Contents
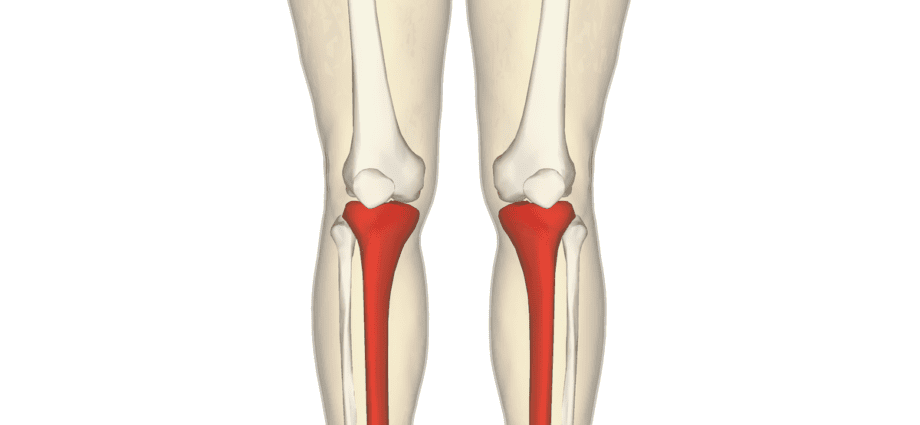
Tibia
The tibia (from Latin tibia, flute) is a bone of the lower limb located at the level of the leg, between the knee and the ankle.
Anatomy of the tibia
The tibia and fibula, also known as the fibula, form the skeleton of the leg, an anatomical region located between the knee and the ankle. These two bones are connected together by an interosseous membrane.
Structure. The tibia is a long bone that is the second largest bone after the femur. It consists :
- of one extremity, or epiphysis, proximal to the voluminous aspect and allowing to articulate with the femur and the fibula to form the knee.
- of a body, called diaphysis, triangular in shape when cut.
- of one end, or epiphysis, distal, less voluminous than the proximal, and articulating with the fibula and the talus to form the ankle (1).
Insertions. The tibia is the site of various ligament insertions, participating in the knee and ankle joints, as well as muscle insertions participating in the movements of the leg.
Functions of the tibia
Body weight support. The tibia transmits the body’s weight from the femur to the foot (2).
Knee dynamics. The dynamics of the knee pass through the femoro-tibial joint and allow movements of flexion, extension, rotation and laterality (3).
Ankle dynamics. The dynamics of the ankle pass through the talocrural joint and allow dorsiflexion (flexion) and plantar flexion (extension) movements (4).
Pathologies and diseases of the tibia
Leg fracture. The tibia can fracture. One of the most affected parts is the tibial shaft, the narrowest area of the bone. The fracture of the tibia may be accompanied by that of the fibula.
Tibial périostitis. It corresponds to a lesion appearing as an inflammation on the level of the internal face of the tibia. It manifests as a sharp pain in the leg. This pathology most often appears in athletic athletes. (5)
Maladies of the os. Many diseases can affect the bones and change their structure.
- Osteoporosis: This is a low bone density that is most commonly found in people over the age of 60. Their bones are then fragile and prone to fractures.
- Bone dystrophy. This pathology constitutes an abnormal development or remodeling of bone tissue and includes many diseases. We find in particular Paget’s disease (6), one of the most frequent, causing densification and deformation of the bones and manifested by pain. Algodystrophy corresponds to the appearance of pain and / or stiffness following a trauma (fracture, surgery, etc.).
Shin treatments
Medical treatment. Depending on the disease, different treatments may be prescribed to regulate or strengthen bone tissue or reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical treatment. Depending on the type of fracture, a surgical operation can be carried out with the installation of a screw-retained plate, nails or even an external fixator.
Orthopedic treatment. Depending on the type of fracture, a plaster cast will be performed.
Shin exams
Medical imaging examination. X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy or bone densitometry examinations can be used to assess bone pathologies.
Medical analysis. In order to identify certain pathologies, blood or urine analyzes can be carried out such as, for example, the dosage of phosphorus or calcium.
History and symbolism of the tibia
The etymology of the term tibia (from the Latin tibia, flute) can be explained by the analogy between the shape of the bone and the musical instrument.