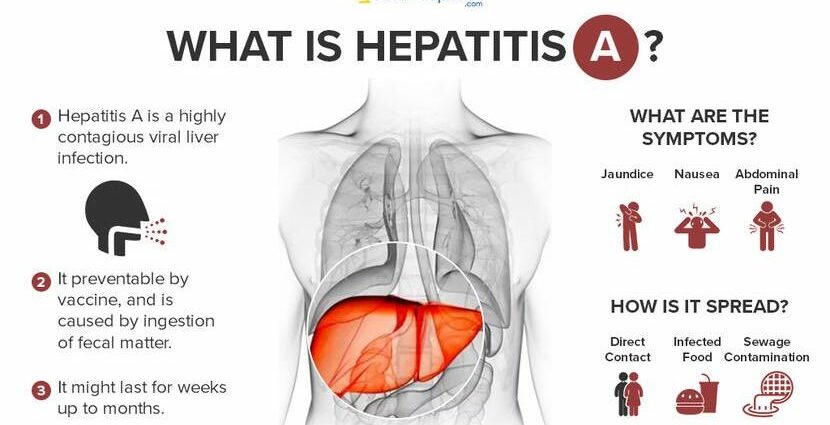
Hepatitis A: what is it?
Hepatitis A is caused by a virus that is passed with the stool by the patient. The hepatitis A virus is therefore transmitted through water, contaminated food or even contaminated hands, but also through oral-anal sex.
All age groups are at risk and, according to the American Liver Foundation, up to 22% of adults who contract the disease are hospitalized. Hepatitis A is the most common form of viral hepatitis, but it is also the mildest form of viral hepatitis. There is never a progression to chronicity and fulminant or subfulminant hepatitis is rare (0,15 to 0,35% of cases). After exposure to the virus, the incubation period varies from 15 to 45 days. Most patients make a full recovery within 2 to 6 months.
Risk of relapse: the blood now contains specific antibodies which normally provide total protection for life. Between 10 to 15% of infected people can have a relapse within 6 months after the acute phase of the infection, but there is no progression to chronicity1.
Risk of contagion: Since hepatitis A is often asymptomatic, it is easy to spread the virus without knowing it. The affected person is contagious two weeks before symptoms appear and seven to ten days after they disappear.