Contents
General description of the disease
Smallpox is a viral infectious disease.
Smallpox types:
- 1 natural (black);
- 2 monkey;
- 3 cows;
- 4 chickenpox – unlike the above varieties, this type of disease has no similarities with the smallpox virus (chickenpox is provoked by the herpes virus, in some cases shingles).
Natural smallpox
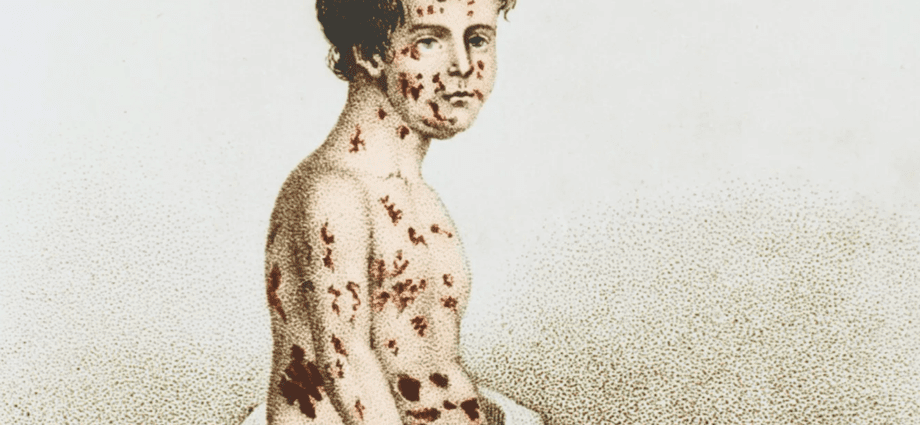
Smallpox affects only people. It is characterized by complete damage to the human body and large rashes on the skin and mucous membranes.
Smallpox symptoms
The first manifestations of the disease are a feverish state and general intoxication of the body (patients have severe pain in the sacrum, lower back, extremities, body temperature rises, vomiting and thirst begins). Then a rash appears (2-4 days after the onset of fever), which goes through several stages: first, a red spot appears on the skin and mucous membranes, which turns into a bubble (on the 4th day of infection), then into a pustule (after which the wound heals, it forms crust, which will soon come off and a scar will remain). The process of drying and falling off the crusts lasts about two weeks.
Mode of transmission, cause, course of smallpox
This type of smallpox is transmitted by airborne droplets, but a person can become infected after contact with a sick person and touching the affected skin. A person is considered contagious all the time from the onset of the chills to the flaking of the crusts. The smallpox virus can be contracted even after the death of a person with smallpox. In severe cases, death can occur before the onset of the rash. With a mild course of smallpox, the rash is insignificant, the bubbles do not turn into pustules, and after the healing of the wounds, no scars remain on the skin, the patient recovers within two weeks. With a mild course, only general malaise is observed. Mild smallpox occurs in vaccinated people.
After transferring the disease, complications are possible in the form of encephalitis, pneumonia, keratitis, sepsis, iritis, keratitis and panophthalmitis.
Smallpox monkey
This type of smallpox is rare. The causative agent, a poxvirus, is similar in etiology to the variola virus.
The source of the disease is infected monkeys; in rare cases, the virus was transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one.
The symptoms of monkeypox are the same as for human smallpox. But there is a major difference – lymphadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes). It proceeds in a milder form than smallpox.
Cowpox
First of all, it is worth noting that this is a disease of cows (less often of buffalo), during which a rash appears on the udder or teats. Nowadays, domestic cats and rodents can get sick with smallpox of cows. The disease is rare. Basically, people who directly care for cattle are sick with it. The vaccinia virus is very similar to natural (it is possible to distinguish from it only by carrying out various laboratory tests). Epidemics occur mainly in India and South America. Milkmaids become infected when they come into contact with a sick animal while milk is being milked.
The symptoms of vaccinia are different from the first two types. After 1-5 days after infection, inflammation appears, which after 10-12 days turns into an abscess with blood and pus. After a while, the abscess becomes covered with a black scab (the skin around it is swollen and red). At 6-12 weeks after the onset of the disease, the scab begins to flake off, after which the abscess begins to heal. Often a trace (pockmark) remains on the site of the former abscess. An abscess can appear on the face or on the hands, it can be one or a pair. In addition, the patient may experience fever, gag reflexes, sore throat, increased weakness and fatigue.
Useful foods for smallpox
The patient needs to eat light, mainly vegetable, food. This is done so that the body’s forces are not spent on digesting food, but on restoring the body. Also, food should be “soft” for the stomach and not irritate the mucous membranes (after all, the rash appears in the mouth and nose). For smallpox nutrition, foods and dishes such as:
- vegetable soups cooked with cabbage, any cereals (you can make mashed soups);
- drinks: fruit drinks, tea (not strong), decoctions of chamomile, lemon balm, rose hips, jelly, juices from vegetables and fruits (necessarily diluted with water);
- vegetables: pumpkin, cabbage, cucumbers, squash, cucumbers, carrots, eggplants;
- fruits: bananas, apricots, avocados, apples;
- Low-fat dairy products (no fillers)
- porridge: oatmeal, rice, semolina, buckwheat, wheat;
- greens (spinach, celery, dill, parsley).
These products envelop the mucous membranes of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, preventing irritation, which will help relieve redness and the appearance of an allergic reaction.
Traditional medicine for smallpox
As such, there is no cure for cowpox. The patient independently forms an immune response, which helps to cope with the virus. Full recovery occurs after 6-12 weeks. The main principle in treatment is the regular treatment of the abscess.
The treatment for smallpox and monkeypox is identical and consists of the following therapeutic measures:
- taking medicinal baths with decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula flowers (to prepare the decoction, you will need 3 tablespoons of chopped herbs per 1 liter of water, you need to boil it for 15 minutes, then add to the bath);
- treating the rash with tea tree oil (it will relieve itching);
- drinking an infusion made from parsley root (it will help to cheer up the patient and speed up the healing of the rash; to make this broth you need to take 4 teaspoons of dried and chopped parsley roots per liter of boiling water, leave for 45-50 minutes, take a teaspoon at a time – a day you need to drink 250 milliliters of infusion);
- rinsing the mouth with a diluted solution of potassium permanganate, boric acid and sage decoction.
For any type of smallpox, it is better to place the patient in a semi-dark room, in the absence of appetite, in no case force to eat, in case of severe fever, help to take a bath with ice and give an antipyretic. The patient should have separate dishes, towels, bed linen, which, after his recovery, it is better to burn, and the room and all things must be disinfected.
Dangerous and harmful foods for smallpox
- alcoholic beverages;
- chocolate, sweet pastries and pastries, confectionery, ice cream;
- onions, garlic, sorrel, horseradish, mustard;
- fatty, spicy, fried, overly salty foods;
- sour fruits with berries (oranges, kiwi, currants, dogwood, lemon, tangerines);
- strongly brewed coffee and tea;
- foods to which the patient is allergic;
- fast food, fast food, convenience foods.
These products irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth and stomach, thereby inflaming the rash and provoking the appearance of new ones. This is due to the inextricable connection between the gastrointestinal tract and the skin – what a person eats is reflected in the condition of his skin (therefore, in order not to aggravate the situation, it is better to refrain from heavy and junk food).
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!