Contents
Diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (heartburn)
Faced with signs that may suggest reflux, the doctor can make what is called a “presumptive” diagnosis. He feels that this person is probably having reflux (with no complete certainty). Given the frequency of gastroesophageal reflux, this presumption authorizes the doctor to prescribe a “test treatment” by drugs, and the hygienic dietary instructions, hereinafter cited.
If symptoms do not improve with treatment, it may be something other than reflux. It is therefore important to see a gastroenterologist on the advice of the attending physician, for the performance of a “high endoscopy” or ” Fibroscopy »After stopping treatment.
The diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (heartburn): understand everything in 2 min
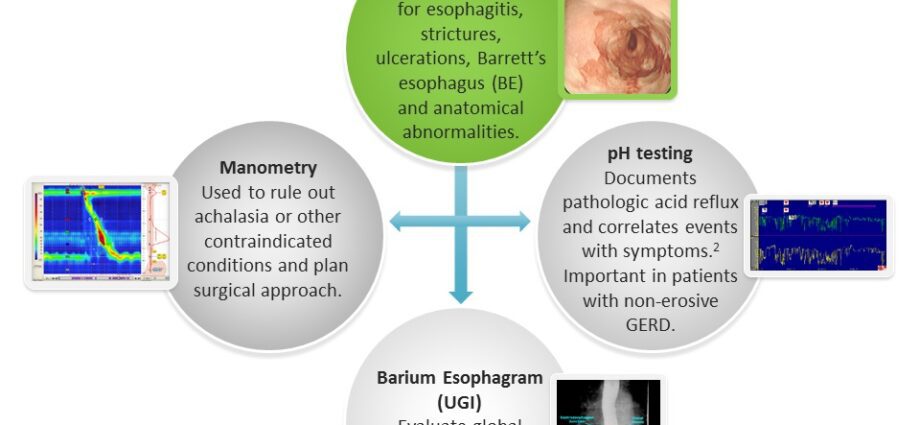
This allows you to see the lining of the esophagus and stomach and, if necessary, to take samples. The specialist thus sometimes detects “eosinophilic esophagitis”, inflammation of the esophagus linked not to reflux, but to an infiltration of specific white blood cells. Likewise, this examination can quickly detect, by seeing them a “peptic esophagitis, stenosis, cancer or endobrachy esophagus”.
Often the fibroscopy is normal, and does not confirm the “reflux”
Gastroesophageal reflux disease will be authenticated by a test called pHmetry which quantifies the existence or not of a reflux over 24 hours by measuring the degree of acidity of the esophagus. This test involves inserting a probe through the nose into the esophagus. On the probe, sensors collect the pH of the esophagus, and differentiate pathological reflux from normal. It must be carried out 7 days after taking any proton pump inhibitor (PPI) type drug so that the results are not disturbed by the drugs.
If symptoms persist in a person with a history of esophagitis or a positive pH measurement without treatment, a “PH-impedancemetry” under treatment can be proposed, which makes it possible to differentiate liquid, gas, acid or non-acid reflux.
Finally, for the sake of completeness, we can try to detect motor disorders of the esophageal conduction by the practice of a TOGD : transit oeso gastro duodenal. It allows to visualize the contours of the esophagus and its movements after ingestion of a radiopaque product. It can detect the contours of a hiatus hernia.
Other examinations, the manometry and “high-resolution manometry” make it possible to analyze, by intra-oesophageal sensors, the motricity of the esophagus.
Some people have a functional disorder, visceral hypersensitivity (the mucous membrane of their esophagus is sensitive): they are found to have a normal endoscopy, a normal acid exposure (pHmetry), a total number of physiological reflux, normal, but a concordance between the symptoms and reflux under impedancemetry.