Contents
Pulmonary nodule
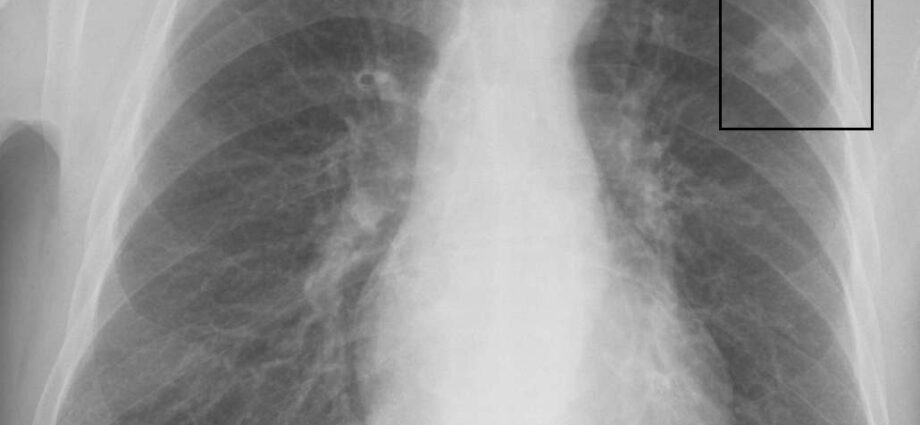
A lung nodule is a small lesion in the lung tissue. This is a common situation. The diagnosis of a lung nodule can be followed by simple medical supervision or surgery.
What is the lung nodule?
Definition of lung nodule
A lung nodule is like a small lump in the lungs. The lesion is more or less rounded with a diameter between 10 mm and 3 cm. We speak of a pulmonary micronodule if the lesion has a diameter less than 10 mm, and a mass in the lungs if the diameter is greater than 3 cm.
It is possible to distinguish several types of pulmonary nodules according to their consistency:
- solid nodules;
- non-solid nodules, also called frosted glass nodules in medical jargon;
- mixed nodules associating a solid part and a non-solid part.
In the majority of cases, the pulmonary nodule is benign. It is also generally unique. We speak of a solitary pulmonary nodule. However, cases of multiple lung nodules can be seen. A lung nodule can also be malignant (cancerous).
Causes of lung nodule
Lung nodules can be the consequence of various pathologies:
- a lung infection, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, which is a common cause of a lung nodule;
- chronic inflammation of the lung, especially with sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis or scleroderma;
- a birth defect;
- a vascular disorder such as a pulmonary artery aneurysm;
- a benign tumor (non-cancerous tumor);
- a malignant tumor (cancerous tumor);
- a metastatic tumor (tumor secondary to primary cancer in another area of the body).
Diagnosis of the lung nodule
The discovery of a pulmonary nodule is usually accidental. It is observed during a medical imaging examination of the thorax carried out as part of a medical check-up or at the request of a doctor to deepen the diagnosis of a pathology.
The lung nodule shows up as an abnormal spot on the results of a chest CT scan. This examination makes it possible to describe precisely the characteristics of the nodule: its location, size, contours, density and content with the presence or absence of calcifications.
Depending on the case, the diagnosis can be deepened by additional examinations such as:
- a bronchial fibroscopy, that is to say an exploration of the trachea and bronchi to visualize the nodule and take samples;
- a PET-scanner, that is to say a scanner associated with a scintigraphy to assess the activity of the nodule.
Persons concerned
The discovery of a lung nodule is a common situation. Statistics show, for example, that a solitary lung nodule is discovered every 500 X-rays on average in the United States. In Europe, it has been observed that 30% of adult smokers over 50 years of age performing a pulmonary assessment of the lungs presented one or more pulmonary nodules.
Symptoms of a lung nodule
Usually asymptomatic lesion
A lung nodule rarely causes symptoms, especially because of its small size. It is usually mild but can sometimes be accompanied by abnormalities. It can also be malignant, that is to say synonymous with a cancerous development.
Associated symptoms
In some cases, the development of a lung nodule may be accompanied by other abnormalities. These are not due to the nodule but to its underlying cause. For example, fever, chest pain and swelling of the glands may be seen in cases of lung infection. Breathing problems can occur in the event of pleural effusion, a characteristic sign of cancer of the pleura (lung envelope).
Lung nodule treatments
Medical supervision
When the lung nodule is benign and has a very low risk of complications, no treatment is necessary. Simple medical supervision can be set up if the origin of the pulmonary nodule remains uncertain and if the pulmonary nodule presents a risk of complications. Medical surveillance generally consists of performing a chest CT scan on a regular basis to assess the evolution of the nodule and identify any complications as soon as possible.
Surgical excision
If there is a suspicious lung nodule, surgery is considered. It consists of removing the nodule. In the event of cancerous development, a more extensive resection may be performed. Removal of the nodule may be accompanied by the removal of a segment of the lung (pulmonary segmentectomy) or a lobe of the lung (pulmonary lobectomy).
Prevent lung nodule
It is possible to limit the occurrence of certain causes of pulmonary nodules. Prevention can consist in particular of:
- maintain a healthy lifestyle (sleep, diet, exercise, etc.);
- do not smoke or quit smoking;
- wash your hands regularly to limit the risk of infections;
- review his vaccines with his doctor.










በጣም አመሰግናለሁ ለሙሉ መረጃችሁ