Contents
Tooth decay: all you need to know about cavities
Definition of tooth decay
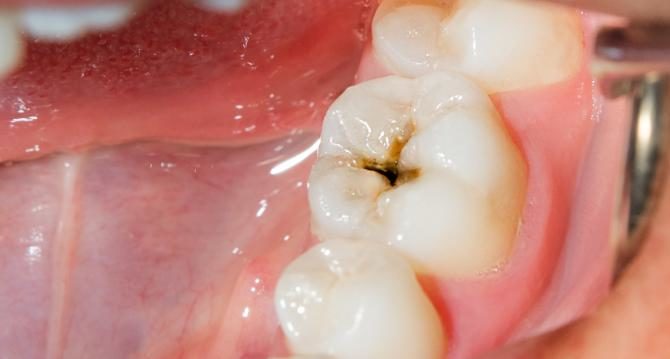
Tooth decay is a infectious disease. The enamel of the tooth is the first affected. A cavity forms in the tooth and then the decay spreads to depth. If the decay is not treated, the hole enlarges and the decay can reach the dentin (layer under the enamel). Pain begins to be felt, especially with hot, cold or sweet. Cavities can spread pulp of the tooth. We then speak of toothache. Finally, a tooth abscess can appear when bacteria attack the ligament, bone or gum tissue.
Sugars are believed to be one of the main culprits in the attack onE-mail. This is because the bacteria present in the mouth, mainly the bacteria Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli, break down sugars into acids. They bind to acids, food particles and saliva to form what is called dental plaque, which causes tooth decay. Brushing your teeth removes this plaque.
Dental caries, which is very common, affects milk teeth (a decayed milk tooth must be treated even if it is likely to fall out) and permanent teeth. Rather, they affect the molars and premolars, which are more difficult to clean when brushing. Cavities never heal on their own and can lead to tooth loss.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of dental caries are very variable and depend in particular on the stage of development of the caries and its location. At the very beginning, when the enamel is the only one affected, decay can be painless. The most common symptoms are:
- dental pain, which gets worse over time;
- sensitive teeth;
- sharp pain when eating or drinking something cold, hot, sweet;
- biting pain;
- brown spot on the tooth;
- pus around the tooth;
People at risk
L’heredity plays a role in the appearance of cavities. Children, adolescents and the elderly are more likely to develop cavities.
Causes
There are many causes of dental caries, but the sugars, especially when consumed between meals, remain the main culprits. For example, there is a link between sugary drinks and cavities or between honey and cavities2. But other factors such as snacking or bad brushing are also involved.
Complications
Cavities can have serious consequences for teeth and general health. It can, for example, cause pain important des abscess sometimes accompanied by fever or swelling of the face, problems with chewing and nutrition, teeth that break or fall out, infections… Cavities must therefore be treated as soon as possible.
Risk factors
L’oral hygiene is a very important parameter in the appearance of dental caries. A diet high in sugar also greatly increases the risk of developing cavities.
Un lack of fluoride would also be responsible for the appearance of cavities. Finally, eating disorders such as anorexia and bulimia or gastroesophageal reflux are pathologies that weaken the teeth and facilitate the onset of cavities.
Diagnostic
The diagnosis is easily made by the Dentist since cavities are often visible to the naked eye. He asks about the pain and tenderness of the teeth. An x-ray can confirm the presence of cavities.
Prevalence
Cavities are very common. More nine out of ten people would have had at least one cavity. In France, more than a third of six-year-olds and more than half of 12-year-olds1 would have been affected by this infection. In Canada, 57% of children between the ages of 6 and 12 have had at least one cavity.
The prevalence of caries affecting the crown of the tooth (the visible part that is not covered by the gums) increases until the age of forty and then stabilizes. The prevalence of cavities that affect the root of the tooth, often through loosening or erosion of the gum, continues to increase with age and is common among seniors.
Our doctor’s opinion
As part of its quality approach, Passeportsanté.net invites you to discover the opinion of a health professional. Dr Jacques Allard, general practitioner, gives you his opinion on the tooth decay :
Prevention is better than cure. In the case of tooth decay, prevention is effective and involves good oral hygiene with regular brushing, at least twice a day, ideally three times a day after each meal. The important thing in the treatment of cavities is to consult quickly. Regular visits to the dentist are essential because they allow cavities to be treated before they reach an advanced stage. An installed decay that has attacked the pulp of the tooth requires more complicated and expensive care than a decay that has not crossed the enamel. Dr. Jacques Allard MD FCMFC |