Contents
Lipid balance: cholesterol and triglycerides
The lipid profile is a blood test that targets lipid compounds in the blood: cholesterol and triglycerides. The doctor prescribes it to determine the risk of developing cardiovascular disease in his patient.
What is the lipid profile?
The lipid balance refers to an examination of the various lipid compounds present in the blood, namely:
- total cholesterol (a fatty substance which enters into the composition of cell membranes in particular and which is used for the synthesis of steroid hormones);
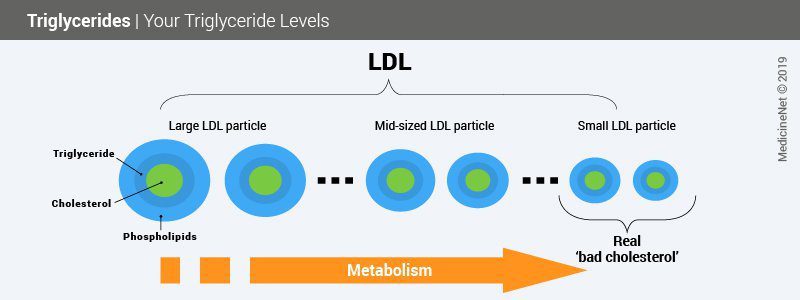
- LDL-cholesterol, which is considered to be the “bad” cholesterol. The fatty body is effectively linked to transporters, the LDL (for low-density lipoproteins) which navigate from the liver to the rest of the body;
- HDL-cholesterol, referred to as the “good” cholesterol. It is linked to HDL (for high-density lipoproteins) which circulate to the liver. In this place, cholesterol is stored;
- triglycerides (a type of fat which constitutes an important reserve of energy and which comes mainly from sugars and alcohol ingested in large quantities).
Why perform a lipid balance?
Lipid testing is a routine checkup that should be done every 5 years in adults. It allows to evaluate:
- the atherogenic risks of his patient, that is to say the propensity for him to develop atheroma plaques on his arterial walls;
- and therefore the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
To better understand that atheroma plaques are plaques essentially made up of lipids (but also of blood, fibrous tissue, lime deposits):
- they can cause damage to the lining of the arteries (this is called sclerosis);
- block the blood vessels;
- or even cause them to break.
People with a known risk of cardiovascular disease should have this check-up more regularly:
- women over 60;
- men over 50;
- people with a family history of coronary heart disease (such as a myocardial infarction), high blood pressure, diabetes or smokers.
The test is also prescribed to check the effectiveness of a treatment targeting cholesterol or triglycerides, or before prescribing a contraceptive pill in women.
How is the lipid assessment carried out?
To establish a lipid profile, medical personnel take a sample of venous blood, usually from the crease of the elbow. Then he analyzes the components of interest: total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and triglycerides.
In order not to distort the results and lead to a bad reading of the balance sheet, the patient must be fasting for at least 12 hours and must not consume alcohol during the 48 hours preceding the blood sample.
How to interpret the results of a lipid assessment?
The lipid profile is considered normal when:
- total cholesterol <2 g / l (the level is considered high if it exceeds 2,4 g / l)
- LDL-cholesterol <1 g / l (the level is considered high if it exceeds 1,6 g / l)
- HDL-cholesterol between 0,4 and 0,6 g / l
- triglycerides <1,5 g / l (the level is considered high if it exceeds 2 g / l)
Note that the reference values of these lipid parameters vary according to the age and sex of the patient. They may also vary slightly depending on the country.
Depending on the results of the assessment and the risks already known to the patient, the doctor will suggest a treatment aimed at reducing the level of fat in the blood. We talk about lipid-lowering or cholesterol-lowering treatment: fibrates, resins, fish oils or statins are usually recommended).
Read also : How to interpret your blood test result ? How to regulate your cholesterol level? Everything you need to know about cardiovascular diseases |