Contents
Cryptosporidiosis: symptoms, treatments, what is it?
Cryptosporidiosis is protozoan infection, that is to say an infection caused by a protozoan parasite, Cryptosporidium spp, which develops in the intestine, in particular in epithelial cells, and which manifests itself in particular by diarrhea.
Who does it affect?
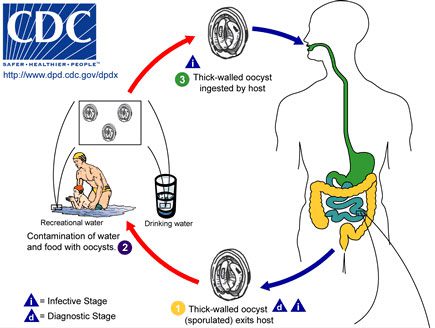
It is a disease that affects both humans, at all stages of their life, and most animals, especially cattle and birds. The two main species that parasitize man are C. hominis and C. Parvum. The parasite describes an asexual cycle inside the intestinal cell, then a sexual cycle resulting in the release of infectious oocysts. Humans become infected by ingesting these oocysts.
Cryptosporidiosis is a disease found all over the world and has already caused several epidemics. The infection rate varies between 0,6% and 2% in industrialized countries against 4% to 32% of the population in developing countries.
In France, the reported epidemics were due to faecal contamination of drinking water distribution networks because the infectious agent is not destroyed by the disinfectants usually used for water treatment. Chlorination of drinking water or swimming pool water is therefore not sufficient to destroy the parasite.
Note that the parasite becomes inactive by freezing under certain conditions: it must be subjected to a temperature of −22 ° C for at least 10 days or to more than 65 ° C for at least two minutes.
How is it transmitted?
Drinking water, swimming pools, nurseries and domestic animals are all reservoirs of this pathology. Very contagious, this parasitosis is transmitted to humans especially by domestic animals, in particular calves, lambs, kids, piglets, foals and reptiles. The origin of transmission is mainly by direct contact with animals, by their secretions or excretions and by the faecal-oral route. It is also possible to become infected indirectly by consuming contaminated food or by consuming vegetables from a garden fertilized with contaminated manure or untreated water.
Person-to-person transmission occurs via the fecal-oral route. For example, not washing your hands after changing the diaper of an infected child.
Its contagion is sporadic or epidemic.
The diagnosis of cryptosporidiosis is most often made using a parasitological examination of the stool which reveals a parasite of the genus Cryptosporidium. An intestinal biopsy can also be done. Cryptosporidiosis should be distinguished from cyclosporiasis which is a parasitic disease caused by ingestion of the coccidia Cyclospora cayetanensis.
What are the symptoms ?
With the animals
In animals, symptoms are seen mainly in younger animals and manifest as profuse yellowish watery diarrhea, weight loss, vomiting, and severe weakness. In turkeys and chicks, signs of respiratory infection may appear.
In humans
In a healthy person, the infection is usually asymptomatic. It can result in classic gastroenteritis with stomach aches, fatigue, watery diarrhea, nausea and a slight fever. Cryptosporidiosis can also affect the lungs, but this is exceptional.
The duration of the disease is variable: it goes from three to fourteen days.
The case of immunodeficient people
In people with immunodeficiency, the disease is much more serious. It manifests itself by severe febrile diarrhea with sometimes a choleriform syndrome (= caused by toxinogenic germs). The main germs involved in choleriform syndrome are Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium perfringens as well as enterotoxigenic E. coli and Vibrio cholerae.
Higher infection rates have been observed in AIDS patients who present with chronic diarrhea. However, in France, the number of cases of this disease in AIDS patients has fallen sharply since the HIV treatments that are prescribed.
The case of immunocompromised people
In immunocompromised people, the elderly and children, diarrhea is longer and prolonged and can become chronic. They can be directly or indirectly associated with the death of the patient.
Cryptosporidiosis can be life-threatening when it occurs in an immunocompromised person.
What treatment for cryptosporidiosis
The treatment is done by taking anti-parasitic drugs. However, no treatment is 100% curative, that is, none eliminates the pathogen. Certain drugs have a relative effectiveness such as paromomycin or nitazoxanide. Rifaximin appears to be the most effective molecule.
In the acute phase of the disease, normal food intake is prevented, which may require infusions to provide all the nutrients needed by the body, especially mineral salts because these are evacuated by diarrhea.
Prevention
Prevention consists in reducing the risk of contamination by oocysts, by respecting the rules of hygiene: wash your hands well after having been in contact with animals, after going to the toilet, before eating etc; and avoid ingestion of water or food which may be contaminated with faeces.