Contents
What is polysomnography?
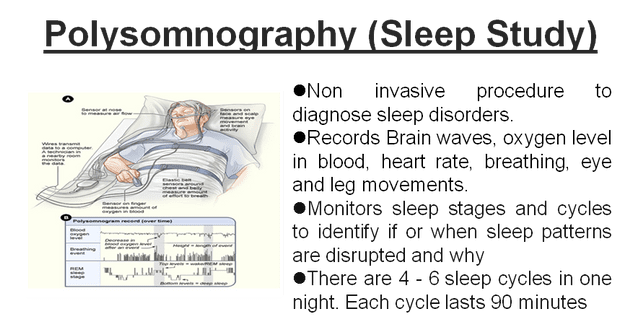
Polysomnography is a study of sleep. By monitoring many physiological closely, the aim of the examination is to determine the presence of sleep disturbances.
Definition of polysomnography
Polysomnography is a comprehensive and benchmark examination that allows the physiology of sleep to be studied. The aim is to assess the presence of sleep disorders and to quantify them.
The exam is painless and risk-free. It takes place most of the time in the hospital but can, in some cases, take place at the home of the person who takes it.
Why do this review?
Polysomnography can detect the presence of several types of sleep disorders. Let us quote:
- obstructive sleep apnea, ie short breathing stops during sleep;
- restless legs syndrome, that is, involuntary movements of the limbs;
- narcolepsy, i.e. severe drowsiness and sleep attacks during the day);
- excessive snoring;
- or even insomnia.
How is the exam going ?
Polysomnography is most often done at night. The patient therefore arrives at the hospital the day before and is placed in a room provided for this purpose.
Electrodes are placed on the scalp, face, chest, but also on the legs and arms, to measure:
- brain activity – electroencephalography ;
- muscle activity in the chin, arms and legs – electromyography ;
- heart activity – electrocardiography ;
- eye activity, i.e. eye movements – electrooculography.
Also, polysomnography can measure:
- ventilation, ie the flow of air entering through the nose and mouth, thanks to a nasal cannula placed under the nose;
- the activity of the respiratory muscles (that is to say the thoracic and abdominal muscles), thanks to a strap placed at the level of the thorax and the abdomen;
- snoring, ie the passage of air through the soft tissues of the palate or uvula, thanks to a microphone placed on the neck;
- saturation of oxygen in hemoglobin, ie the level of oxygen present in the blood, thanks to a specific sensor placed at the tip of the finger;
- daytime sleepiness;
- or even involuntary movements related to sleep, the position of the sleeper or blood pressure.
Note that it is advisable not to consume coffee and to avoid excess alcohol the day before the examination. Also, it is important to inform the doctor of any drug treatments followed.
Analysis of the results
Usually, a single polysomnogram is sufficient to assess sleep and accurately detect the problem if it exists.
The exam monitors:
- waves characteristic of the different sleep cycles;
- muscle movements;
- the frequency of apnea, i.e. when breathing is interrupted for at least 10 seconds;
- the frequency of hypopnea, that is, when breathing is partially blocked for 10 seconds or more.
The medical staff determines an index of apnea hypopnea, that is to say the number of apnea or hypopnea measured during sleep. Such an index equal to or less than 5 is considered normal.
If the score is greater than 5, it is a sign of sleep apnea:
- between 5 and 15, we speak of mild sleep apnea;
- between 15 and 30, it is a moderate sleep apnea;
- and when it is over 30, it is severe sleep apnea.