Contents
Why white discharge appears in women
There are many diseases that are accompanied by white discharge. Since leucorrhoea is a rather non-specific symptom and it is difficult to differentiate the disease only by them, it is necessary to use additional diagnostic methods. Consider the most popular causes of white discharge from the vagina.
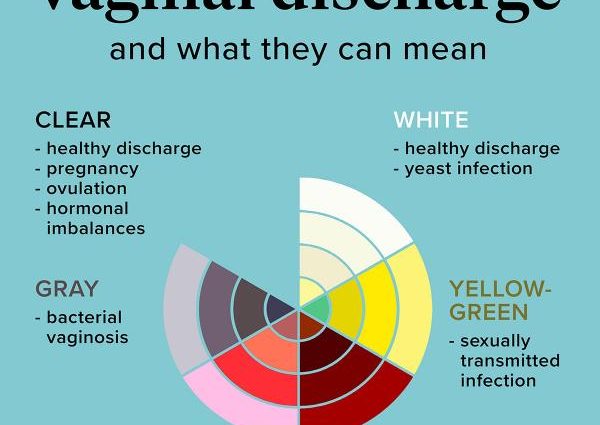
Bacterial vaginosis – a non-inflammatory syndrome that occurs due to the replacement of the normal microflora of the vagina with a conditionally pathogenic one. Another name for this disease is vaginal dysbacteriosis. Vaginal bacteriosis occurs in 16-65% of women.
The cause of the development of vaginal dysbacteriosis are:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- douching;
- taking hormonal and / or antibacterial drugs;
- use of spermicides, vaginal rings;
- transferred STIs (chlamydia, trichomoniasis);
- reduced levels of estrogen in the body.
Bacterial vaginosis does not apply to sexually transmitted infections, however, there is a directly proportional relationship with sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis:
- copious discharge of white or light gray color with a characteristic odor (stale fish), which intensifies when semen or soapy water enters the vagina;
- discomfort during intercourse;
- very rarely itching and burning in the vulva.
Important! Swelling and redness with dysbacteriosis are absent. The acidity of the vagina becomes alkaline (pH 4,5-7,5). Positive amine test (when mixing a 10% solution of potassium hydroxide, the smell of stale fish appears or becomes stronger).
Complications:
- inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs;
- preterm delivery;
- spontaneous abortion.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (thrush) – an infectious disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida. 75% of women of childbearing age have experienced thrush at least once.
Causes of vulvovaginal candidiasis:
- violations of local immunity;
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, obesity, thyroid disease);
- concomitant gynecological diseases;
- taking certain medications (antibiotics, cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids and others);
- the use of tight underwear, synthetic fabrics;
- constant use of sanitary pads;
- douching, use of spermicides.
Thrush symptoms:
- itching and burning (possible swelling) in the vagina and vulva;
- cheesy discharge;
- pain and / or discomfort during urination, sexual intercourse.
Complications:
- inflammatory processes of the urinary system (cystitis);
- complications of pregnancy (premature birth, infection of the fetus in severe cases).
What does white discharge mean in women
White discharge may be a variant of the norm, and may indicate diseases of the genitourinary system. There are characteristics by which you can independently guess whether these whites are the norm or are a manifestation of the pathological process. Consider the most common questions women have regarding discharge.
Liquid
Liquid homogeneous discharge from the vagina in most cases is a variant of the norm. They appear immediately after menstruation, during arousal (they are a lubricant), after intercourse, during pregnancy.
Thick
Thick white discharge without lumps, without itching and odor is a normal variant and is present during ovulation and in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
curdled
White curdled discharge is characteristic of vulvovaginal candidiasis (thrush). Leucorrhea is accompanied by itching and burning in the vulva and vagina. There is also pain during urination and sexual intercourse. During pregnancy, thrush bothers women more often than usual.
With smell
Normal white discharge before period may have a sour smell.
But in most cases, the presence of smell indicates the active life of pathogenic microflora. Most often, this symptom is observed with STDs (sexually transmitted diseases). The smell of sour milk or yeast is characteristic of thrush (vulvovaginal candidiasis). The smell of fish is characteristic of bacterial vaginosis (increased by the ingress of sperm or soap solution into the vagina).
Without smell
White, odorless discharge may be a normal variant: during ovulation, in the second half of the menstrual cycle. They are also a symptom of infectious diseases (thrush). In pathological processes, there are necessarily accompanying symptoms: the presence of smell, itching, and more.
With itching
White discharge with itching is characteristic of thrush. Whites have a curdled texture. Itching in the vagina and vulva. Unpleasant sensations appear 1-3 days from the onset of the disease and continue until the time of treatment with antifungal drugs.
No itching
White, cloudy discharge from the vagina may indicate inflammation. Transparent discharge is most often a variant of the norm. It can be both sexually transmitted diseases, and conditions after taking hormonal drugs, wearing tight synthetic underwear, stress.
Before menstruation
After ovulation, white discharge becomes viscous and takes on a creamy consistency. A variant of the norm is light beige discharge. Compared to the rest of the cycle, the amount of whites in terms of volume is minimal. Not accompanied by itching. The smell may be sour.
After menstruation
Liquid, clear discharge that looks like raw egg white. The consistency is slimy and stretchy. Compared to the discharge after ovulation, it is quite plentiful.
How to treat white discharge in women
Pathological white discharge does not appear just like that. There is some specific provoking factor (virus, bacterium, fungus) that caused the development of an inflammatory or non-inflammatory syndrome.
For example, with vulvovaginal candidiasis (thrush), the causative agent is a fungus of the genus Candida. In this case, the necessary drugs are – antifungal. They can be in the form of suppositories, tablets, ointments.
With bacterial vaginosis, the causative agent is a conditionally pathogenic microflora (that is, organisms that are normally present in a minimal amount in the body, and under some factors begin to actively multiply and cause unpleasant symptoms). In this case, it is necessary to use antibacterial drugs.
With sexually transmitted infections, with inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs, specific treatment is prescribed.
The choice of the drug, dosage, route of administration and duration of administration is selected individually by the doctor based on the history of the disease, examination, laboratory and instrumental data.
Popular questions and answers
We discussed important issues regarding white discharge with вgynecologist of the first category Ada Kosareva.
White discharge is accompanied by pain in the abdomen, what could be the reasons?
When should you see a doctor for white discharge?
What discharge is considered normal in women?
● quantity – from 0,06 to 4 ml per day (for simplicity, a spot on a daily pad is determined – it should not exceed 5 cm);
● consistency – liquid or creamy;
● color – light – from transparent to white (when interacting with oxygen, the excretions are oxidized and acquire a yellow tint);
● structure – homogeneous (small lumps are acceptable, which are particles of the renewing epithelium of internal organs);
● smell – absent (before menstruation, the appearance of a sour smell is acceptable);
● itching – absent.
Sources:
- Federal clinical guidelines “Diagnosis and treatment of diseases accompanied by pathological discharge from the female genital tract”, Moscow, 2013.
- Ledina A.V. Vaginal discharge: causes, patient management algorithm and modern approaches to treatment and prevention / OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY: news, opinions, training Vol. 7, No. 3, 2019.
- L.V. Kudryavtsev. Normocenosis. Bacterial vaginosis. Complex laboratory diagnostics of bacterial vaginosis: the current state of the problem // L.V. Kudryavtseva, A.E. Gushchin / LABORATORY SERVICE, No. 1, 2013.