Syn.: Hyper-IgM immunodefi ciency X-linked (XHIM).
Def .: Primary immunodeficiency from the group of complex immunodeficiencies.
Epid .: A rare variant of complex immunodeficiency, inherited recessively in X-linkage (70%), the frequency of approximately 1: 1 live births for boys, there are autosomal recessive forms.
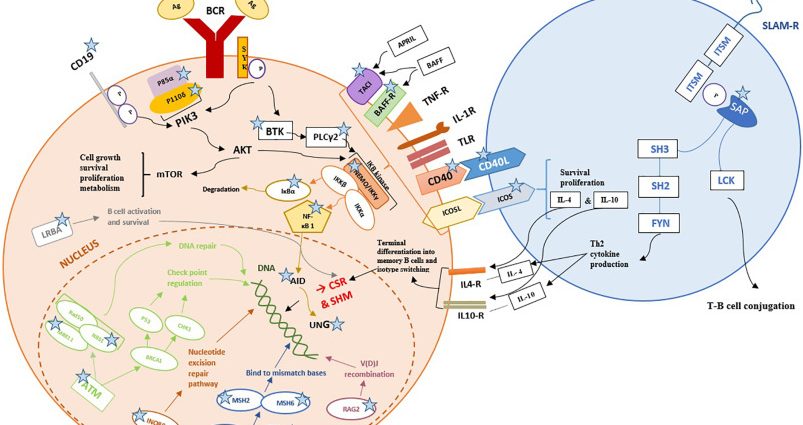
Etiol .: Mutation within the gene located on chromosome X26.3-27.1, encoding CD40L ligand – defect in immunoglobulin isotype switching control.
Clinical: Recurrent infections of the respiratory tract, mainly of the bronchi and lungs, lead in some cases to bronchiectasis, chronic diarrhea (Cryptosporidium) leading to growth disorders. Massive warts. Often, neutropenia is associated with ulceration and inflammation of the mouth, gingivitis. Splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy coexist.
Hist .: There are no reproductive centers in the lymph nodes.
DL: Normal or elevated serum IgM values with significantly decreased or undetectable levels of IgA, IgG and IgE. Neutropenia.
DI: Flow Cytometry: no CD40 (CD154) ligand on the surface of T cells after activation. No specific antibody production.
DR: Agammaglobulinaemia, CVID, transient infant hypogammaglobulinaemia.
Healing: Infusions of intravenous immunoglobulins, bone marrow transplantation, antibiotic prophylaxis, live vaccines must not be used
Year: There is a high susceptibility to lymphoproliferative and autoimmune diseases (haemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, sclerosing cholangitis).
Lit.: [1] Ramesh N., Seki M., Notarangelo L.D.: Th e hyper- IgM (HIM) syndrome. Spring Semin Immunopathol 1998, 19; 383-99. [2] Winkelstein J.A., Marino M.C., Ochs H.: Th e X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome: clinical and immunologic features of 79 patients. Medicine 2003, 82; 373-84.
Source: A. Kaszuba, Z. Adamski: “Lexicon of dermatology”; XNUMXst edition, Czelej Publishing House