- general description
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Types
- Complications
- Prevention
- Diagnostics
- Treatment in mainstream medicine
- Healthy foods
- ethnoscience
- Dangerous and harmful products
General description of the disease
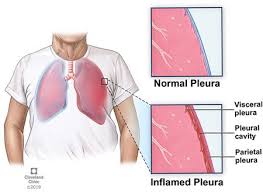
This is a lung disease characterized by an inflammatory process of the pleural layers. It is a smooth serous membrane. With pleurisy, effusion can accumulate in the pleural cavity or fibrous overlays can form. Pleurisy can often aggravate the course of various diseases in the field of pulmonology, cardiology, oncology, rheumatology. According to statistics, this disease is more often diagnosed in elderly and middle-aged men.
When a person breathes, the double, thin shell that covers the lungs and chest area comes into contact in layers. This is usually not a problem because it is smooth and does not create friction. But with inflammation or infection of this tissue, irritation and swelling appear on it, which provokes unpleasant painful sensations. This condition is called pleurisy.
The causes of pleurisy
Viral infections are the most common cause of pleurisy. Other causes of pleurisy are:
- bacterial pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- chest wounds;
- bronchitis;
- fractures of the ribs;
- chest wall injury;
- tumors of the chest or lungs;
- blood clots in the arteries of the lung, also called pulmonary embolisms;
- immune system disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis;
- sickle cell anemia;
- pancreatitis – a condition in which the pancreas becomes inflamed;
- complications of cardiac surgery;
- lungs’ cancer;
- lymphoma;
- fungal or parasitic infections;
- inhalation of chemicals or toxic substances, exposure to certain cleaning agents such as ammonia;
- pleural tumors: mesothelioma or sarcoma;
- heart failure;
- pneumothorax – air in the pleural space that occurs spontaneously or from trauma;
- taking certain medications.
Pleurisy symptoms
The main symptom associated with pleurisy is sharp pain when breathing. It can disappear the moment a person holds their breath or puts pressure on a painful area. However, the pain often gets worse with sneezing, coughing, or movement. Fever, chills, and loss of appetite are also possible symptoms, depending on the condition causing pleurisy.
Additional pleurisy symptoms include:
- pain on one side of the chest;
- pain in the shoulders and back;
- shallow breaths to avoid feeling pain;
- headache;
- pain in the joints and muscles;
- shortness of breath.
Pleurisy can be accompanied by a buildup of fluid that puts pressure on the lungs and prevents them from functioning properly. This process is called pleural effusion… The fluid may initially act as a pillow, causing the chest pain to disappear. But ultimately, the person with the effusion experiences shortness of breath when the amount of fluid increases. Fever, chills, and dry cough may also occur. These symptoms can be a sign of an infection in the fluid and a collection of pus in the pleura called empyema.
Types of pleurisy
There are two types of pleurisy: dry (fibrinous) and wet (exudative). With dry pleurisy, it is more common for the inflamed pleural tissue to rub directly against each other. With moist pleurisy, fluid seeps from the inflamed tissue into the space between the lungs and the chest wall. It can constrict the lungs, making it difficult to breathe and causing discomfort to the person.
Both types of pleurisy often occur as complications of respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia, viral infections, and tuberculosis, and are more likely to develop in people who are highly susceptible to such infections. They can also be caused by a tumor or injury to the chest.
Complications of pleurisy
In most cases, pleurisy does not cause problems after the underlying cause has been treated. However, some patients may have complications. The most common ones are listed below.
Pleural effusion – This is the accumulation of fluid between the pleura. They can be caused by excess fluid production or poor fluid drainage. When fluid builds up, pressure on the lungs causes difficulty breathing, coughing, and cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to reduced oxygen supply to the blood).
Collapsed lung: Thoracic surgery, if performed incorrectly, can cause the lung to deflate. The chest cavity is filled with air and prevents the normal transfer of oxygen to the blood. Another name for this phenomenon is pneumothorax.
Pleural fibrosis: rare but can occur due to inflammation or exposure to asbestos. This is a thickening of the pleura that causes scarring and impaired lung function. In the future, it can provoke other health problems.
Prevention of pleurisy
Since pleurisy is most often caused by an infection, it is difficult to prevent it. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle will improve immune function and reduce the risk of infection.
It is known that some diseases, such as lupus and tuberculosis, can also provoke pleurisy. Therefore, in the presence of such, it is very important to keep them under control. It is of great importance to conduct regular examinations and timely seek medical help when the first symptoms and signs of illness appear.
Another way to prevent pleurisy is to vaccinate. Vaccinations can reduce the chances of contracting infections that can lead to pleurisy. An influenza vaccine is recommended annually.
It is also advisable to quit smoking. Smoke is an irritant to the lungs and makes pleurisy worse. Avoiding secondhand smoke will also help reduce lung exposure to irritants.
Diagnosis of pleurisy
The first priority in diagnosing pleurisy is to determine the location and cause of the inflammation or edema. The doctor conducts a medical examination and listens to the medical history, complaints of the patient. Further, he assigns one or more of the listed studies.
- 1 Chest x-ray will allow the doctor to see if there is inflammation in the lungs. Also, a chest X-ray can be taken while the patient is lying on their side to check for fluid accumulation in the lung area.
- 2 Blood test – helps to determine if there is an infection in the body. And also to establish what provoked it, if it was nevertheless discovered. In addition, blood tests will show if a person has an abnormality in the functioning of the immune system.
- 3 Pleurocentesis – a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the chest area. In this way, fluid material is taken for analysis for infections. For a standard case of pleurisy, such a diagnosis is rarely prescribed.
- 4 Computed tomography – in order to investigate in more detail any abnormalities found on chest x-ray, the doctor may prescribe tomography. CT images create a detailed view of the inside of the pleura. This allows the doctor to take a closer look at the irritated tissue.
- 5 US – in ultrasound, high-frequency sound waves create an image of the inside of the chest cavity. This allows the doctor to see if there is inflammation or fluid formation in the lungs.
- 6 Biopsy – This procedure is useful for determining the cause of pleurisy. The pleura is the layer of membranes that surrounds the lungs. During the procedure, the doctor will make small incisions in the skin of the chest wall. He then uses a needle to take a small sample of pleural tissue. This tissue is then sent to a laboratory to be tested for infection, cancer, or tuberculosis.
- 7 Thoracoscopy – During a thoracoscopy, the doctor makes a small incision in the chest and then inserts a tiny camera attached to the tube into the pleural space. A camera is used to locate the irritated area and then take a tissue sample for analysis.
Pleurisy treatment in official medicine
Once the doctor identifies the source of the inflammation or infection, he can choose the right treatment. Rest is an important ingredient in helping the body to recover. The most common treatments include:
- antibiotics to fight bacterial infection;
- the use of pain relievers, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- prescription pain relievers;
- medicines to help clear up blood clots or a buildup of pus and mucus
- administration of bronchodilators via metered-dose inhalers, such as those used to treat asthma.
If the patient has large amounts of fluid in the lungs (pleural effusions), they will most likely be temporarily advised to stay in the hospital and have a drainage tube installed.
Useful products for pleurisy
A pleurisy diet should be aimed at combating inflammation and reducing the increased reactivity of the body. Therefore, it is important to limit your intake of carbohydrates and salt. And increase the daily intake of calcium salts. Your doctor may recommend reducing your fluid intake to 500-700 ml per day.
It is important to enrich the diet with foods that contain large amounts of vitamins A, P and D. Namely:
- a fish;
- liver;
- milk;
- apricots;
- rose hips;
- boiled carrots;
- black currant;
- kidney;
- citrus;
- buckwheat grain;
- plums;
- Cherries
- fermented milk products – kefir, sour cream, cottage cheese.
Traditional medicine for pleurisy
- 1 An effective remedy for fighting infections is a mixture of onion juice and honey. They must be mixed in equal proportions and taken on a spoonful after meals, twice a day. By the same principle, you can prepare another remedy for infections – mix black radish juice and honey, take it three times a day.
- 2 At the initial stage of the disease, a compress from a sponge dipped in water with the addition of sea salt helps.
- 3 In order to relieve unpleasant painful sensations, a compress with mustard should be applied to the area.
- 4 To strengthen the immune system, it is important to drink cherry juice three times a day after meals for a quarter of a glass.
- 5 Remedy for the treatment of wet pleurisy – you need to take a glass of linden honey, aloe juice, vegetable oil, 50 g of heart-shaped linden flowers and 150 g of birch buds. Pour linden and birch buds with 500 ml of boiled water, heat for 15 minutes in a water bath, let it brew for half an hour, and then strain. Add aloe and honey to this infusion, heat for another 5 minutes, cool, and then add oil while stirring. Take 1 tablespoon before meals 3 times a day.
- 6 Take 1 part sage leaves and pine buds, 2 parts each marshmallow root, licorice and anise fruit. Mix, 1 tbsp. l. pour this mixture with a glass of boiling water, cover and let it brew for several hours. Then strain and take a tablespoon 4 times a day.
- 7 Another effective compress is prepared from camphor oil (30 g), eucalyptus and lavender oils (2,5 g each). It is rubbed twice a day on the sore side, and then bandaged tightly.
Dangerous and harmful products with pleurisy
To improve the dynamics of recovery from pleurisy, it is important to exclude products from the diet that can provoke inflammation in the body, and also cause thirst. These include:
- salt;
- smoked products;
- fried food;
- sweets, bakery products;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- sauces and ketchups;
- conservation.
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!