Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis is most often caused by the presence of yeasts (Candida albicans), less often by other species of fungi. It is an ENT ailment that affects people with reduced immunity, treated with immunosuppressants, and people with cancer. The mycosis is accompanied by a sore throat and redness.
What is fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis?
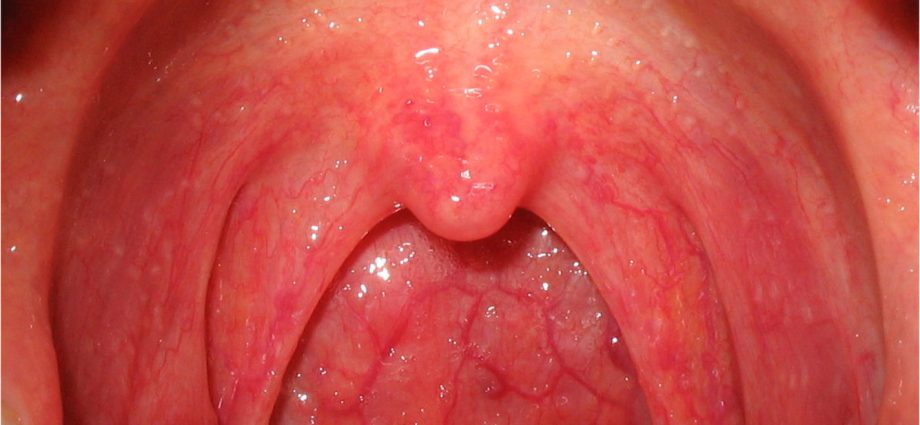
Fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis is an ENT condition that occurs due to the presence of yeasts (Candida albicans) or other types of fungi. This ailment may accompany fungal inflammation of the entire mouth, it may also coexist with mycosis of the palatine tonsils. Inflammation can be acute and chronic. It is most often characterized by presence white raid on the tonsils and the throat wall. In addition, there is pain and redness in the throat.
Over 70% of the population has Candida albicans on their mucous membranes, and yet they remain healthy. Mycosis attacks when the body’s immunity is significantly lowered, then it can also attack the gastrointestinal tract, e.g. the rectum or stomach.
The causes of fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis
The most common mushrooms belonging to the group Candida albicans and causing fungal inflammation are:
- Candida krusei,
- candida albicans,
- Tropical Candida.
As previously mentioned, fungal inflammation occurs due to decreased immunity. Diabetes and AIDS patients are particularly vulnerable to this type of ailment. Young children and the elderly (wearing dentures) are also at increased risk. In addition, patients who take the antibiotic for a long time may also develop fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis. The risk factors also include this:
- smoking,
- hormonal disorders,
- taking too much sugar
- alcohol abuse,
- reduced amount of saliva secretion,
- radiation therapy,
- chemotherapy,
- iron and folic acid deficiencies in the body,
- chronic inflammation of the oral mucosa,
- slight mucosa injuries.
It is worth noting that fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis quite often occurs with various oral mycoses. It could be:
- chronic mycosis erythematosus;
- acute and chronic pseudomembranous candidiasis – usually occurs in newborns and children as well as in elderly people with reduced immunity;
- acute and chronic atrophic candidiasis – occurs in patients suffering from diabetes or in patients taking antibiotics.
Fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis – symptoms
The symptoms of acute fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis depend on the cause, the age of the child, and the state of immunity:
- usually whitish patches appear on the tonsils, and necrosis develops under them,
- The mucosa of the mouth and throat bleeds easily, mainly when trying to remove raids,
- there is a sore throat,
- burning throat
- sore,
- in patients wearing dentures, the so-called prosthetic or linear gingival erythema appears,
- there is a high body temperature,
- patients complain of dry cough and general weakness,
- lack of appetite
- soreness and enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes,
- in infants, fungal pharyngitis and oral cavity causes the so-called thrush, or a white-gray coating.
Chronic disease manifested by increased body temperature and discomfort in the throat. When compressing the tonsils, pus appears and the palatine arches are bloodshot. Lymph nodes may enlarge, but this is not always the case.
If you have throat problems, it is worth drinking FOR THE THROAT – a fix tea that soothes inflammation. You can buy it at an attractive price on Medonet Market.
Fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis – diagnosis
The diagnosis of ailments is based mainly on taking a swab from the throat and taking a sample from the throat wall and palatine tonsils for examination. The ENT doctor also performs a physical examination, which can reveal enlarged lymph nodes, which most often suggest that your body is inflamed. The doctor also looks down the throat to see if the patient has a white coating on the tonsils, throat, the walls of the mouth and tongue. In addition, mycological culture is performed.
Already have the test results? Do you want to consult them with an ENT specialist without leaving your home? Make an e-visit and send the medical documentation to the specialist.
Treatment of fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis
In the treatment of the oral cavity and tonsils, it is important to have proper oral hygiene and the use of antifungal preparations (e.g. in the form of oral rinses). Before using the drug, the patient should undergo an antimycogram to determine the degree of sensitivity of a given strain to drugs. In addition to rinses, patients can use drugs showing antiseptic, fungicidal and disinfecting properties, e.g. hydrogen peroxide, iodine with water or potassium permanganate. Toothpastes and gels containing chlorhexidine (antifungal activity) are also recommended. Sometimes doctors prescribe prescription preparations that are made to order directly at the pharmacy.
Although treatment of fungal pharyngitis and tonsillitis is sometimes long-term, it must not be abandoned, because if ignored, mycosis can cause systemic infection. Treatment should be continued for approximately 2 weeks after symptoms have resolved to prevent relapse.
If you have a sore throat, you can also try sage and plantain lozenges, which eliminate unpleasant ailments.
Read also:
- Acute catarrhal pharyngitis – symptoms, treatment and causes
- Chronic purulent tonsillitis – treatment Overgrown tonsils – excise or not?
- Oesophageal mycosis – symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website.