Bronchiolitis
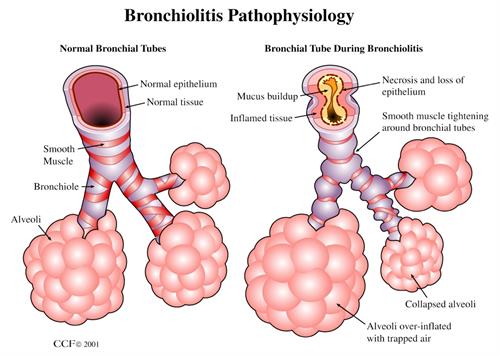
Bronchiolitis is an acute viral infection of the lungs that affects children under two years of age. It is characterized by inflammation of the bronchioles, these small ducts following the bronchi which lead air to the pulmonary alveoli. Children with it have difficulty breathing and wheezing.
This disease is one of the most common causes of hospitalization in children under two years of age. Complications, rare, can be serious.
Autumn and winter are the most common seasons for bronchiolitis.
Causes
- Infection with respiratory syncytial virus or VRS, in the majority of cases. However, not all children infected with this virus develop bronchiolitis. Indeed, the majority of them have a specific immune defense against it, even before the age of two.
- An infection with another virus: parainfluenza (5 to 20% of cases), influence, rhinovirus or adenovirus.
- A disorder of hereditary origin: certain genetic diseases interfere with the proper functioning of the bronchi and could be taken into account. See the People at risk section.
Contagion and contamination
- The virus involved is transmitted through the airways, and can be carried by soiled objects, hands, sneezing and nasal secretions.
Evolution
Symptoms of bronchiolitis last 2 to 3 weeks, with the median duration being 13 days.
Patients with bronchiolitis will often develop asthma in the years to come.
Complications
Generally benign, bronchiolitis may nevertheless cause certain more or less serious complications, as the case may be:
- bacterial superinfection, such as otitis media or bacterial pneumonia;
- seizures and other neurological disorders;
- respiratory distress;
- central apnea;
- asthma, which can appear and persist for several years thereafter;
- heart failure and arrhythmias;
- death (very rare in children who do not have another disease).