Contents
What is lactose intolerance?
Lactose intolerance is characterized by digestive disorders, a consequence of poor intestinal absorption of lactose. Lactose is the main sugar found in dairy products).
Definition of lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is characterized by digestive problems as a result of the indigestion of lactose (the main sugar in milk) from milk and its derivative products (yoghurts, cheese, etc.).
An enzyme in the body (lactase) transforms the lactose in dairy products to make it absorbable and digestible. Lactase deficiency then leads to a reduction in the body’s ability to digest lactose. The latter ferments, causing the production of fatty acids and gas. Intestinal transit is therefore accelerated and digestive symptoms appear (diarrhea, gas, pain, bloating, etc.).
The prevalence (number of people with lactose intolerance) in France is between 30% and 50% of adults.
A test for identifying and evaluating the level of lactose intolerance is known and available and allows the diet to be adapted accordingly.
Causes of lactose intolerance
The origins of lactose intolerance depend on the age of the individual.
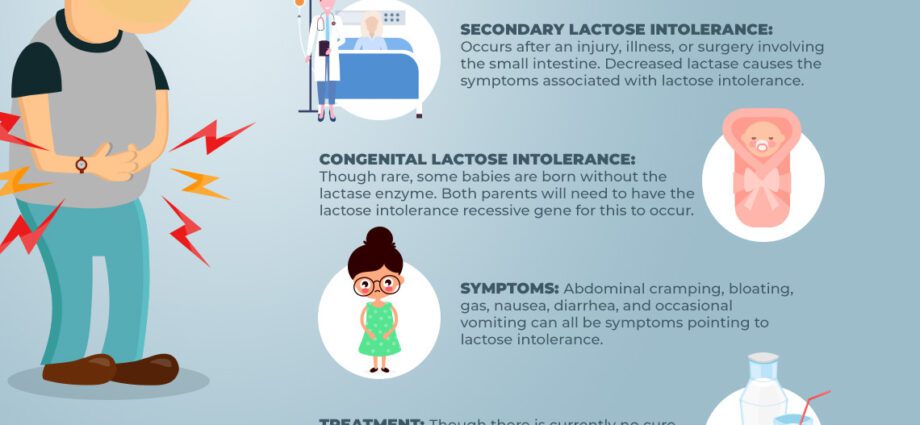
Indeed, in infants, lactose intolerance results in a generalized lactase deficiency. This is a rare disease called: congenital lactase deficiency.
In children, this intolerance may be the result and / or a side effect of gastroenteritis, for example.
You should know that the actions of lactase decrease over time. As a result, lactose intolerance is more and more present with advancing age. Adults therefore form a category of people more prone to the development of lactose intolerance.
Intestinal pathologies can also be the source of the development of lactose intolerance (giardiasis, Crohn’s disease, etc.).
Who is affected by lactose intolerance?
The majority of cases of lactose intolerance are found in adults. However, children can also be confronted with it.
In infants, lactose intolerance is often the result of an underlying disease: congenital lactase deficiency.
Evolution and possible complications of lactose intolerance
Few of the changes and complications associated with lactose intolerance.
Moreover, this intolerance is to be distinguished from allergies to proteins, which themselves can generate complications.
Symptoms of lactose intolerance
The clinical signs and symptoms associated with lactose intolerance are the consequence of a definition of the enzymatic activity of lactase. These result in intestinal and digestive symptoms such as:
- intestinal pain
- diarrhea
- nausea
- bloating
- gases
These symptoms can be more or less important depending on the individual, the amount of lactose ingested and the level of intolerance.
Risk factors for lactose intolerance
Risk factors for lactose intolerance may be the presence of an underlying gastrointestinal disease in children or adults. Or a congenital lactase deficiency in infants.
How to treat lactose intolerance?
The first step in the treatment of lactose intolerance is a diet depleted in dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt, etc.).
A lactose intolerance test is available to assess the level of intolerance. From this assessment, the diet is adjusted accordingly.
If changes in eating habits are not sufficient to optimally manage lactose intolerance treatment in the form of lactase capsules / tablets is possible.