Contents
What is jaundice
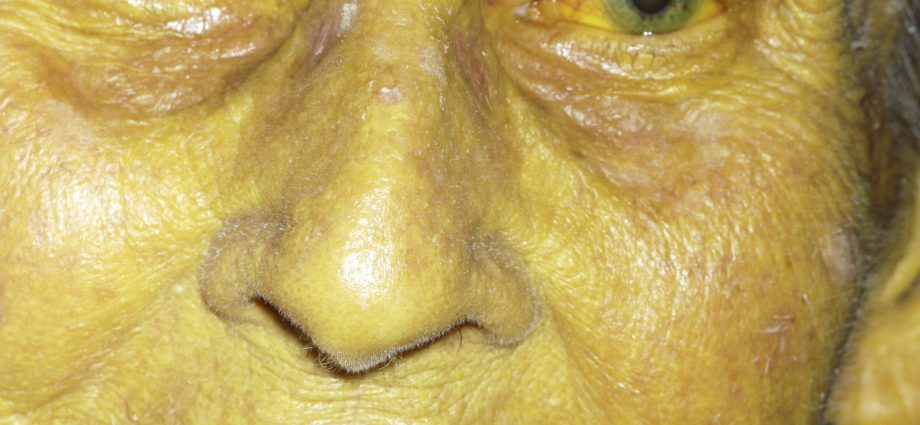
Jaundice (hyperbilirubinemia) is a condition of the body in which, due to an excessive amount of bilirubin in the blood, the skin and mucous membranes become yellow.1.
When the red blood cells (erythrocytes) that carry oxygen break down, a yellowish substance called bilirubin is formed. Next comes the liver, which filters the decay products. However, if there are any pathologies in the body, the liver may not be able to cope with its tasks. As a result, bilirubin accumulates in the body, making itself felt in the form of yellowness of the skin, sclera of the eyes and mucous membranes.
Types of jaundice
Jaundice is divided into three types.
- Hemolytic (adrenal) jaundice. Occurs when excessive breakdown of red blood cells. In this case, the liver may not be able to cope with the release of a large amount of bilirubin at once.
- Parenchymal (hepatic) jaundice. This type of jaundice is already associated with damage to hepatocytes – liver cells. The membrane of the liver cells is damaged, because of this, the ability of the organ to filter qualitatively is disrupted, and an excessive amount of bilirubin enters the bloodstream.
- Mechanical (subhepatic) jaundice. This type of jaundice occurs when there is a physical obstruction (tumor, stone, or inflammation) to the flow of bile, preventing bilirubin from entering the intestine and leaving the body.2.
In addition to the three main types of jaundice, there is another so-called false jaundice or pseudojaundice. This type is not associated with any disease. An excess of carotene in the daily menu can give the skin an orange tint, but the general condition of the body and the color of the mucous membranes will not change. In this case, it is enough to reduce the consumption of foods rich in carotene: pumpkins, carrots, peaches, orange bell peppers. If the correction of the diet did not change the situation, an urgent consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Causes of jaundice in adults
More often jaundice occurs in children, but if it appeared in an adult, there are a number of reasons for this:
- hereditary types of anemia, in which there is a rapid breakdown of red blood cells;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- blocked bile ducts;
- Gilbert’s syndrome;
- complications after surgery;
- infestation with parasites;
- infectious diseases;
- long-term drug therapy;
- pancreas cancer3.
Symptoms of jaundice in adults
The name “jaundice” already indicates one of the main symptoms – yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. But already at this stage, experienced specialists can assume which type of jaundice manifested itself in a person.
With adrenal jaundice, the skin turns pale, acquiring a lemon or pale yellow tint. Hepatic jaundice gives an orange tint. With obstructive jaundice, the skin becomes darker, acquiring earthy-green hues.
Other symptoms include:
- heat;
- chills;
- abdominal pain;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- dark urine;
- light chair;
- weight loss;
- tendency to bruising;
- itching.
Treatment of jaundice in adults
Jaundice is not an independent disease, it is one of the symptoms of more serious changes in the body. After passing the diagnosis and the diagnosis, the doctor will build an individual treatment strategy for each patient.
Diagnostics
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- analysis for direct and total bilirubin;
- urinalysis for total and direct bilirubin;
- antibodies to hepatitis viruses.
In addition to laboratory tests, an ultrasound examination of the liver and biliary tract, as well as MRI or tomography, may be prescribed.
Prevention of jaundice in adults at home
The main measures to prevent jaundice are:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- thorough washing of fruits and vegetables;
- healthy lifestyle;
- timely vaccination against hepatitis;
- regular visits to narrow specialists in the presence of chronic or hereditary diseases.
Popular questions and answers
Viral hepatitis A transmitted through contaminated food or water. In some cases, simple contact with the patient is enough for infection.
Viral hepatitis B transmitted most often by parenteral route (infection occurs through a needle, the blood of an HIV patient, when using non-sterile medical instruments during dental procedures, in a tattoo parlor or piercing). It can go into a chronic form or cirrhosis of the liver.
Viral hepatitis C – transmission occurs mainly by the parenteral route (bypassing the intestines).
Viral hepatitis D often occurs together with hepatitis B and is transmitted parenterally.
Viral hepatitis E the signs may be similar to hepatitis A. Infection occurs by the fecal-oral route. Often it is this form that leads to a severe course of the disease and death.
Jaundice caused by hepatitis B and C can be transmitted through the blood, such as through a transfusion. There is a possibility of infection of the fetus in the womb or during childbirth. Also, jaundice caused by these viruses can be transmitted sexually.
Sources of
- Kostin S.V., Belyaev A.N. Analysis of the causes of obstructive jaundice // Health is the basis of human potential: problems and ways to solve them. 2014. No. 2. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/analiz-prichin-vozniknoveniya-mehanicheskoy-zheltuhi
- Kalinina M.A., Varzin S.A. The role of minimally invasive technologies in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with obstructive jaundice (aggravated by concomitant diseases) // Health is the basis of human potential: problems and ways to solve them. 2018. No. 1. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/rol-maloinvazivnyh-tehnologiy-v-diagnostike-i-lechenii-patsientov-s-mehanicheskoy-zheltuhoy-otyagoschennyh-soputstvuyuschimi
- Podymova SD Acute hepatitis in infectious diseases // EiKG. 2013. No. 4. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/ostrye-gepatity-pri-infektsionnyh-zabolevaniyah
- Kalinina E.N., Emelyanova A.N., Chuprova G.A., Nakhapetyan N.A. Viral hepatitis a: features of the clinical course in adults // Sib. honey. magazine (Irkutsk). 2017. No. 2. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/virusnyy-gepatit-a-osobennosti-klinicheskogo-techeniya-u-vzroslyh










rram sheidleba gamoiwvios prchxilis sikvitlee an romeli organizmis daaavadebis problemaa