The term “fat necrosis” means focal necrosis of adipose tissue due to the action of various factors. Fat necrosis occurs in the pancreas, in the retroperitoneal adipose tissue, among the fat of the omentum, mesentery, in the fatty tissue of the mediastinum, in the epicardial fat, in the fat layer under the parietal pleura, in the subcutaneous fatty tissue and in the bone marrow.
The anatomical structure of the pendants in the sigmoid colon suggests their volvulus and the development of inflammation and necrosis. The cause of suspension volvulus may be soldering them to the parietal peritoneum or other organs. Many examinations of elderly people suffering from constipation have led to the conclusion that their sigmoid colon is enlarged in size and therefore fatty pendants are pressed against the anterior abdominal wall.
The muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, due to hypotrophic changes, have hernias in the most vulnerable places, fatty suspensions of the free edge of the sigmoid colon fall into the depression or fossa of the parietal peritoneum, become inflamed and soldered to it. Subsequently, necrosis may develop.
There are several types of fat necrosis
· Enzymatic fat necrosis is a consequence of acute pancreatitis and damage to the pancreas, is formed when pancreatic enzymes exit the ducts into the surrounding tissues. Pancreatic lipase breaks down triglycerides in fat cells into glycerol and fatty acids, which in turn interact with plasma calcium ions to form calcium soap. White, dense plaques and nodules appear in adipose tissue. If lipase enters the bloodstream, then fat necrosis can be detected in many areas of the body.
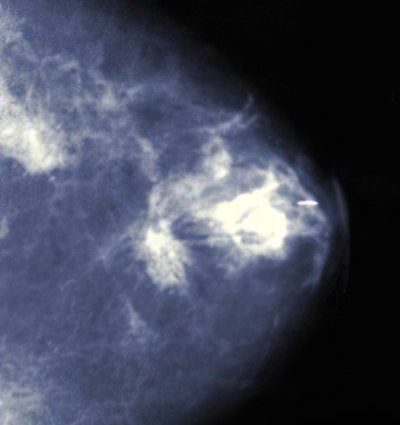
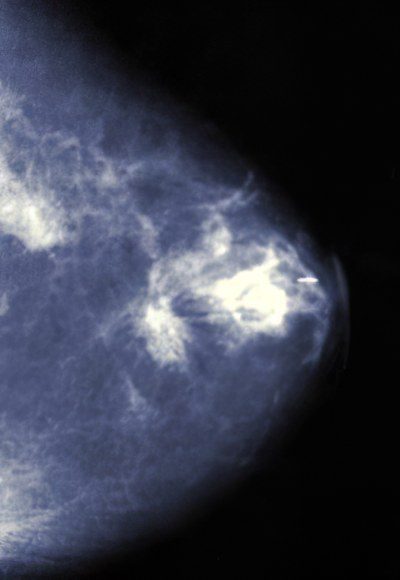
· Non-enzymatic fat necrosis diagnosed in the mammary gland, subcutaneous adipose tissue and in the abdominal cavity, it is called traumatic fat necrosis. It causes an increase in the number of macrophages with foamy cytoplasm, neutrophils and lymphocytes. The process of formation of connective tissue (fibrosis) may occur, often mistaken for the formation of a tumor.
It is known that fat necrosis does not transform into a malignant tumor, but can simulate it. Fatty necrosis of the mammary gland occurs as a result of trauma, as a result of which small vessels are damaged, blood supply is lost. This pathology can occur during radiation therapy, with rapid weight loss.
The disease can proceed painlessly or with a feeling of pain on palpation. It is characterized by an increase in lymph nodes and the formation of dimples on the skin. Treatment consists in removing the focus of fat necrosis by sectoral resection.
Inflammatory disease or necrosis of the subcutaneous adipose tissue occurs mainly in newborns.
To date, the reasons have not been clarified. The main localization of the pathology is observed on the buttocks, thighs, back, upper arms and face. The formation of this process is preceded by a dense swelling of the skin. Necrosis in this case can be focal or widespread. It is determined by the presence of painful nodes of skin color or reddish with a purple tint and irregular shape.
At the sites of lesions, arbitrary neutralization of pathological phenomena can occur, from which no traces remain. If calcium salts are formed in the area affected by necrosis, then the liquid content comes out, and then small scars can form. In rare cases, the following symptoms are possible: lowering blood pressure, exhaustion, vomiting and feverish conditions.
Analyzes state an increase in the concentration of calcium in the blood plasma and an abnormally elevated level of lipids. Fat necrosis in children develops as a result of birth trauma, asphyxia, the influence of low temperatures or a decrease in core body temperature. In the study, histological changes are very important, expressed by thickening of fibrous septa, deposition of crystals inside fat cells and granulomatous cell infiltrates.
The disease is spontaneous, so treatment is not required, it is not advisable to aspirate with a needle from fluctuating skin elements, this can cause infection, and then unforeseen complications are possible. There is also disseminated adipose tissue necrosis, where the adipose tissue around the joints becomes necrotic.
In this case, the body temperature always rises, arthritis develops, and the joints are destroyed. Disseminated necrosis of adipose tissue also arises from the fact that pancreatic enzymes enter the blood or lymph. The death rate in this type of adipose tissue necrosis is very high, you should always remember that you should report any symptoms of poor health to your doctor. Only timely medical care contributes to the preservation of health.