Contents
Bone or muscle contusion: what is it?
Contusion is a lesion of the skin without a wound. It is the consequence of a shock, a blow, a fall or a trauma. Most of the time, it is not serious.
What is a contusion?
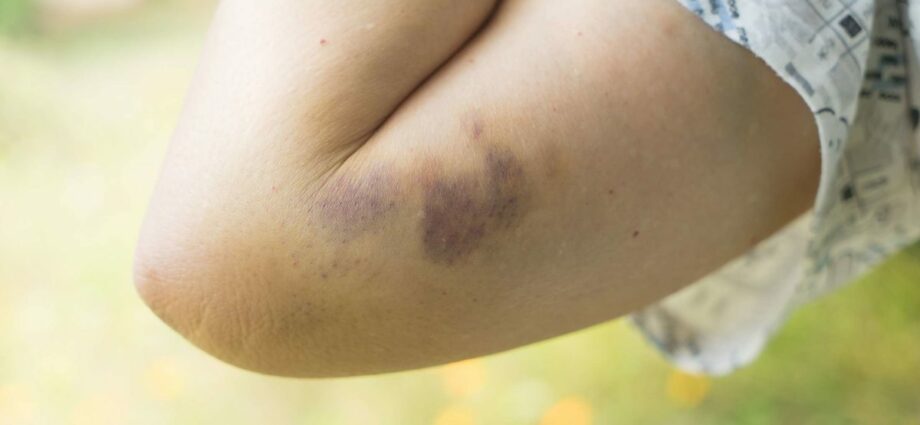
Contusion is the result of a blow, shock, fall or compression. It is a lesion of the skin, without tearing of the skin or sore. We also talk about bruising or bruising, in case of bleeding under the skin; or a hematoma if a blood bag forms, causing swelling. It is possible to get a bruise anywhere on the body. However, certain areas are more prone to impact: the knees, shins, elbows, hands, arms, etc.
There are different kinds of bruises:
- muscle contusion that affects muscle fibers and represents the most cases;
- bone contusion which is a lesion of the bone without there being a fracture, often associated with a small internal bleeding;
- pulmonary contusion that affects the lungs, without perforation, after severe trauma to the chest;
- cerebral contusion which causes compression of the brain, following a very severe shock to the head.
In most cases, these are muscle or bone contusions. They are most often injuries without apparent seriousness. They may be taken seriously depending on the location and the intensity of the shock. In rare cases, following a particularly violent shock, a sprain or a fracture may be associated with the contusion. In the case of a pulmonary or cerebral contusion, medical intervention is necessary.
What are the causes of a contusion?
The main causes of contusion are:
- shocks (impact against an object, fall of an object on the foot, etc.);
- strokes (team sports, combat sport, wrestling, etc.);
- falls (domestic accidents, moment of inattention, etc.).
The impact causes damage to the organs of the injured region:
- muscle fibers;
- tendons ;
- small blood vessels;
- nerve endings;
- etc.
A contusion can occur at any time. Some people are more exposed to the risk of contusion, such as athletes who take blows and shocks or the elderly, more susceptible to the risk of falling.
What are the consequences of a contusion?
Muscle contusion can cause the following symptoms:
- area sensitive to touch, even pain;
- possible pain during movement;
- slight swelling;
- absence of wound;
- Purplish-blue or greenish-yellow skin discoloration, if there is or no bleeding under the contusion.
Bone contusion can be very painful if the lining that covers the bone (periosteum) becomes inflamed.
Lung contusion can result in shortness of breath, difficulty in breathing, chest pain, cough with coughing up blood.
Brain contusion usually includes hemorrhage and edema. Its severity depends on the extent and location of the lesion.
What treatments to reduce the contusion?
Most of the time, a contusion is a benign lesion that heals on its own in a few days, without causing complications. It may require local care such as disinfection and taking pain medication. Most of the time, it does not require the intervention of a doctor. Self-medication is possible on the advice of a pharmacist. If there is no improvement after three days of self-medication, it is important to see a doctor.
It is possible to put in place measures to relieve the symptoms while the lesion resolves. The treatment should be implemented as quickly as possible (24 to 48 hours after the contusion) and will be based on:
- rest of the affected muscles: no weight on the affected joint, crutches or slings if the impairment requires it;
- the use of cold to reduce pain and swelling: application of cold compresses wrapped in a cloth for 20 minutes several times during the day following the shock;
- compression: wrapping the painful area with a bandage, splint or orthosis;
- elevating the injured area above the level of the heart to decrease swelling;
- the possible intake of oral analgesics or the application of an analgesic gel;
- taking oral or local anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain and prevent swelling.
When to consult?
It is necessary to consult if:
- if walking or movement is difficult or impossible;
- in case of formation of a blood bag;
- if the injured area becomes red, hot and painful;
- if the limb is swollen or deformed;
- if there is a blow to the eye or its area, it can lead to internal bleeding or detachment of the retina;
- in the case of a pulmonary or cerebral contusion;
- in case of doubt as to a possible sprain or fracture;
- if there is no improvement after three days of self-medication.
The cases described above are not the most common. Most of the time, the contusion does not require the intervention of a doctor.