Contents
Meatus (foramen): what does this orifice in a bone or organ correspond to?
Urinary, auditory, nasal, cranial… The meatus or foramen is an orifice located in a bone or an organ.
What is a meatus?
A meatus is an orifice (or more colloquially a “hole”) observed in a bone or organ. It is also called “foramen” (plural “foramina”). These holes have the function of allowing passage to various elements (liquids, substances, nerves, vessels, channels, cavities, sinuses, etc.).
The term most often applies to the ureter (conduit for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder) or to the urethra (outlet duct of the bladder). We speak for this reason of urinary tract comprising the ureteral meatus and the urethral meatus.
But there are a number of other meat areas in the body, in the bones (and in particular the skull), the ear canal or even the nasal cavities.
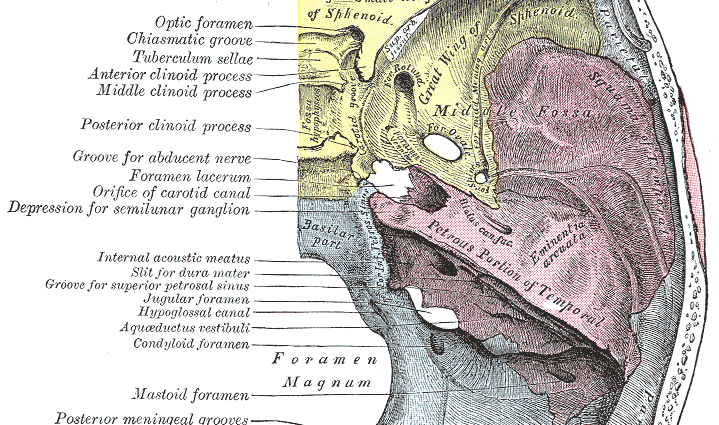
The cranial meatus and their roles
There are 11 holes at the base of the skull, their role is most often to let nerves or vessels pass:
- the holes of the riddled blade of the ethmoid : the riddled lamina of the ethmoid is a horizontal bony lamina, located just above the nasal cavity. Its holes are crossed by the threads of olfactory nerves from the nasal cavity;
- the optic canal: it is located inside the anterior clinoid processes. It contains the optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery, a collateral branch of the internal carotid artery. The optic canal is not visible on a frontal view of the skull. A specific radiological incidence is necessary to highlight it;
- ophthalmic orbital fissure : she is at between the large wing and the small wing of the sphenoid. It is crossed by all the oculomotor nerves: the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve, the abducens nerve and the ophthalmic nerve (first sensitive branch of the trigeminal nerve). The ophthalmic orbital fissure also contains the ophthalmic veins;
- le foramen around : it is located in the large wing of the sphenoid, is crossed by the trigeminal nerve (V2);
- le foramen ovale : it is located behind the round foramen. It is crossed by the mandibular nerve (third sensitive branch of the trigeminal nerve and its motor branch);
- the thorny foramen : it is located in the large wing of the sphenoid. It contains the middle meningeal artery;
- the torn anterior or carotid foramen : it is located between the rock and the sphenoid. It is crossed by the internal carotid artery which supplies the brain;
- the acoustic meatus(or the internal auditory canal): it is located on the postero-superior face of the rock. It is crossed by the stato-acoustico-facial bundle composed of the facial nerves, the intermediate Wrisberget nerve of the auditory nerve;
- the posterior torn hole : it is located between the rock and the sphenoid. It is crossed by the internal carotid artery;
- le foramen hypoglosse : it lets the hypoglossal nerve come out of the cranial box;
- the foramen magnum: it is the largest foramen in the skull. It is the place of transition between the medulla oblongata and the spinal cord. It passes through vertebral arteries and the medullary root of the spinal nerve.
The urinary tract and their roles
The kidneys (whose role is to filter and purify the blood in order to transform it into urine) are connected to the bladder by 2 ducts: the ureters. Urine therefore leaves the kidney and flows through the ureteral meatus. The bladder is connected to the urinary orifice (or urethral meatus) by the urethra duct.
The male urethra is long, it goes from the bladder to the urethral meatus crossing the penis. The female urethra is short, it starts from the bladder and very quickly ends in the vulva through the urethral meatus.
The meatus of the nasal cavities and their roles
At the level of the nasal cavities, each meatus corresponds to one of the turbinates and occupies the space between the lateral face of the nasal fossa and the turbinate. The pneumatic cavities adjacent to the nasal cavities communicate with the latter through the meatus.
- the superior nasal meatus overhangs the middle turbinate. In this meatus open the posterior ethmoidal cells and the sphenoid sinuses;
- the middle nasal meatus is located under the middle turbinate. In this meatus open the maxillary sinus, the frontal sinus and the anterior ethmoidal cells;
- the inferior nasal meatus is located under the lower turbinate. In this meatus opens the lacrymo-nasal duct;
- supreme meat (Santorini and Zuckerkandl meat) are inconstant. Each of them presents the orifice of an ethmoidal cell.
Acoustic meatuses and their roles
- Le external acoustic meatus, also called the ear canal or external auditory canal, is the part of the outer ear, located between the pinna and the eardrum.
- Le internal acoustic meatus opens onto the postero-superior face of the rock through the internal acoustic pore. It is 10mm long and 5mm wide.