Contents
The word “metabolism” used in speech of nutritionists and athletes, fitness instructors and always slimming.
Most often the term is used in the meaning of “metabolism”. But what is it actually? People know, not all. Let us figure out.
What is it?
Metabolism is the processes in any living organism to maintain its life. Metabolism allows the body to grow, reproduce, heal damage, and respond to the environment.
For this really required a constant exchange of substances. To divide the processes into two streams. One destructive – catabolism, the other constructive anabolism.
Disassembly at the molecular level…
Any nutrient that gets in the body, can not immediately go for our needs. For example, proteins from nuts, milk and human muscles are quite different, they can’t replace each other.
However, they consist of the same “building blocks” — amino acids. Although each of the proteins is their different set and ratio.
To obtain a material for, for example, bicep, special enzymes are dismantled found in milk or chicken protein into individual amino acids that are used afterwards.
Parallel to the released energy, measured in calories. The opposite process is catabolism. Another example of catabolism is the breakdown of the usual refined sugar into fructose and glucose.
… and Assembly shop
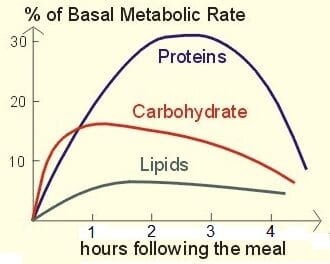
The body is not enough to dismantle the proteins from eaten food into amino acids. It Needs to assemble new proteins for the same biceps muscles.
The construction of complex molecules from smaller components require energy. It uses the same calories that the body received when “disassembly”. This process is called anabolism.
A couple of illustrative examples of work “Assembly shop” of the body – growth of nails and the healing of fractures in bones.
And where is the fat?
If in the process of splitting of nutrients we get more energy than it requires to build new cells in the body, there is a clear excess that needs to be stored.
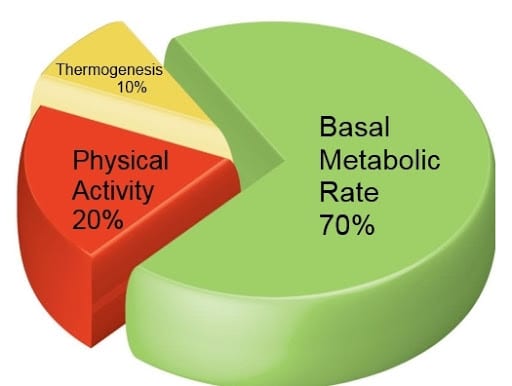
When the body is in rest, metabolic process runs in “background” mode and does not require active fission and fusion substances. But as soon as the body begins to move, all processes are accelerated and amplified. Increasing demand for energy and nutrients.
But even with the movable body there can be the excess calories if you eat too much food.
A small portion of received and unspent energy in the form of carbohydrate – glycogen – an energy source for active muscles. It is stored in the muscles and liver.
The rest accumulates in fat cells. And for their creation and support the body requires much less energy than to build muscles or bones.
Why metabolism associated with body weight
We can say that the weight of the body is catabolism minus anabolism. In other words, the difference between the amount ingested and energy used.
So, eaten one gram of fat gives 9 kcal and the same amount of protein or carbohydrate 4 kcal. The same 9 calories the body will put in the form of 1 gram of fat already inside your body, if you fail to spend them.
A simple example: eat a sandwich and lie down on the sofa. Bread and sausage…. the body received fats, proteins, carbohydrates and 140 kcal. When lying, the body will spend calories just for the breakdown of food eaten and maintenance functions of respiration and circulation – about 50 kcal per hour. The remaining 90 kcal will turn into 10 g of fat and will be delayed in the fat depot.
If a fan of the sandwiches come on a relaxing walk, these calories the body will spend for about an hour.
“Good” and “bad” metabolism?
Many look with envy at the fragile girl, regularly lucamadeus cakes and did not add a single gram of weight. It is considered that such lucky people have good metabolism, and those for whom a piece of sugar in tea threatens to gain weight – have bad metabolism.
In fact, the results show that indeed a slow metabolism is observed only in a number of diseases, e.g., hypothyroidism – lack of thyroid hormone. And most people who are overweight do not have disease, but there is energy imbalance.
That occurs when the body receives much more than it should really, and energy is stored.
Calorie consumption
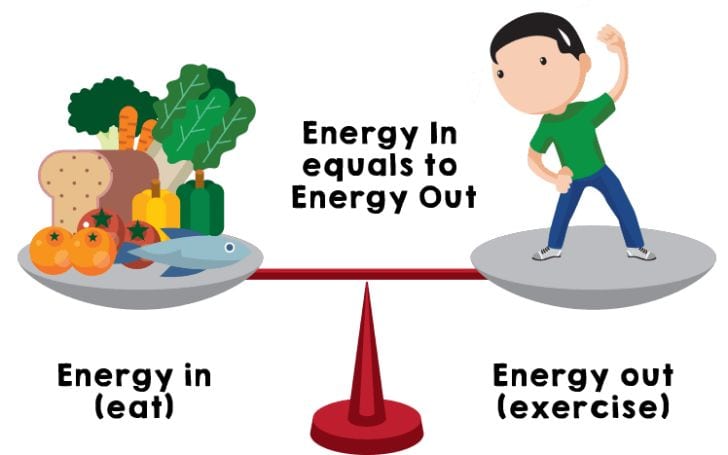
To keep under control calorie intake, it is worth remembering the main directions of additional energy.
- The higher the body mass, the more calories it needs. But, as we know, adipose tissue have very little energy consumption, but the muscle consumes enough. Therefore, a 100-kilogram bodybuilder will spend at least two times more calories for the same work that his 100-pound friend who has immature muscles and high body fat percentage.
- The older the person becomes, the higher it is the difference between energy intake and its expenditure due to hormonal imbalance and a sharp decline in physical activity.
- In the metabolism of the male body is actively involved hormone testosterone. It is a natural anabolic that causes the body to spend energy and resources for growing additional muscle. That is why muscle mass in men body is typically much higher than in women.
And as for the maintenance of muscles requires more energy than to maintain fat, the man and woman of the same height and weight spend a different amount of calories on the same action.
Simple conclusion: men spend more energy, they require more food and they lose weight much faster.
What you need to know about metabolism
The whole life of an organism is a balance between the breakdown of nutrients and getting out of them energy and energy consumption in creating new molecules and cells.
If energy intake is too high – it is deposited in reserve in the form of adipose tissue. To increase energy consumption you can, move a lot or grow a sufficient amount of muscle mass.