What is opisthorchiasis?
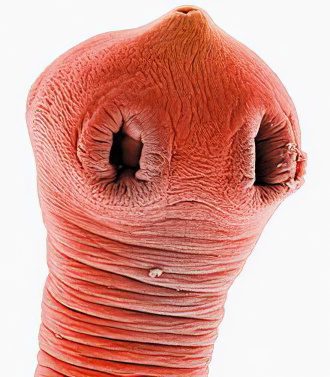
Opisthorchiasis is caused by helminths (hepatic trematodes) that affect the liver and pancreas. According to statistics, the number of infected people worldwide is approximately 21 million people, with two-thirds of all patients suffering from opisthorchiasis living in Russia. The most urgent problem of helminth carriage is in the Dnieper region and in the Siberian region (in Western and Eastern Siberia).
Causes of opisthorchiasis
The cause of the appearance of opisthorchiasis in humans is the cat, or Siberian, fluke (Opisthorchis felineus). The causative agent of the disease parasitizes in the liver, gallbladder and its ducts, as well as the pancreas of humans, cats and dogs. The source of infection is a sick person or animal. Parasite eggs, along with the feces of the carrier of the infection, enter the water, where they are swallowed by snails. In the body of snails, larvae appear from eggs and they reproduce. Then the larvae in the form of cercariae enter the water, with the flow of water they penetrate into the body of cyprinids. Infection of people and animals with opisthorchiasis occurs when eating fish, the meat of which has not undergone sufficient heat treatment, is lightly salted or not dried. Such fish may contain invasive larvae that pose a health hazard to humans and some mammals. In the endemic focus, infection very often occurs when using unwashed cutting equipment containing particles of fish tissue, when cooking or cutting products for which no further heat treatment is provided (bread, fruits, etc.).
In the stomach of a person or animal, the metacercariae capsule is destroyed, the larva breaks the thin hyaline membrane on its own, already in the duodenum, after which the parasite larvae enter the gallbladder and its ducts and the pancreas. When carrying out diagnostic procedures, opisthorchia are found in the ducts inside the liver and in the bile ducts in 100% of patients, pathogens are detected in the gallbladder in 60% of the invaded, in the pancreas – in 36% of patients. Metacercariae that have penetrated the hepatobiliary system and pancreas become sexually mature after 3–4 weeks and begin to lay eggs. Consequently, the full cycle of development of parasites lasts from four to four and a half months and includes all stages of development of the pathogen – from the egg to the mature individual, after which the mature helminths begin to lay eggs. In the body of humans and animals, which are considered the final hosts of parasites, an increase in invasion can occur only after re-infection. The life expectancy of pathogens is 20-25 years.
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis depend on the individual characteristics of the organism, the intensity of infection and the time that has passed since the patient was infected. The disease is acute or chronic. In the acute stage, the disease lasts 4-8 weeks, in some cases the pathology proceeds for a longer time. Chronic opisthorchiasis lasts for years: 15–25 years or more.
In the acute stage, patients note the following symptoms: fever, skin rashes like urticaria, aching muscles and joints. After some time, patients begin to worry about pain in the right hypochondrium, the examination reveals an increase in the liver and gallbladder. Then pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, heartburn join the manifestations of the pathology, the stool of patients becomes frequent and liquid, flatulence appears, and appetite decreases. When fibrogastroscopic examination diagnosed erosive gastroduodenitis, marked ulceration of the gastric mucosa and duodenum. In some cases, opisthorchiasis occurs with symptoms that are characteristic of lung tissue diseases of allergic origin, namely, asthmatic bronchitis.
In the chronic course of the disease, the symptoms of opisthorchiasis have much in common with the manifestations of chronic cholecystitis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis: the patient complains of constant pain in the right hypochondrium, which are paroxysmal in nature and resemble biliary colic in their intensity, while the pain can move to the right side chest. Also, the disease is characterized by: dyspeptic syndrome, pain during palpation in the gallbladder, dyskinesia of the gallbladder. Over time, the stomach and intestines are involved in the pathological process, which is accompanied by symptoms inherent in gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis and disruption of the normal functioning of the intestine.
Invasion also causes disorders of the central nervous system, which is expressed in frequent complaints of patients about decreased performance, irritability, sleep disturbance, headache and dizziness. There is also a trembling of the eyelids, tongue, fingers on the hands. Asthenic condition is usually accompanied by general weakness, rapid physical and mental fatigue. In some cases, a disorder of the nervous system may come to the fore, such patients are often diagnosed with neurocirculatory dystonia or autonomic neurosis.
Chronic opisthorchiasis, accompanied by an allergic syndrome, is manifested by itching of the skin, urticaria, Quincke’s edema, arthralgia, food allergies. The specificity of chronic opisthorchiasis lies in the fact that after the complete elimination of parasites, the patient has irreversible changes in the internal organs. Patients have chronic hepatitis, cholangitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, disorders of the immune system. For such patients, wellness procedures are of great importance after the completion of the full course of treatment, aimed at improving the functioning of the gallbladder, improving the liver, and normalizing digestion processes.
As a result of the decay of pathogens, the release of their metabolic products, and also as a result of necrosis of the body’s own tissues, intoxication occurs, which is accompanied by an allergic reaction. In addition, helminths (young to a lesser extent, mature individuals to a greater extent) injure the epithelium of the bile and pancreatic ducts, while triggering the process of hyperplastic tissue regeneration. Among the consequences of the disease, there is also often a mechanical violation of the outflow of bile and pancreatic juice due to the accumulation of parasites, eggs of pathogens, mucus, and epithelial cells in the ducts.
The most severe complications of opisthorchiasis are biliary peritonitis, abscess, cirrhosis or primary liver cancer, some pathological conditions of the pancreas, such as acute destructive pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, which occurs in very rare cases.
Treatment
At the first (preparatory) stage of the treatment of opisthorchiasis, measures are taken to stop allergic reactions, relieve inflammation of the biliary tract and gastrointestinal tract, ensure normal outflow of bile and pancreatic juice, improve the functioning of hepatocytes, relieve intoxication, cleanse the intestines.
The effectiveness of the second stage of treatment of the disease largely depends on how well the preparatory stage was carried out. During treatment, patients need to follow a special diet: only low-fat foods should be included in their diet. Of the drugs prescribed antihistamines, sorbents. In some cases, patients need to take prokinetics, antispasmodics, probiotics and enzymes.
In the stage of remission in the chronic course of the disease, the course of preparatory therapy is about two weeks, if the patient has signs of cholangitis, pancreatitis or hepatitis, then the course of therapy lasts 2-3 weeks.
At the second stage of treatment, broad-spectrum anthelmintic therapy is carried out, which helps to get rid of most trematodes and cystodes. Due to serious side effects, the course of treatment with this drug is recommended to be carried out in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor.
At the third stage (rehabilitation), the motor and secretory functions of the internal organs affected by helminthic invasion are restored. Tubage is carried out with xylitol, sorbitol, magnesium sulfate, mineral water, laxatives can be prescribed for additional bowel cleansing. Complex treatment is supplemented by hepatoprotectors, choleretic herbal remedies.
Preventive measures are reduced to eating fish that was at a temperature below -40 ° C for 7 hours or at a temperature below -28 ° C for 32 hours, was salted in brine with a density of 1,2 g / l at 2 ° C for 10–40 days (the exposure time depends on the mass of the fish), it was boiled for at least 20 minutes from the moment the broth boiled or fried for at least 20 minutes in a sealed container.









