Contents
Many parents experience neonatal jaundice. This is especially true for premature babies, it develops in more than 80 percent. But in babies who were born at term, this is also a common occurrence – it occurs in 50-60 percent of cases.
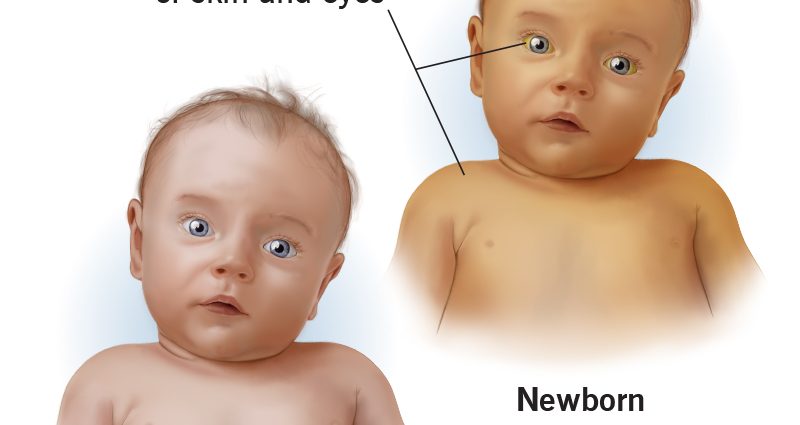
Jaundice develops in the first few days after the birth of the baby, and the change in skin color usually becomes noticeable on the 3-4th day, just when the mother and the baby return home from the hospital.
Why is this happening? It’s all about bilirubin. In any person, it is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells (blood cells that are responsible for transporting oxygen) throughout life and is easily excreted from the body with the help of the liver. But in a newborn, it, like many other body systems, has not yet fully matured, so the baby’s liver does not yet have enough enzymes to break it down and excrete it. And the level of hemoglobin in the blood of a newly born baby is quite high. As a result, bilirubin accumulates in the blood, and the skin of the newborn turns yellow. The whites of the eyes may also be stained.
At the same time, the child feels well. This is the so-called physiological jaundice of newborns, which does not require treatment and completely disappears by the end of the first month of life. But there is also pathological jaundice in newborns. This is already a very serious condition that can have negative consequences for the child. Such jaundice requires mandatory treatment.
Causes of jaundice in newborns
Unlike physiological, pathological jaundice usually develops in the first hours after the baby is born. There may be dark urine and discoloration of feces, anemia, and pale skin. At the same time, the level of bilirubin is very high – above 256 µmol in children born on time, in premature babies – above 171 µmol.
“Pathological jaundice can be caused by several reasons,” says pediatrician Anna Levadnaya, Candidate of Medical Sciences, author of a blog about pediatrics. – The most common is an increased breakdown of hemoglobin due to an Rhesus conflict or a blood type conflict between mother and child. Also, the cause of jaundice can be a pathology of the liver or a pathology of excretion of bile into the intestines. In addition, jaundice can be a sign of an infection, hypothyroidism (due to a decrease in thyroid function), polycythemia (an increased level of red blood cells in the blood), intestinal obstruction, or pyloric stenosis (this is a congenital narrowing of the part of the stomach before entering the intestines, which makes it difficult for food to pass through). into it). It can occur with certain medications and for other reasons.
Also, there is jaundice in newborns from breast milk, when the level of bilirubin in the baby rises due to the ingestion of certain hormones that are contained in the mother’s milk into the child’s body. This jaundice can last up to 6 weeks. If, when HB is canceled for 1-2 days, the level of bilirubin begins to decrease, and the yellowness disappears, then such a diagnosis is made. But with positive dynamics, the abolition of breastfeeding is not required, it resumes after 1-2 days. During the pause, the mother must definitely express herself in order to maintain lactation at the required level.
Treatment of jaundice in newborns
Physiological jaundice of newborns, as we have said, does not require treatment. Sometimes pediatricians recommend supplementing such children with water, but only if lactation is established and using a spoon, not a bottle.
As for the pathological jaundice of a newborn, it requires mandatory treatment, which is prescribed by a doctor.
The most effective treatment for this condition today is phototherapy. To do this, use a special lamp with “blue” light: under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, bilirubin breaks down and is excreted from the body of the newborn with urine and feces. The intensity and duration of phototherapy depends on the baby’s body weight at birth and the level of bilirubin, which is constantly monitored. As a rule, three-hour sessions under the lamp are prescribed with a break of 2-3 hours. The newborn must be undressed, but the eyes must be protected, the boys also have the genitals.
In severe cases of neonatal jaundice, when the life of the child is at risk, a blood transfusion may be prescribed.
– It is important to note that now most experts agree that the appointment of sorbents, drugs such as phenobarbital, Essentiale, LIV-52, the abolition of breastfeeding, UV (ultraviolet blood enrichment), electrophoresis or excessive infusion therapy for jaundice are ineffective (and for phenobarbital and not safe) – says Anna Levadnaya.
Consequences of jaundice in newborns
The physiological jaundice of newborns, as we have already noted, passes by itself and does not bear any negative consequences for the health of the baby. But the consequences of pathological jaundice in a newborn can be very serious, especially if treatment is not started on time.
– Too high an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood can lead to brain damage, – says Anna Levadnaya. – As a rule, this occurs in children with hemolytic disease according to the Rh factor, with an increase in the level of bilirubin above 298-342 μmol / l. And the higher the level of bilirubin, the higher the risk of encephalopathy.
Prevention of jaundice in newborns
The best prevention of neonatal jaundice is a healthy lifestyle for the mother during pregnancy, giving up bad habits, good nutrition.
Breastfeeding is also very important. Mother’s milk is the best food for a newborn, it is very easy to digest, the intestines are stimulated faster, it is populated with beneficial microflora, and the necessary enzymes are produced. All this helps the body of the newborn to cope with jaundice faster and more efficiently.