Contents
Ethmoïdite
Ethmoiditis, or ethmoid sinusitis, is inflammation occurring in the ethmoid sinuses. Its acute form results in the appearance of a swelling on the upper eyelid at the corner of the eye. This is accompanied by pain and fever. More common in children than in adults, acute ethmoiditis requires rapid medical treatment.
What is ethmoiditis?
Definition of ethmoiditis
Ethmoiditis is a type of sinusitis, which is inflammation that occurs in the mucous membranes covering the sinuses. As a reminder, the sinuses are bone cavities located in the face. There are different sinuses including the ethmoidal sinuses. They are located on either side of the ethmoid, an odd and median bone located between the two orbits.
Ethmoiditis, or ethmoid sinusitis, is inflammation of the ethmoid sinuses. It can manifest itself in the following ways:
- unilateral or bilateral;
- isolated or associated with involvement of other sinuses;
- chronic or acute.
Causes of ethmoiditis
Ethmoiditis is caused by a microbial infection. Most often these are bacterial infections. The germs involved are in particular:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae or pneumococcus;
- Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus aureus;
- Haemophilus influenzae.
Diagnosis of ethmoiditis
It is initially based on a clinical examination. Several additional examinations can then be performed at the request of the health professional:
- medical imaging examinations, in particular by scanner or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- bacteriological samples.
These additional examinations make it possible to confirm the diagnosis of ethmoiditis, to identify the pathogenic strain in question and / or to look for complications. If complications are noted, hospitalization is necessary.
Acute ethmoiditis is more common in children. It most often appears around 2 to 3 years old.
Symptoms of ethmoiditis
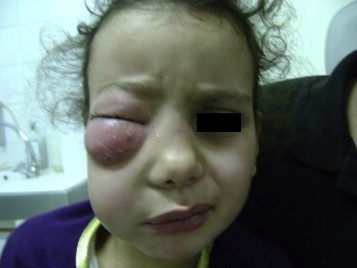
Edema of the eyelid
Acute ethmoiditis causes inflammatory swelling of the orbital region. In other words, painful edema appears on the upper eyelid in the inner corner of the eye. This edema is accompanied by a high fever. We speak of edematous ethmoiditis.
Accumulation of pus in the eye
After the edematous form, a collected form may occur. Pus collects in the eye socket. The eyes tend to be bulging and sore.
Risk of intra-orbital complications
In the absence of adequate management, intra-orbital complications can occur:
- a paralytic myriad which corresponds to a dilation of the pupils by paralysis of the oculomotor nerve;
- corneal anesthesia which is a loss of sensitivity of the cornea;
- ophthalmoplegia, that is, partial or complete paralysis of eye movements.
Risk of intracranial complications
Intracranial complications can also occur:
- oscillating fever with chills;
- meningeal syndrome which is particularly characterized by severe headache, stiff neck and vomiting.
Treatments for ethmoiditis
In the majority of cases of acute ethmoiditis, antibiotic treatment is prescribed. It aims to fight the infection causing the inflammatory reaction. A clinical check-up is generally carried out 48 hours after the start of treatment.
In the event of complications, hospitalization is necessary for the establishment of broad-spectrum parenteral antibiotic therapy. It can be accompanied by corticosteroid therapy to relieve pain. Surgical drainage can also be done to remove the abscess formed.
Prevent ethmoiditis
Ethmoiditis can be caused by pneumococcal or pneumococcal infections. Haemophilus influenzae type B. These infections can be prevented by immunizing the infant.
The prevention of complications linked to ethmoiditis requires early treatment. At the slightest sign, an urgent medical consultation is recommended.