical (and not practical) contraceptive efficacy in clinical studies, is very high for the implant: 0,006.
However, in practice, no contraceptive method can be considered 100% effective. However, the practical effectiveness of the contraceptive implant is estimated at 99,9%, which is therefore very high.
When is the contraceptive implant effective?
If no hormonal contraceptive has been used in the previous month, implant placement should take place between the 1st and 5th day of the cycle in order to avoid pregnancy. If the implant is inserted after the 5th day of menstruation, an additional contraceptive method (condom for example) must be used for 7 days after insertion, because there is a risk of pregnancy during this latency period.
Taking enzyme-inducing drugs (certain treatments for epilepsy, tuberculosis and certain infectious diseases) can reduce the effectiveness of the contraceptive implant, so you should talk to your doctor.
The importance of implant placement
Improper insertion of the implant during the break can decrease its effectiveness, and lead to an unwanted pregnancy. To limit this risk, the first version of the contraceptive implant, called Implanon, was replaced in 2011 by Explanon, equipped with a new applicator intended to reduce the risk of faulty placement.
ANSM recommendations
In addition, following cases of nerve damage and migration of the implant (in the arm, or more rarely in the pulmonary artery) most often due to incorrect placement, the ANSM (National Medicines Safety Agency) and health products) issued new recommendations regarding implant placement:
- the implant should be inserted and removed preferably by healthcare professionals who have received practical training in implant placement and removal techniques;
- at the time of insertion and removal, the patient’s arm must be folded, the hand under her head in order to deflect the ulnar nerve and thus reduce the risk of reaching it;
- the insertion site is modified, in favor of an area of the arm generally devoid of blood vessels and major nerves;
- after placement and at each visit, the healthcare professional must palpate the implant;
- a check-up is recommended three months after implant placement to ensure that it is well tolerated and still palpable;
- the healthcare professional must show the patient how to check for the presence of the implant herself, by delicate and occasional palpation (once or twice a month);
- if the implant is no longer palpable, the patient should contact her doctor as soon as possible.
These recommendations should also limit the risk of unwanted pregnancy.
Does a contraceptive implant stop menstruation?
The case of amenorrhea
According to women, the implant can indeed change the rules. In 1 in 5 women (according to the laboratory instructions), the subcutaneous implant will cause amenorrhea, that is to say an absence of periods. Taking into account this possible side effect and the efficiency rate of the implant, it does not seem necessary to perform a pregnancy test in the absence of menstruation under a contraceptive implant. In case of doubt, it is of course advisable to speak about it to your healthcare professional, who remains the best advice.
The case of irregular periods
In other women, periods can become irregular, rare or, on the contrary, frequent or prolonged (also 1 in 5 women), spotting (bleeding between periods) may appear. On the other hand, the periods rarely get heavier. In many women, the bleeding profile that develops during the first three months of using the implant is generally predictive of the subsequent bleeding profile, the laboratory specifies on this subject.