Contents
the hyoid
The hyoid bone, (from the Greek huoeidês, meaning Y-shaped) is a bone located in the neck and is particularly involved in swallowing.
Anatomy
the unique. If the hyoid bone is often described with the bones of the skull, it is a separate and unique bone because it does not articulate with any other (1) (2).
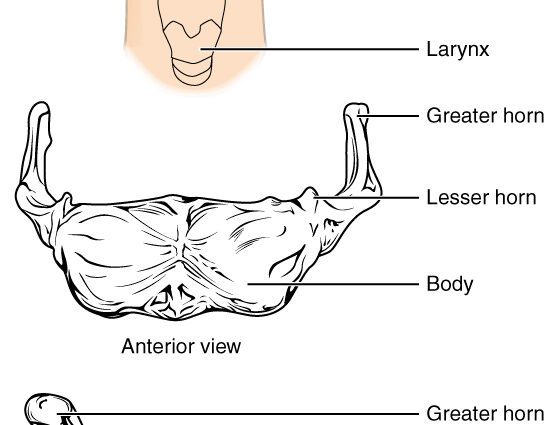
Position. The hyoid bone is located at the front of the neck, below the mandible.
Structure. The hyoid bone has a horseshoe shape, rounded forward, made up of several parts:
- of a body, constituting the central part;
- a pair of large horns, located on either side of the body and extending dorsally;
- of a pair of small horns, located between the body and the large horns and extending upwards.
These parts serve as a mobile attachment point for the tongue, as well as attachment points for the muscles of the neck and in particular those of the pharynx.
Fixing. The hyoid bone is attached to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx and to the styloid processes of the temporal bones by the small horns through the stylohyoid ligaments.
Functions of the hyoid bone
Swallowing. The hyoid bone allows movement of the muscles of the neck, raising or lowering the larynx during swallowing (2).
passwords. The hyoid bone allows movement of the muscles of the neck, raising or lowering the larynx when speaking (2).
Breathing. The hyoid bone allows movement of the muscles of the neck, raising or lowering the larynx during breathing.
Pathologies and associated issues
Thyroglossal cyst. This pathology is one of the most frequent congenital anomalies of the neck (3). The cyst of the thyroglossal tract corresponds to an increase in the volume of the tissue, at the level of the region of the hyoid bone. This type of cyst can be associated with local inflammation. The cyst can also grow and increase in size and sometimes turn out to be malignant.
Traumatic pathology. Traumatic pathologies of the hyoid bone are complex and can only occur through voluntary action. Hyoid bone fractures are often seen in cases of strangulation (3).
Bone pathologies. Certain bone pathologies can affect the hyoid bone.
Bone tumors. Rare, bone tumors can develop in the hyoid bone (3).
Treatments
Medical treatment. Depending on the pathology diagnosed, certain drugs may be prescribed such as painkillers.
Surgical treatment. Depending on the pathology diagnosed, surgery may be performed. In the case of a cyst of the thyroglossal tract, part of the hyoid bone may be removed.
Chemotherapy, radiotherapy or targeted therapy. Depending on the type and stage of the tumor, these treatments may be used to destroy cancer cells.
Hyoid bone examinations
Physical examination. First, a clinical examination is performed to identify and assess the symptoms perceived by the patient.
Imaging exams. In some cases, additional examinations may be performed such as ultrasound, cerebral CT scan or cerebral MRI.
History
Forensic medecine. The hyoid bone plays an essential role in the field of forensic medicine. It is particularly studied to identify a case of strangulation (4).