Contents
Coronary artery: can you live with a blocked artery?
The blood that carries oxygen in the arteries is essential for the proper functioning of the body. If an artery becomes blocked, the organ it supplies is in danger. Causes, examinations, and treatments of a blocked artery.
How to define the coronary arteries?
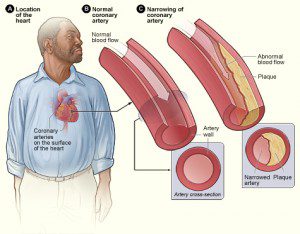
The coronary arteries supply the heart, which can thus function. They appear at the initial part of the aorta and advance towards the surface of the heart.
The coronary arteries, are two in number, the right and the left are located on the heart and they deploy branches around and in the heart muscle.
Coronary arteries, like all other arteries in our body, are made up of three layers each having a significant role, but the central one is particularly important in the development of cholesterol plaques.
Blockage of a coronary artery can lead to serious complications. Coronary artery disease (coronary artery disease) is one of the main causes of death in France, in both men and women. It is possible to live with a blocked artery, but a coronary artery that is completely blocked is a sign that part of the heart is damaged because it is no longer properly supplied with water.
What are the causes of coronary artery disease?
The presence of cardiovascular risk factors promotes coronary artery disease:
- high blood pressure ;
- diabetes ;
- the tobacco ;
- cholesterol;
- family history;
- overweight.
All these risk factors will lead to the appearance of a progressive accumulation of calcium cholesterol and other substances carried by the blood in the wall of the coronary artery.
The accumulation will therefore generate complications because this process can affect many arteries and not just those of the heart.
Coronary artery disease or coronary artery disease is the most common form of heart disease. It is a heart disease that occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to the myocardium. This pathology is potentially dangerous.
Coronary artery disease is caused by the accumulation of fatty deposits on the lining of the arteries which will gradually block the coronary arteries and make them rigid and irregular. This is called osteoarthritis.
What treatment for blocked coronary arteries?
The first treatment for coronary heart disease is to take charge of the different risk factors and apply these tips:
- adopt a diet low in saturated fat;
- to quit smoking;
- to practice regular physical activity.
Drug treatment can also be offered with antiplatelet agents to reduce the formation of clots and β-blockers which reduce the consumption of oxygen by the heart.
Coronary revascularization, the moment when the blood supply restarts after being obstructed by the strictures or occlusions, can be carried out by two techniques whose bases are different:
- percutaneous trans-luminal angioplasty which will act directly on the narrowing;
- surgery that will perform a bypass route.
Diagnostic
If the doctor suspects coronary artery disease, he will refer the person to a cardiologist, a specialist in the heart, arteries and veins.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor asks about symptoms, medical history and risk factors. Based on this information, your doctor can take tests to assess the condition of your arteries.
Exams
The most common exams are:
- coronary angiography is the reference examination to see precisely the coronary arteries and their branches;
- Bypass surgery can only be performed after performing a coronary angiography because the injection of a contrast product into each of the two coronary arteries makes it possible to see the interior of these arteries and to specify the exact anatomy of the network coronary, the position, the course of the arteries, the site of the pathological zones, narrowed, calcified or occluded;
- certain associated endovascular techniques (FFR, IVUS, OCT) make it possible to further refine the results of coronary angiography;
- MRI by magnetic resonance is inevitable to evaluate coronary disease but also to detect the repercussions of coronary disease, either through the evaluation of the myocardial infarction scar caused by the rupture of plaque, or by evaluating the impact of strictures on the perfusion of the heart muscle;
- the coronary scanner is less invasive than the coronary angiography and makes it possible to visualize the coronary arteries directly and to analyze them. It makes it possible to detect coronary lesions and to specify the lesion (number of damaged arteries and the topography of the lesions), the type of lesions (occlusions, stenoses), the severity of the lesions, the study of atheromatous plaque (soft plaque , fibrous plaque, mixed plaque, calcified plaque).