Contents
Vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the pneumogastric nerve, is the tenth pair of cranial nerves, involved in many functions of the body.
Anatomy of the vagus nerve
Mixed nerve. The vagus nerve is made up of motor, sensory and vegetative nerve fibers (1) (2).
Nerf pair. Two in number, the vagus nerves are located on either side of the body (2).
Innervation. The vagus nerve is the cranial nerve that covers most of the body, from the brain to the abdomen (2) (3).
Branches. During its journey, the vagus nerve divides into different branches supplying numerous organs (3):
- Cervical branches. At the level of the cervical portion, the vagus nerve gives a meningeal branch, an auricular branch, pharyngeal branches, upper cardiac branches and the superior laryngeal nerve.
- Thoracic branches. In the thorax, the vagus nerve gives rise to the lower heart branches, bronchial branches, esophageal branches and the lower laryngeal nerve.
- Abdominal branches. In the abdomen, the vagus nerve gives rise to gastric branches, gastric branches, celiac branches and renal branches.
Functions of the vagus nerve
Motor function. The vagus nerve has in particular a motor role on certain muscles of the soft palate, pharynx and larynx.
Sensitive function. The vagus nerve provides sensitivity to the veil and base of the tongue, pharynx, larynx and epiglottis.
Vegetative or autonomous function. The vagus nerve is particularly involved in the autonomic reactions of the cardiovascular, tracheobroncho-pulmonary and digestive systems. This vegetative activity is linked to the secretion of acetylcholine during stimulation of the vagus nerve. This substance is a neurotransmitter, ie it allows the transmission of messages between neurons. Its action allows for example the slowing down of the heart rate, the contraction of certain muscles of the digestive tract, the contraction of the bronchi or the gastric acid secretion (4).
Pathologies of the vagus nerve
Given the length of the vagus nerve and the various innervated organs, a lesion of this nerve can result in various effects, including in particular:
Bradycardia. It corresponds to a slowing of the heart rate. This cardiac arrhythmia may be due to vagus nerve activity.
Syncope vagale. Also called vagal discomfort, this syncope corresponds to a sudden and brief loss of consciousness. Often benign, it is due to excessive stimulation of the vegetative function of the vagus nerve, which is responsible for slowing the heart rate (5).
Peptic ulcer. It results from inflammation of the stomach wall (gastric ulcer) or the duodenum, the first part of the intestine (duodenal ulcer). The secretion of gastric acid, regulated by the vagus nerve, can promote the development of ulcers.
Dysphonie. Speech disorders can be observed following a lesion of the vagus nerve, and more generally of the pharyngeal branches.
Epilepsy. It is characterized by abnormal nerve impulses in the brain (6).
Vagus nerve treatment
Medical treatment. In the event of peptic ulcer, certain drugs may be prescribed to decrease acidity and treat infection: antibiotics, antihistamics, antacids.
Vagotomy. Performed if the drug treatment is not sufficient in the event of peptic ulcer, this surgical intervention consists in partially or completely cutting the vagus nerve at the level of the abdomen.
Speech therapy rehabilitation. In case of dysphonia and if the nerve is not completely severed, speech therapy will be implemented.
Surgical treatment. As a last resort, surgery will be performed.
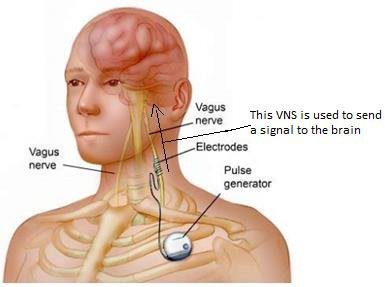
Stimulation of the vagus nerve. Depending on the diagnosis, different methods of vagus nerve stimulation (vagal maneuvers) may be performed.
Vagus nerve exams
Physical examination. Studying the different symptoms can help identify vagus nerve damage.
Electrophysiological exploration. The electromyogram makes it possible to study the electrical activity of the vagus nerve and to identify potential lesions.
Electrocardiogram: This test records the electrical activity of the heart in order to detect abnormalities.
Medical imaging. Additional examinations can be performed to confirm the diagnosis: x-ray, cerebral MRI, abdominal MRI, cerebral and spinal CT scan, chest CT scan, abdominal CT scan, etc.
History and symbolism of the vagus nerve
The discovery of acetylcholine, secreted during stimulation of the vagus nerve, has enabled great progress in neurology, particularly in the understanding of neurotransmission. This medical revolution won the two scientists Henry Hallet Dale and Otto Loewi the Nobel Prize for Physiology in 1936 “for their discoveries concerning the chemical transmission of nerve impulses” (7).