Contents
In this publication, we will consider what the digits of numbers are, and give examples for a better understanding of the theoretical material.
Rank Definition
As we know, everything consists of numbers, of which there are only ten: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9.
Discharge – this is the place / position that the digit occupies in the number.
The position is counted from the end of the number to its beginning. And depending on the place occupied, the figure can have a different meaning.
The digits are arranged in the following order (in ascending order: from the youngest to the oldest, i.e. from right to left):
- units;
- children;
- hundreds;
- thousands, etc.
Examples
As an example, let’s take a closer look at the number 5672 (read as five thousand six hundred and seventy two), or rather, we decompose it into digits.
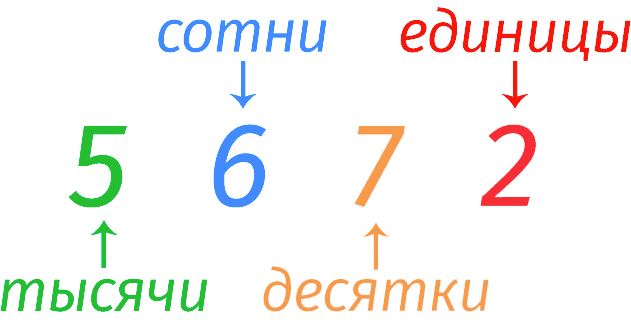
- the number 2 in the last place means two units.
- 7 is seven tens;
- 6 – six hundred.
- 5 – five thousand.
Those. the number 5672 can be decomposed into digits as follows:
Notes:
- There are numbers that do not contain some kind of digit, as evidenced by the number zero in its place. For example, the layout into digits of the number 10450 looks like this:
10 ⋅ 10000 + 0 ⋅ 1000 + 4 ⋅ 100 + 5 ⋅ 10 + 0 = 10450. - Ten units of any category are equal to one unit of the next, higher category. For example:
- 10 ones = 1 ten;
- 10 tens = 10 hundred;
- 10 hundreds = 1 thousand, etc.
- Taking into account the point above, it turns out that the value of the digit in each next digit (older) increases 10 times, i.e. one unit is 10 times less than one ten, one ten is 10 times less than one hundred, and so on.










