Contents
Treat a sore throat

|
Sore throat is a symptom, not a disease. It can have various causes, so we will only discuss the treatment of the sore throat itself (symptomatic treatment) here, and not that of the causative disease. Sore throat of non-infectious origin, for example allergic, secondary to gastroesophageal reflux, tumor, etc. requires specific support.
Symptomatic treatments for a sore throat
- Against pain and fever, one can take analgesics (painkillers) of the paracetamol type.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen should be avoided and only taken if prescribed by a doctor and for a short period if the sore throat seems viral because they can promote the sometimes serious complications of bacterial tonsillitis.
- To fight against fever, think about drinking a lot (at least one and a half liters per day)
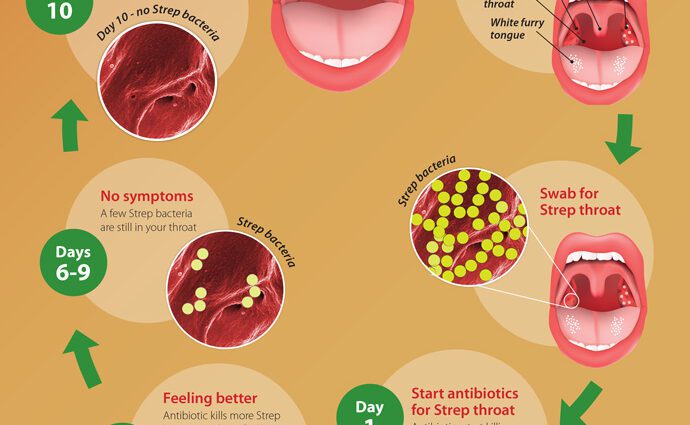
- Antibiotics are reserved for strep throat or complicated with abscesses
- Locally, mouthwashes, lozenges or gargles based on antiseptics may be used, whether or not associated with products that anesthetize the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
- Fumigations or inhalations may be of interest, in particular in the event of rhinitis (runny nose) or associated rhinosinusitis. They can be made with German chamomile, eucalyptus, thyme… etc.
- In the event of a blocked nose or sensation of discharge behind the throat, disinfect the nasal cavities with physiological saline or nasal drops.
- Warm milk with honey or a mixture of honey and lemon calms the irritation of the throat and is believed to have antiseptic properties. A “homemade” gargle can be made with the juice of half a lemon and a teaspoon of honey diluted in a glass of lukewarm water.
- Sore throats associated with allergic nasopharyngitis or gastroesophageal reflux require specific treatment in addition to symptomatic treatment, antihistamine for the former, anti-acid for the latter.
It is essential to consult a doctor in the event of:
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Fever above 38 ° C
- Persistence of sore throat despite symptomatic treatment or its resumption at the end of treatment
- Association with other signs such as glands in the neck, rash, cough.
- If the sore throat affects a more fragile person due to age, pre-existing diseases or treatments that disrupt immunity
Preventive treatment for sore throat
- Do not smoke or expose yourself to passive smoking,
- Avoid close contact with people complaining of sore throat, rhinitis or flu,
- Limit exposure to pollution and chemical irritants such as certain household products,
- Avoid excessively dry atmospheres (heating at high temperatures and in particular electric heaters or air conditioning) which promote sore throats. Use a humidifier if the air in your home or office is too dry and drink regularly.
For more information, the full sheet on sore throat.
Writing : Dr. Maïa Gouffrant July 2017 |











Managodiya